Injection Well Permitting - Railroad Commission of Texas
advertisement

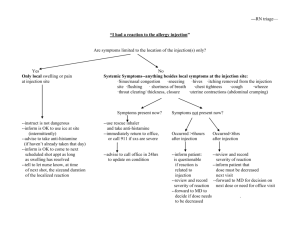
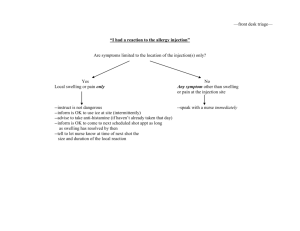
Railroad Commission of Texas Injection Well Permitting Oil and Gas Regulatory Conference September 24-25, 2013 - Austin, Texas Rick Behal 1 Injection Well Permitting Introduction • Filing a complete and correct application initially is the most effective way to expedite an application. • Injection/Disposal Well Permit Testing and Monitoring Seminar Manual http://www.rrc.state.tx.us/forms/publications/HTML/index. php • Filing Requirements: Forms and attachments • Technical Review: What are we looking for? 2 “Crossing the Pecos River” • • • RRC – ESTABLISHED 1891 TO REGULATE RAILROADS, ACQUIRED JURISDITION OVER OIL & GAS IN 1917 TO PREVENT MONOPOLIES, UNFAIR PRICING, PIPELINE DISCRIMINATION POWERS EXPANDED IN 1919 TO REGULATE PRODUCTION TO PREVENT WASTE NOW HAS AUTHORITY OVER O&G, PIPELINES, GAS UTILITIES, & SURFACE MINING, NO LONGER HAS ANY AUTHORITY OVER RAILROADS Injection Well Permitting • There are over 409,000 oil and gas industry wells in Texas • First injection well in Texas permitted in 1936 • There have been about 107,000 wells permitted for injection • Over 55,000 have current permits, approximately 33,000 are active 4 Injection Well Permitting Objectives • Protect surface and groundwater, public health and safety • Prevent waste and promote conservation • Protect correlative rights to develop mineral resources 5 Injection Well Permitting Statutory Authority (Oil and Gas Division) • Safe Water Drinking Act (1974): - RRC primacy on April 23, 1982. • Chapter 27 of the Texas Water Code: - Well is in the public interest - No harm to oil, gas or other mineral formation - Both ground and surface water protected - Financial responsibility • Title 3 of the Texas Natural Resource Code 6 Injection Well Permitting Railroad Commission Rules Permitting • 16 TAC § 3.8 – Water Protection (pits, discharges, waste haulers) • 16 TAC § 3.9 – Oil and Gas Waste Disposal into Nonproductive Formations (Chapter 27 of the Water Code) - About 15,000 permitted (approx. 5000 active) • 16 TAC § 3.46 – Fluid Injection into Productive Formations (Natural Resources Code) - About 40,000 permitted (approx. 28,000 active) 7 Injection Well Permitting Permitting Forms: Which to file? • Is the injection formation productive or non-productive? • “productive” = current or past production within a 2 mile radius of the proposed injection well • File original application to Austin office • Mail a copy to the district office 8 Injection Well Permitting Forms • Form W-14 – To apply for Disposal into a Non-Productive Formation – Statewide Rule 9 • Form H1 and H1A – To apply for Injection /Disposal into a Productive Formation – Multiple Zones: If a mix of Productive and NonProductive – Statewide Rule 46 9 Injection Well Permitting Fees • Rule 9 (Forms W-14) – non-productive formations $100 permit application fee (per wellbore) • Rule 46 (Form H-1/H-1A)– productive formations $500 permit application fee (per wellbore) • Exception Request $375 (additional) each exception request • These filing fees are non-refundable 10 Injection Well Permitting Administrative Staff: • Juanita Jimenez (512) 463-3576 Juanita.Jimenez@rrc.state.tx.us • Molly Edwards (512) 463-4032 Molly.Edwards@rrc.state.tx.us 11 Injection Well Permitting Preliminary Review • Check Organization Report (Form P-5) - Must have active P-5 before application is reviewed • Check Certificate of Compliance (Form P-4) - Verify that applicant is operator of lease - Check for any outstanding violations • Check UIC (Underground Injection Control)well Inventory - Is this application for a new or amended permit? 12 Injection Well Permitting Dual Authorities • Only one permit may be valid on an injection/disposal well at any given time - An amended permit supersedes the old permit • Plan re-permitting to coincide with workover • Whenever a dual authority is discovered, the older permit is cancelled 13 Injection Well Permitting Attachments • Electric Log • “Water Board Letter” • ¼ mile Area of Review (AOR) plot and table • Notice: ½-mile AOR, notice list and signed/dated certification statement • Publication clipping and affidavit • Fresh Water H-7, questionnaire, analysis and plat 14 Injection Well Permitting Attachments: Electric Log • A complete electric log or similar log of the proposed injection/disposal well • If well log is not available for proposed well, a log from a nearby well may be submitted. • If multiple wells covered by one Form H-1, only one representative well log is required. 