Personality & Social Psych
advertisement

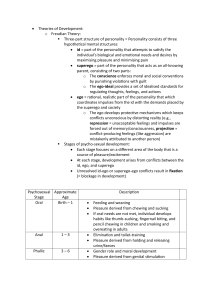
Personality and Social Psychology By: Sky, Rachel, Isaac, Kayla, Chase, Gabby, Malia, and Mark Personality Structure Freud’s view of human personality—including its emotions and striving—arises from a conflict between our aggressive, pleasure-seeking biological impulses and the internalized social restraints against them. 3 interacting systems: Id Ego superego ID, Ego, and Super-ego ID • • Unconscious Satisfies basic needs: survival, reproduction, and aggression EGO • • • Conscious mind Thoughts, judgments, perceptions Gratifies the ID’s impulses in realistic ways Super-ego • • Preconscious (outside awareness but accessible) Strives for perfection, judging actions, and producing positive feelings of pride, or negative feelings of guilt Freud’s Psychosexual Stages Oral (0-18 months) Pleasure centers on the mouth- sucking, biting, chewing Anal (18-36 months) Pleasure focuses on bowel and bladder elimination, coping with demands for control Phallic (3-6 years) Pleasure zone is the genitals coping with incestuous sexual feelings Latency (6 to puberty) Dormant sexual feelings Genital (puberty on) Maturation of sexual interests The Big Five Personality Factors Conscientiousness Agreeableness Neuroticism Openness Extraversion Personality 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 3. 4. Biological influences Genetically determined temperament Autonomic nervous system reactivity Brain activity Psychological Influences Learned Responses Unconscious thought processes Optimistic or pessimistic attributional style Social-Cultural influences Childhood experiences Influence of the situation Cultural expectations Social support Personality Defense Mechanisms Ego protects itself with defense mechanisms Repression-banishes anxiety-arousing thoughts and feelings from consciousness Regression-allows us to retreat to an earlier, more infantile stage of development Reaction formation-when the ego unconsciously makes unacceptable impulses look like their opposite Projection-disguises threatening impulses by attributing them to others Rationalization-occurs when we unconsciously generate self-justifying explanations to hide from ourselves the real reasons for our action Displacement-diverts sexual or aggressive impulses toward an object or person that is psychologically more acceptable than the one that aroused the feeling. Social Thinking Fundamental Attribution Theory – the tendency to overestimate the influence of personality and underestimate the influence of situations. Foot-in-the-door Phenomenon – the tendency for those who complied to a small request to comply later to a larger demand. Cognitive Dissonance Theory – theory that we act to reduce the discomfort we feel when two thoughts are inconsistent. Social Influence Conformity – adjusting one’s behavior or thinking to coincide with a group standard. Normative social influence – influence resulting from a person’s desire to gain approval or avoid disapproval. Informational social influence – influence resulting from one’s willingness to accept others’ opinions about reality. Social Facilitation – stronger responses on simple or well-learned tasks in the presence of others. Social Loafing – tendency for people in a group to exert less effort when pooling their efforts toward a common goal. Groupthink can be prevented when a leader welcomes various opinions and invites experts’ critiques of developing plans or assigns people to identify possible problems. Antisocial Relations Prejudice – an unjustifiable attitude toward a group and its members. Discrimination – unjustifiable behavior towards a group or its members. Ingroup Bias – “Us.” The tendency to favor our own group. Outgroup– “Them” Scapegoat Theory – theory that prejudice offers an outlet for anger by providing someone to blame. Frustration-Aggression Principle – principle that frustration creates anger, which can generate aggression. Social Trap – a situation in which the conflicting parties become caught in mutually destructive behavior. Prosocial Relations Passionate Love – intense positive absorption in another, at the beginning of a relationship Companionate Love – deep affectionate attachment we feel for those whose lives intertwine with ours Self-disclosure – revealing intimate aspects of oneself to others Altruism – unselfish regard for the welfare of others Mere exposure effect – phenomenon that repeated exposure to novel stimuli increases liking of them. Similarity – opposites attract is a myth. We often tend to like someone similar to us. Similarity breeds content. Our Song Lyrics “Moves Like Jagger” There’s a man who’s names Freud He’s doctor who had lots of toys There’s a structure that’s totally his It starts with the Id Beginning with this And it goes like this The id seeks total gratification The ego gratifies Id impulses And the superego It’s the superego It makes yooooooooou have good judgment But of course that’s not all There are stages The lists not so tall It’s a short one It starts with the mouth and then travels south I’ve got this figured out And it goes like this First it starts out with only just one tooth Then I learn how to use that bathroom And I begin to wonder What’s the thing down under? Now you’re fiiiiiiiiiinding sexual interests