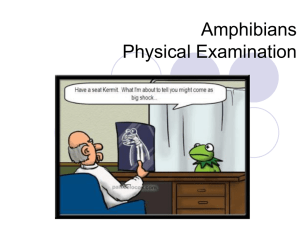
Amphibians
advertisement

Amphibians BY: John C. Meagan B. Matt F. Dalton C. Kalob S. Key Terms • Amphibians- an ectodermic vertebrate that spends its early life in water and its adult life form of a frog or a toad. • Lung- an organ found in air breathing. • Atrium- each of the two upper chambers Common characteristics • • • • • They all have sticky pads on their feet. Skin covered with mucus. They are cold blooded. Use stinky tug to get food. They have eardrums. Internal conditions stable • Amphibians are cold blooded so when they get cold they get out in the sun. When it is hot they go in the shade. Some of them hibernate. Reproduction They reproduce by going to the water. Adult frog’s reproduce sexually, then eggs are fertilized outside the females body. Tadpoles from eggs, then hind legs develop, then front legs develop, then the tail absorbs and development is complete. Circulatory system/oxygen A tadpole circulatory system is a single loop and a heart with two chamber’s. An adult circulatory system is two loops, one heart, and three chamber’s. They get oxygen when they are in the water and they get the oxygen out of the water. When they are a adult their gill don't help them get oxygen so they get it from the air. Movement • Amphibians move in a variety of ways. Some amphibians live in water, especially in the larvae stage. Also some amphibians live on land, and fins do not live on land. They have to use limps which are very muscular. Types of Organisms • Frogs which are the largest group of amphibians have very strong legs for jumping. They are also carnivores or meat eaters. • Toads which are different from frogs have short legs for short jumps. They also have rough skin made of scales • Salamanders are the only group that have tails, do not move the same as the others they crawl. Other Interesting Facts Amphibians larvae’s at herbivores than grow up to be carnivores. They are 4,000 kinds of amphibians. 3 classes in order: Anuran , caudate, gymnophior Amphibian means “ double life” and “ 2 lives”. Reproduce in the water. 22- 24 families. 3 major groups : frogs ,salamanders, and toads. Works cited • It’s a frogs life Densey Clyne 1995 Pg. 29 • Encyclopedia Pg. 63 1996 Dailey • The amphibians and reptiles of Missouri Jordon 1987 pg. 108 • http://www.frogweb.gov/portal/server.com • http://www.livingunderworldorg/bioloy/ • http://kidstuff.homestead.com/