15 Injection Well Permitting Attachments: “Water Board letter” • RRC Groundwater Advisory Unit (GAU) formerly TCEQ Surface Casing Unit. • Commonly referred to as the “Water Board letter”, “surface casing letter”, “No Harm letter”, “TCEQ letter” and now “GAU letter” • Two different types of depending of whether application is H-1 or W-14 • http://www.rrc.state.tx.us/environmental/environ support/gau/index.php 16 Injection Well Permitting Attachments: “Water Board letter” • Form H-1: States the Base of Usable Quality Water (BUQW – TDS 3,000 ppm) that must be protected. May be for area well and no more than 5 years old. • Form H-1 submitted for the purpose of disposal: Must also include the depth to the Usable Source of Drinking Water (USDW – TDS 10,000 ppm) • Form W-14: Well specific and includes BUQW, USDW and disposal interval. 17 Injection Well Permitting H-1 “Water Board” letter 18 Injection Well Permitting W-14 “no-harm letter” Must cover proposed injection interval States BUQW and USDW 19 Injection Well Permitting Attachments: Area of Review (1/4-mile AOR) • Provide the data of record for wells that penetrate the proposed injection interval within one quarter (1/4) mile. (expanded when appropriate). • Confirm wells have been plugged (or cased and cemented) in a manner that will prevent the movement of fluids into strata other than the authorized injection or disposal interval. 20 Injection Well Permitting Attachments: Area of Review (1/4-mile AOR) Submit: • Plot showing well location and operator of AOR wells • Tabulated data keyed to AOR plot: - Lease name and number, well number, API number , total depth, date drilled, current status, plug date (if applicable) - Note: Providing copies of plugging reports may expedite processing 21 GIS Map 22 (Insert Graph Here) Delete if un-needed Add API# Then > 23 Map Tools: Select ¼ or ½ mile Then click on well location to generate AOR 24 Injection and Disposal Well Permitting Map tools: Identify Wells Then click on well 25 Injection Well Permitting Click link for wellbore record and current status 26 Type Well = Status Injection Well Permitting “On Schedule” = Producing, Injecting, ShutIn. “Unknown Status”(maybe?) = Dry, blank, Historic If well status unknown, will require either: • plugging record; • completion report (W-2/G-1) to add well to schedule; • Pressure Front Calculation • Plug well before injection . Submit Summary Table and not this printout for every well! 27 28 29 Injection Well Permitting Attachments: Notice • Mail or deliver a copy of the application form (W-14 or H1/H-1A, front and back) to: – – – – – The surface owner Adjoining surface owners (Commercial Disposal) Operators of wells within a ½ - mile The county clerk The city clerk if well is located within corporate city limits • Recommend including a cover letter briefly explaining the nature of the application. 30 Injection Well Permitting Attachments: Notice Submit: • Plot (½-mile AOR) showing well location & operator • A table of the names and addresses of those parties required to be notified along with a signed and dated statement indicating the date that notice was mailed or delivered. • A plat showing clearly the owner of record of the surface and adjoining surface tracts and tract boundaries (Commercial Disposal) 31 Injection Well Permitting Example: Adjoining or “offset” surface owner plat 32 Example: Signed and dated notice certification page Offset operator and surface/ adjacent surface owner names identified on AOR plot/adjoining surface owner plat must be consistent with names on notice table 33 Injection Well Permitting Attachments: Publication • Publish - notice for one day in a newspaper with general circulation in the county. • Submit - Notarized affidavit of publication - Newspaper clipping • Publication and affidavit shells available on Injection/Disposal Well Permitting Manual • 15 day waiting period after notice and publication 34 Injection Well Permitting Publication Guidelines • The newspaper need not be in the same county as the well, but must have general circulation in that county. • The affidavit must state that the newspaper is of general circulation in the county where the proposed injection/disposal well is to be located. • The legal authority, notice