Chapter 9 Lesson 1
advertisement

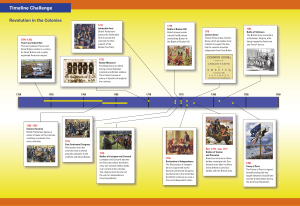
Chapter 9 Lesson 1 OPA - Chino Americans and the Revolution Pg. 366 - 372 Anticipatory Set California Standards 6.1 – Identify and map 6.3 – Identify the the major military battles, campaigns, and turning points of the Revolutionary War, the roles of the American and British leaders, and the Indian leaders’ alliances on both sides. different roles women played during the Revolution. California Standards 6.4 – Understand the personal impact and economic hardship of the war on families, problems of financing the war, wartime inflation, and laws against hoarding goods and materials and profiteering. 6.7 – Understand how the ideals set forth in the Declaration of Independence changed the way people viewed slavery. Input – Timeline of the Revolutionary War 1774 – The First Continental Congress Meets 1775 – The Battles of Lexington and Concord are Fought 1776 – The Declaration of Independence is signed 1778 – The colonies sign a treaty with France 1781 – Americans force British to surrender at Yorktown, the last major battle of the war. Language of the Discipline Patriot – People in the colonies who supported independence Loyalist – People in the colonies who remained loyal to the king. Neutral – Those who took neither side Language of the Discipline Inflation – An increase in the price of goods (often due to shortage). Profiteering – charging extra-high prices for their crops or goods. Regiment – A large group of soldiers Personal Hardships Pg. 367 Input The Declaration of Independence united the colonies, but not all colonists were united. Many supported the king (loyalists), and many remained neutral. Sometimes families were split because of differing beliefs. The British army also robbed colonists Some colonists would destroy their own belongings to keep it away from the British. Economic Hardships Pg. 368 Input Shortage of imported goods made supplies limited. The British blockaded American ports Shortages brought on inflation. Colonists needed more money to buy what they needed. In 2 months the price of wheat and beef doubled. Input The Second Continental Congress was also printing money to fund war. Money became less valuable. Taxes were not enough for American government because all states needed to give permission. Profiteering hurt the colonies as well. People would charge extreme prices on scarce items. Laws were created to stop this from happening. Women and the War Pg. 369 Input Women ran households, worked as carpenters, blacksmiths, shipbuilders, etc. Some raised money and collected clothing for the war. Martha Washington and others followed their husbands from battle to battle. Some also fought in the battles. Input 16-year-old Sybil Ludington rode to tell American soldiers of an attack in 1777. Deborah Sampson dressed as a man to fight as “Robert Shirtliffe.” Margaret Corbin was wounded after taking her husband’s place in battle. She was the first woman recognized as a war veteran by Congress. Input Mercy Otis Warren wrote patriotic poems and stories, as well as a history of the American Revolution. Abigail Adams wrote letters to her husband arguing for freedom. She also sheltered many children who were homeless due to war. African American, Free and Enslaved Pg. 370 Input 1/5 of all people in the colonies were of African descent. Most were slaves in south. 5,000 African Americans fought for the Continental Army. Many promised freedom as reward. Input James Armistead served as a spy for George Washington His information helped win the battle of Yorktown The British in Virginia also offered freedom to those who fought. People in the Western Lands Pg. 371 Input Despite the Proclamation of 1763 people continued to move west into Indian lands. Angered some, but many Indians used these as trading partners. At the start of the war, many tribes remained neutral. Eventually alliances were made on both sides. Input Chief Logan fought for British because his family was killed by settlers. Mohawk leader Thayendanegea (Joseph Brant) fought for British to stop Americans from settling on his lands. Oneida and Tuscarora tribes fought for Americans. Input Many western settlers also stayed neutral at first. These people did not want to be ruled by any strong government. Summary - Modeling During the Revolutionary War, Americans faced personal and economic hardships. Many women and African Americans contributed to the Patriot cause. At first, settlers in the western lands and American Indians were neutral, but later they joined the fighting. Check for Understanding What were slaves promised by both sides in exchange for fighting? Freedom What was the name given to people in the colonies who stayed loyal to the king of England? Loyalists Unanswered Questions – (Guided Practice) What would have happened if all American Indian tribes had fought for the British? Were these alliances important to the Americans? Create 2 more (You must have 3 written down). Patterns – Independent Practice Bloom’s Taxonomy: Analyze WHAT MOTIVE IS THERE for people to join either side of the American Revolution; patriotic pride or self gain? Find at least 3 examples in the book that back up your answer.