Specialized Cells: Animal & Plant Biology Presentation
advertisement

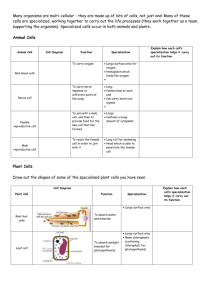
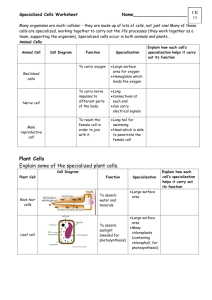
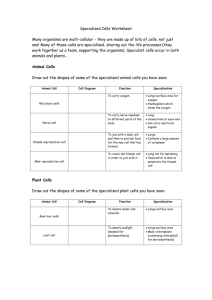
Specialized Cells D. Crowley, 2007 Specialized cells Animal and plant cells are adapted for different functions The way the cell is formed depends on the job it must perform Review What parts of a cell are found within animal cells and plant cells? Animal cells: Nucleus Cell membrane Cytoplasm Plant cells: All of the above + Cell wall Large Vacuole Chloroplasts Specialization Many organisms are multi-cellular - they are made up of lots of cells, not just one! Many of these cells are specialized, sharing the life processes (they work together as a team, supporting the organism) Specialized cells occur in both animals and plants… Animal Cells The table below shows some specialized animal cells Animal Cell Cell Diagram Function Specialisation Red blood cells To carry oxygen Large surface area for oxygen Hemoglobin which binds the oxygen Smooth, round to allow for travel through small vessels Nerve cell To carry nerve impulses to different parts of the body Skin cells To serve as a barrier between your body and outside elements Like a brick wall…fit together edge to edge Male reproductive cell To reach the female cell in order to join with it Long tail for swimming Head which is able to penetrate the female cell Long Connections at each end Can carry electrical signals Plant Cells The table below shows some specialized plant cells Plant Cell Cell Diagram Function Root hair cell To absorb water and minerals Leaf cell To absorb sunlight (needed for photosynthesis) Specialisation Large surface area Large surface area Many chloroplasts (containing chlorophyll, needed for photosynthesis) located along edges of cell Tissue Specialization Tissue is a group of cells that works together to perform a specific function Organ Specialization Organs are composed of two or more types of tissue combined to perform a single task Organs often contain several types of tissue Ex: Heart is composed of muscle,connective,epithelium, and nervous tissue.