of opportunity/instructions to protest application, and RRC contact information must be included in publication. • The newspaper publication must state that the application is for a “commercial” disposal well. 35 Injection Well Permitting Attachments: Fresh Water Injection • If application to inject fresh water, the following attachments are required: – Fresh water questionnaire – Form H-7 • Required unless fresh water is purchased commercially • Include plat of fresh water rights – Chemical analysis of the fresh water 36 Injection Well Permitting Permit Amendments • Filing requirements vary with type and magnitude of amendment. • Filing fee (per well) is required in all cases. • Well log, groundwater letter, AOR map and table are usually required when amending injection interval up-hole or permits issued prior to April 1982. • Refer to Guidelines for Permit Amendments in the Injection/Disposal Well Permitting Manual. 37 38 Injection Well Permitting Technical Review: Surface Casing • Commercial and new injection wells must set and cement surface casing through the BUQW • Applications for wells with “short surface casing” converted from production to lease injection/disposal are reviewed on a case by case basis. If permitted, requires more frequent testing and monitoring (annual mechanical integrity (MIT) testing and weekly tubingcasing annulus monitoring (TCAM) vs. 5-year MIT and monthly TCAM if well is constructed to current standards. 39 Injection Well Permitting Technical Review: Casing Cement • Cement must be adequate to confine fluids to the injection interval • Top of Cement (TOC) Requirements: - At least 600 feet if TOC is based on volume calc - 250 feet if TOC is determined by temperature survey run at time of cementing - 100 feet if TOC is determined by cement bond log • RRC rules have required 600 feet of cement above casing shoe, or shallowest productive interval since 1932 40 Injection Well Permitting Technical Review: Geological Requirements • Proposed injection interval must be isolated from overlying usable quality water by a sufficient thickness of relatively impermeable strata (accumulative total of at least 250 feet of clay or shale). • Verify that the proposed injection zone is adequately isolated by relatively impermeable strata to confine injected fluids to the proposed injection interval. 41 Injection Well Permitting Technical Review: Area of Review • Amendments to SWR 13(a)(4)(C) effective 1-14-2014: Casing of AOR wells must be cemented across and above all formations permitted under SWR 9 or cemented immediately above all formations permitted for injection under SWR46 • All abandoned wells within the ¼ - mile AOR must be adequately plugged (cement plug between top injection formation and BUQW). (May add as condition of permit). • Pressure Front Calculation (PFC): The applicant may calculate the actual affected radius to justify a lesser radius than ¼ -mile. PFC must be prepared by a Texas Registered Professional Engineer. 42 Injection Well Permitting Technical Review: Packer setting depth • Rule 9: – The packer must be set within 100 feet • Rule 46: – While Rule 46 allows for flexibility in the packer setting depth (150 feet below deepest groundwater and 200 feet below TOC), staff recommends the packer be set within 100 feet of the permitted zone – There may be no potential injection/disposal zones between the packer and the top of the permitted zone 43 Injection Well Permitting Technical Review: Injection Pressures • The maximum injection pressure limited to 0.5 psi/ft. • In some areas injection pressure is limited to ¼ psi/ft (ex: shallow coastal wells, Barnett Shale). • Applicant may perform a fracture step-rate test to measure the actual fracture pressure and to justify a higher permit pressure. 