Europe and america - ALHS American Literature
advertisement

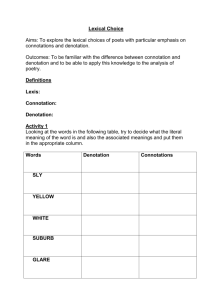
EUROPE AND AMERICA American Literature Honors Mr. Gallegos Semester One Primary and Secondary Sources Cornell Notes-Notes for Warm-Up • Primary Source: An original document containing firsthand information about a subject. (Examples: Original photograph, original work of art, letters, diary entries, videos, Interview) • Secondary Source: Discussion or commentary on a primary source; they key feature of a secondary source is that if offers interpretation of information gathered from primary sources. (Examples: Biographies, encyclopedias, Books Analyzing Civil War, Article Critiquing Art, History Book) Primary and Secondary Sources T-Chart • Please turn to page 7 in your SpringBoard book. At the bottom of the page, you will find a list of sources. Underneath the definitions you copied into your spiral notebooks, make a t-chart like the one below and place the source in the appropriate column. Primary Sources Secondary Sources Learning Objectives • Content Objective: Students will be able to analyze the use of denotation and connotation in a poem and describe the connotation of specific words. • Language Objective: Students will take Cornell Notes on primary and secondary sources. • Language Objective: Students will read the poem titled “Europe and America” on Page 10. Read the whole poem firs before completing the graphic organizer. • Language Objective: Students will complete the graphic organizer on Page 11. In the last column, students need to describe the effect of the reader by writing a short response to the question. Where Is the American Dream Realized? • Our educational system. • Freedom of religion and faith. • Right to pursue your dreams. • The careers we choose. • The structure of our families. • In hard work. • A free press. • Scientific endeavors. • Equality of opportunities. Key Vocabulary • Record these definitions in your spiral notebooks. • Denotation: The exact literal meaning of a word. • Connotation: The associations and emotional overtones attached to a word beyond its literal definition or denotation. A connotation may be positive, negative, or neutral. • For Example: When you think of the word Hollywood, what comes to mind? Is it positive or negative? What about the word Columbine? Denotation Versus Connotation Word or Phrase Bedded on soft green money. Denotation Connotation Effect on the Reader BeddedResting SoftComfortable and soothing. Money- Used to make purchases for good and services. This phrase reflects the relative comfort he experiences on a daily basis; a stark contrast from that of his father. The reader is supposed to be able to visualize the privilege the son has. Denotation Versus Connotation Word or Phrase Bed of anguish Denotation BedFurniture used for sleeping and resting. AnguishExtreme pain and suffering. Connotation This phrase reflects the severe hardships and pain his father experienced on a daily basis. It was a part of his routine. Effect on the Reader The reader is supposed to feel the pain of the father through the imagery and feel pity or admiration for him. Denotation Versus Connotation Word or Phrase Vast continent of breezes, storms to him. Denotation Connotation Continent- vast area of the world comprised of several countries and or regions. Breezes- A soft and calming wind. Storms- When severe or inclement weather occurs. This phrase continues to highlight the stark differences between the lives of him and his father. His father feels pain as often as his son feels pleasure. Also, the phrase implies the differences are not just physical. Effect on the Reader Sympathy/E mpathy Imagery Exit Ticket • Please record your responses in your spiral notebook. • What are the differences between denotation and connotation and how does connotation contribute to the tone of a passage? • Make a list of words that have a positive connotation and a list of words that have a negative connotation.