Grade 10 Academic Science
advertisement

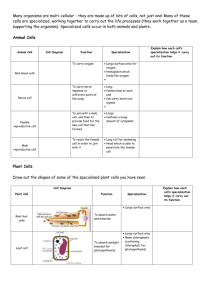
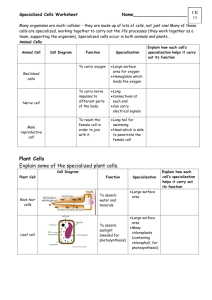
Grade 10 Academic Science Specialized Cells Section 2.9 Pages 58-60 Unicellular organisms are not specialized. That is, each cell must carry out all the functions of life. Multi-cellular organisms...such as you and I...benefit from cell specialization. In specialization, each cell is designed to carry out a specific function, and to do so, cells come in a variety of sizes and shapes. Recall, the Cell Theory states that every cell comes from a previously existing cell. For example, you started life as a single fertilized egg. Yet, not all cells in a multi-cellular, complex organism are identical. In multi-cellular organisms, cells have different functions and structures. Specialized cells have physical and chemical differences that allow them to perform one specific job…and quite well. Specialized Plant Cells Thin-walled cells are found in the flexible tissues of the leaf such as the flower, leaf and root. Thick-walled cells are designed for support, although the stretchable cell walls are flexible Very thick-walled cells provide rigid support. The cell wall becomes so thick that nutrients cannot enter the cell. In this case, the cell dies leaving an empty chamber surrounded by a thick cell wall. Specialized Animal Cells Nerve cells tend to be long and thin, and many are surrounded by a coating of insulation that prevents short circuiting of the electrical signal. Red blood cells carry oxygen in a special protein – hemoglobin. Of interest, there are about six million red blood cells in one cubic millimeter of human blood. Your entire body contains about 30 trillion red blood cells. White blood cells protect the body from foreign invaders by engulfing and digesting the foreign bodies OR by killing the invaders with antibodies The picture shows both red and white blood cells. Note, each cell has its own unique structure. The red blood cell is “quasi-donut” shaped. The shape provides more surface area to bind O2 and CO2. The shape also makes the cell more flexible so it can squeeze through small blood vessels. On the other hand, white blood cells occur in a variety of shapes. White blood cells fight disease and invasions of foreign substances. The shape variation lets white blood cells respond quickly to a range of invading shapes. The stomach contains hydrochloric acid. Cells of the stomach lining are protected from the acid by a layer of mucous. The small intestine’s cells that line the small intestine absorb food. Finger-like projections, called VILLI, increase the surface area for digestion In fat cells, most of the cytoplasm is occupied by a vacuole that stores fat molecules In the respiratory system, particles trying to enter your lungs are trapped by mucous, and then, swept away from the lungs by cells called CILIA. Cells of the lungs are VERY THIN. This allows gases to exchange rapidly between the air and the blood. Animal and plant cells show a wide variety of specializations. They differ externally and internally. For example, muscle cells use a lot of energy, and consequently, muscle cells contain many mitochondria (energy making organelles) Questions 1. What are the advantages of cell specialization? 2. What is the advantage of a highly folded cell membrane? 3. What advantage does a thick, flexible plant cell wall provide over a thick, rigid cell wall? 4. Why do single-celled organisms NOT show specialization of function? Task Perform the activity 2.10 Observing Specialized Cells on Page 61. Answer Questions 3(b), 3(c) on Page 61