44 Injection Well Permitting Technical Review: Injected Fluids • Limited to the injection of produced salt water unless other fluids are specified • Injection of Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S) requires “wellspecific” authority. Contact the H2S Statewide Coordinator in Midland or San Antonio District Offices (SWR 36) 45 Injection Well Permitting Technical Review: Commercial Facilities • Surface facility requirements are added to deal with spill prevention, containment, pit permitting and security issues • A well is commercial if: – Salt water or waste is partially or wholly trucked in, or – A fee or other compensation is charge for disposal 46 COMMERCIAL DISPOSAL SURFACE FACILITY REQUIREMENTS • • • • • • All collecting pits, skimming pits, or washout pits must be permitted under the requirements of Statewide Rule 8. Catch basin(s) catch oil and gas waste which may spill as a result of connecting and disconnecting hoses or other apparatus while transferring oil and gas waste from tank trucks. Waste storage and pretreatment facilities (tanks, separators, or flow lines) shall be constructed of steel, concrete, fiberglass, maintained so as to prevent discharges. Dikes shall be placed around all waste storage, pretreatment, or disposal facilities. The dikes shall be designed so as to be able to contain a volume equal to the maximum holding capacity of all such facilities. Any liquids or wastes that do accumulate in the containment area shall be removed within 24 hours and disposed of in an authorized disposal facility. Must have security to prevent unauthorized access. Access shall be secured by a 24-hour attendant, a fence and locked gate when unattended, or a keycontrolled access system. For a facility without a 24-hour attendant, fencing shall be required unless terrain or vegetation prevents truck access except through entrances with lockable gates. Storage tank(s) equipped with a device (visual gauge or alarm) to alert drivers when each tank is within 130 barrels from being full. 47 Injection Well Permitting Permit Processing Permit Denials • Application is still incomplete after two additional filings • Denial based on unsatisfactory completion or operating proposal – The applicant may modify the application to allow for administrative approval, or – Request a hearing before the Commission. The application must be administratively complete before a hearing date can be set. 48 Injection Well Permitting Protested Applications • Staff may administratively issue a permit only in the absence of a protest • A protest may be filed anytime before a permit is issued 49 Injection Well Permitting Protested Applications Who can protest? • Affected parties – Operators of wells within ½ mile – Surface owner of record – Adjoining surface owners for commercial well • Local government (such as city or water district) • Other parties must demonstrate that they will be affected reviewed on a case-by case basis – Offset surface or mineral owners – Other government agencies – Members of the general public • Staff does not evaluate the validity of the protest 50 Injection Well Permitting Protested Applications Options for applicant: • Withdraw the application • Obtain a letter from the protestant withdrawing the protest • Request a hearing – The application must be administratively complete before a hearing may be scheduled 51 Injection Well Permitting Post Permitting - MIT • A mechanical integrity test (MIT) must be performed before any fluids are injected into the well. • Once the well is converted to injection, an MIT must be performed periodically (1 or 5 year test schedule), after workover, or whenever mechanical integrity is in doubt. 52 Injection Well Permitting Post Permitting – Completion Report (W2/G-1) • File a completion report (Form W-2/G-1) within 30 days (SWR 16) to reflect the actual completion of the well. • Filing a completion report on-line greatly reduces processing time. • Lease numbers for new leases (Form P-4) are assigned after final processing/approval of completion report. 53 Injection Well Permitting Application vs. Construction • The well must be constructed and operated as proposed in the application and permit • Permit required remedial action (i.e., permit special conditions) must be done before injection begins. • Operation not in accordance with the application and the permit may result in permit modification, suspension or revocation 54 Injection/Disposal Permit Query Imaged Records: W-14, H-1/H-1A: EDMS – Search all Permit Apps since 9/2000 H-10 Query 55 Injection/ Disposal Permits 56 Enter: Tracking# or Oper# County Date range Doc type (W-14/H-1) 57 Injection Permitting Technical Staff: Section Dave Hill, Manager David.Hill@rrc.state.tx.us Jim Moore Jim.Moore@rrc.state.tx.us Robert (Bob) Freymuller Robert.Freymuller@rrc.state.tx.us Nagi Mabruk Nagi.Mabruk@rrc.state.tx.us Jim Davis Jim.Davis@rrc.state.tx.us Cheryl Burns Cheryl.Burns@rrc.state.tx.us Ashley Johnston Ashkey.Johnston@rrc.state.tx.us 463-6792 463-3011 463-6443 936-0981 475-4655 463-6453 463-6454 463-6778 58 THE END