1.05 Honors Bone Markings
Anatomy and Physiology Module 1 Guided Notes
1.00 Getting Started Module
It is highly suggested that you take some time to read through this lesson so you know what to expect in your new course. After completing this lesson, you will understand:
Common Core State Standards
course icons, features, and navigation
important parts of the lesson
materials and requirements specific to the course
tips for success in the course
pace for the course
academic integrity
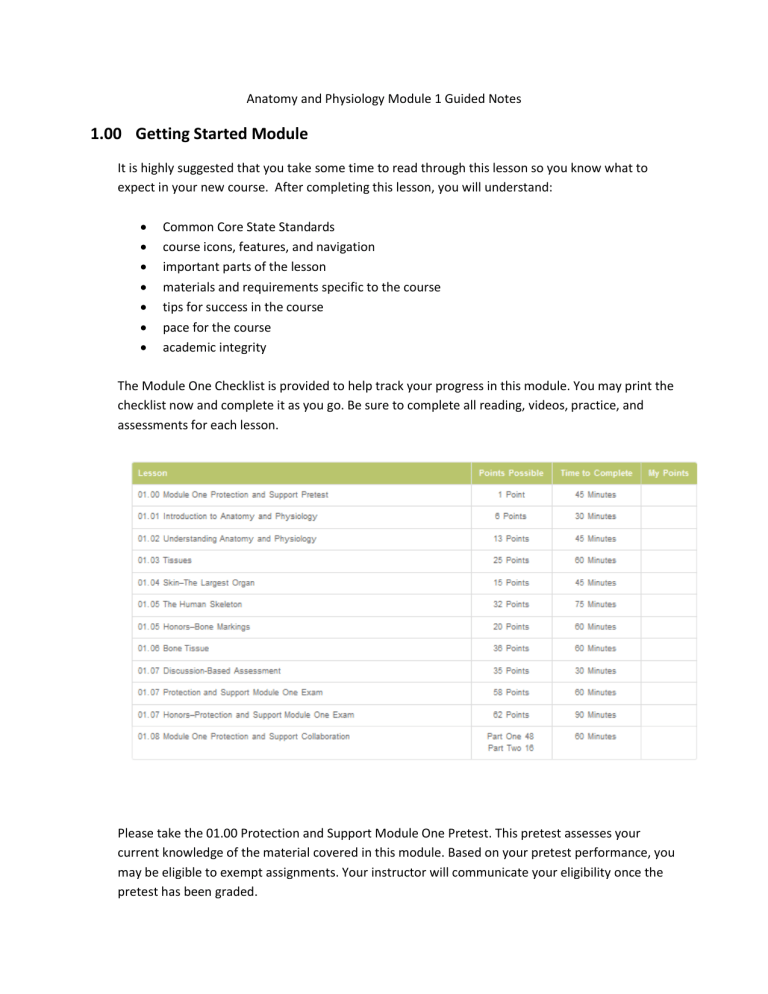
The Module One Checklist is provided to help track your progress in this module. You may print the checklist now and complete it as you go. Be sure to complete all reading, videos, practice, and assessments for each lesson.
Please take the 01.00 Protection and Support Module One Pretest. This pretest assesses your current knowledge of the material covered in this module. Based on your pretest performance, you may be eligible to exempt assignments. Your instructor will communicate your eligibility once the pretest has been graded.
1.01
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
Read pages 1-3 and Watch the Video: The Human Body
Focus Question:
How would you explain the fields of anatomy and physiology to one of your friends?
What are the two major fields of study for Anatomy?
1.
2.
2.
Physiology has many specialties. List and explain 4:
1.
3.
4.
Comparing Anatomy and Physiology (Page 4)
Focus Question:
How does an anatomist study the human body compared to a physiologist?
Using the chart on page 4, answer the following:
How would an anatomist and a physiologist study the small intestine differently?
What about the skin?
And blood vessels?
Scientific Inquiry (Pages 5-6)
Focus Question:
How have the fields of anatomy and physiology changed over time and what led to these changes?
Assessment:
Complete the 01.01 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology quiz in your assessment area.
