What is Science?
advertisement

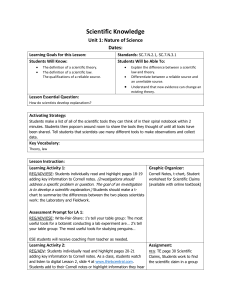
What is Science? Unit 1: Nature of Science Dates: Learning Goals for this Lesson: Students Will Know: Standards: SC.7.N.1.1, SC.7.N.1.2, SC.7.N.1.6 Students Will be Able To: The different areas of science What pseudoscience and empirical evidence are Distinguish what characterizes science and scientific explanation Differentiate between science and pseudoscience Lesson Essential Question: What are the characteristics of science? Activating Strategy: Students will complete “Know your Sciences” crossword to determine various types of scientists and what each studies. Key Vocabulary: Pseudoscience , empirical evidence, science Lesson Instruction: Learning Activity 1: REG/ADV: Students read, “What characterizes science” on page 6 of the unit and underline keynotes. They will then add the definitions of the three areas of science (Life, Earth, and Physical) to their Cornell notes. Students will then do a pair reading of “community consensus” and add notes to their Cornell notes (1’s will read out loud while 2’s underline key words). Students will do a pair reading of “use of empirical evidence” and add notes to their Cornell notes (2’s will read out loud while 1’s underline key words). Students will then do a whole group read of “what is a scientific explanation?” (teacher will read while students underline characteristics). ESE: ESE students will receive cloze notes to go along with the same assignment as their partner Assessment Prompt for LA 1: REG: Write-pair-share: How is the scientist in the photograph exhibiting the characteristics of science? (3-5 sentences) ADV: Same activity but writing will be 5-7 sentences ESE: Same activity but writing will be 2 sentences Graphic Organizer: Characteristics chart, Venn diagram of Science vs. Pseudoscience Learning Activity 2: Assignment: REG/ADV: Students will pair read the 6 different characteristics of a scientist on pages 10-11 of the unit. Students will add notes to a chart that will be given to them and add it to their interactive notebook. REG/ADV/ESE: Distribute handout “Ban Dihydrogen Monoxide”. Teacher reads article aloud to class. Students mark text by highlighting unknown words and circling key terms. Ask students to write a letter to the President of the United States to express their concerns over Dihydrogen monoxide and cite evidence from the text to support their choice. Allow students to choose to agree or disagree with the author and conduct a Philosophical Chairs. After several rounds, break down the word parts to show that the term actually means “water”. Discuss how pseudoscience uses faulty logic and exaggerated thinking. Have students write a summary paragraph that explains what they can look for in the future to be sure that a claim is science and not pseudoscience. ESE: Student will complete the same activity with a chart that will already have some of the characteristics filled in. Assessment Prompt for LA 2: REG/ADV/ESE: Think-pair-share: construct an argument using examples from the text on which traits you think are most important. After each partner has shared, determine a pattern between the traits to show why they are all important. Learning Activity 3: REG/ADV: Students will read “How is pseudoscience similar to and different from science?” while underlining keynotes and adding them to their Cornell notes. ESE: Students will do the same assignment with cloze notes to fill in. Assessment Prompt for LA3: REG/ADV/ESE: write-pair-share: Would it be possible for something to initially be regarded as pseudoscience and then later be supported by science? Explain your answer. Summarizing Strategy: REG/ADV: Students will complete an acrostic for the word SCIENCE using vocabulary and key concepts from the lesson. ESE: Students will do the same summarizing strategy but will be given the starter word for each letter. Student: Modification/Accommodation: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Seat student near teacher. Stand near student when giving directions/presenting. Provide visual aids/graphic organizers. Ensure oral directions are understood. Allow extra time to complete tasks. Simplify complex written directions. Give test items orally. Provide peer assistance/study groups.