1.02
Understanding Anatomy and Physiology
Focus Question:
Can you identify a study tip when it appears in your anatomy and physiology lesson?
Watch the video – “Tips and Tricks” to help you answer your focus question.
Word Meanings (Pg. 3)
Focus Question:
Are you able to determine the meaning of these key terms and phrases used in anatomy and physiology?
Axial Skeleton
Appendicular Skeleton
Homeostasis and Metabolism (Pg. 4)
Focus Question
What is the relationship between homeostasis and metabolism?
Body Positions (Pg. 5-)
Focus Question:
Can you translate the terms for body positions, body planes, relative directions, and body cavities into a diagram and from a diagram into words?
Anatomical Position-
Supine Position-
Prone Position-
Body Planes and Sections (Pg. 6) –
Be sure to click on the green tabs on the left to read about the following planes
Sagittal Plane-
Transverse Plane-
Frontal Plane-
Relative Direction (Pg. 7)
*Be sure to advance the slides and view all 15 terms on this page. The self-check activities are also very helpful to practice using these terms in context so do not skip them!
Why is it important to study anatomical terminology?
Key directional terms that you should be able to define and use in context:
Anterior
Posterior
Superior
Inferior
Medial
Lateral
Bilateral
Answer the following and check your answer using the lesson self-checks:
The belly button is anterior to the (toes/spine).
Which is more posterior (toes/spine)?
Which is more superior (shoulder/hip)?
In anatomical position, which is more inferior, the head or the hands?
What is more medial, the lungs or the shoulders?
In anatomical position, which is more lateral, the hand or hip?
Which structure is not found bilaterally on the body? (Hands/Feet/Stomach/Eyes)
Body Cavities (pg. 8)
I.
Dorsal –
A.
Cranial-
B.
Spinal-
II.
Ventral-
A.
Thoracic –
B.
Abdominopelvic – a.
Abdominal – b.
Pelvic-
Assessment:
Complete the 01.02 Understanding Anatomy and Physiology quiz located in your assessment area.
1.03 Tissues
Levels of Body Organization –page 3
Focus Question:
What do you already know about the structure and function of tissues?
View the slide show:
Atom-
Molecule-
Macromolecule –
Cell –
Tissue –
Types of Tissues-page 4
Use the chart on page 4 to fill in the chart below.
Tissue Type
Epithelial
Muscle
Connective
Nervous
Function Location Characteristics Examples/locations
Engineering Tissues-pg 5 and 2
Focus Question:
How does biotechnology affect you? How does it impact society?
Assessment:
See the instruction on page 6 of the lesson. Be sure to review rubric to learn how you will be graded.
1.04 The Skin
The skin-page 2
Focus Question:
What does the skin have in common with other organs within the body?
The skin, also called the _____________________, is considered an organ because it consists of all four tissue types. It also contains accessory organs, such as __________, hair, and nails.
Use the Skin Worksheet, copied below, and fill it in as you view the video. You can also use the text version of the video to get the sections you miss. Watch the video at least twice to view important structural differences between skin layers.
Word Bank: dermis, epidermis, hypodermis, integumentary
1. The skin and its accessory organs make up the ____________________________system.
2. The skin is made up of three distinct layers, the _____________, ____________, and
____________ .
The Skin
Epidermis (outer layer) General function?
Why is it water resistant?
Dermis Layer (middle layer)
Hypodermis (inner layer)
Healing Wounds-page 3
Focus Question:
How does a wound impact the functions performed by the skin?
Function of the stratum layers?
Role of Melanocytes and melanin?
Function of Merkel cells?
What is it composed of?
How does the dermis help with thermoregulation?
How do sweat glands help with thermoregulation?
Role of blood vessels in the dermis?
Role of nerves in the dermis layer?
What is it composed of?
What are its primary functions?
Skin review-page 4
Complete the skin review activity on this page
Assessment:
See the instruction on page 6 of the lesson. Be sure to review rubric to learn how you will be graded.
1.05 The Human Skeleton
Human Bones- page 2
Focus Question:
What can be determined through the study of human bones?
Skeletal System-page 3, 4, 5
Focus Questions:
What comparisons can be made between the bones of the axial and appendicular skeleton?
View the slides shows on pages 4 and 5 to answer the questions below. Use the Skeleton picture below to label all the bones in the slide shows.
What are the major bones of the axial skeleton?
The _________________ skeleton contains the cartilage and bones that support the organs of the head, neck, and trunk.
Study tip: Remember that the prefix ax- means axis, or a main line of direction, motion, growth, or extension.
Skull-
Hyoid Bone-
Vertebral Column-
Sacrum-
Rib Cage-
What are the major bones of the appendicular skeleton?
The _______________________ skeleton consists of the bones in the upper and lower limbs, as well as the bones that anchor those limbs to the axial skeleton. pectoral girdle- scapula (shoulder blade)- clavicle-
Humerus-
Radius and Ulna-
Carpals-
Metacarpals-
Phalanges- pelvic girdle-
Os Coxae-
Femur-
Tibia-
Fibula-
Patella-
Tarsals-
Metatarsals-
Phalanges-
Complete the Review activity on page 6
Assessment:
See the instruction on page 7 of the lesson. Be sure to review rubric to learn how you will be graded.
1.05 Honors Bone Markings
Palpation- page 2 and 3
Focus Question:
Can you identify key bone markings and explain their importance?
Types of Bone Markings:
Projections-
Depressions-
Openings-
Structure:
The _________________ of a bone marking is related to its function.
Such functions include:
Projections for Movement:
Head:
Facet:
Condyle:
Ramus:
Projections as attachment sites:
Tuberosity:
Tubercle:
Crest:
Epicondyle:
Spine:
Trochanter:
Depressions and Openings:
Sinus:
Fossa:
Sulcus:
Fissure:
Foramen:
Suture:
Complete the Review activity on page 4
Growth Plate-page 5
Focus Question:
What is the function of the bone marking known as the epiphyseal plate?
Assessment:
See the instruction on page 6 of the lesson. Be sure to review rubric to learn how you will be graded. Complete part 1 and 2.
1.06 Bone Tissue
Bone Tissue-page 2
Focus Question:
How is the development of our skeleton similar to the construction of a building?
Bone Matrix-page 3
Focus Question:
What components are found in a bone matrix? Can you identify the different types of bone cells?
Define Key Terms Below and pay careful attention to the labeling of the picture on this picture. You will need to be able to label these same items in the module exam. Don’t forget to click on the bone chart.
Osteogenesis- osteoblasts (bone-forming cells)- osteogenic stem cells-
Osteoblasts-
Osteocytes- haversian canals-
canaliculi - osteoclasts-
Compact and Spongy Bone-page 4
Focus Question:
How does the structure of compact bone differ from that of spongy bone?
During early bone development, bone tissue arises and replaces most _________________ structure (or cartilaginous structures) to form a bony skeleton. This is called
____________________.
There are two types of bone tissues that form during ossification: ____________ and
_____________ bone.
Use the Bone and Cartilage Worksheet (copied below); Fill it in as you view the video.
Bone Layers Periosteum
Compact Bone
Medullary Cavity
What does the outer Layer contain?
What is the function of the outer layer?
What does the inner layer contain?
What is the function of the inner layer?
What is the structure of the osteon?
What is the structure of the haversian canals?
What is the structure of the medullary cavity?
What is found at the end of long bones?
Bone Cells
Bone Repair
Osteogenic cells
Osteoblasts cells
Osteoclasts cells
Osteocytes cells
What is the role of each type of cell in bone repair?
Function?
Function?
Function?
Function?
Osteocytes?
Osteoblasts?
Osteoclasts?
Characteristics of Bone-page 5
Focus Question:
How do the characteristics of bone tissue affect bone strength?
Assessment:
See the instruction on page 6 of the lesson. Be sure to review rubric and the student example to learn how you will be graded.
1.07 Discussion Based Assessment
Once you have studied and completed all lessons in this module, it is time to contact your instructor for a Discussion-Based Assessment.
Your instructor will ask you questions related to the blue focus questions in these module guided notes.
These focus questions are the same questions found at the top of every lesson page.





