File
advertisement

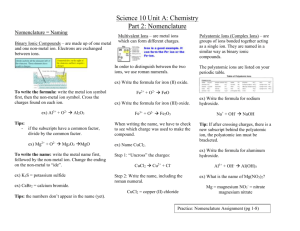
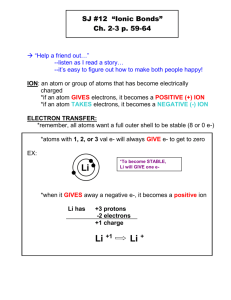
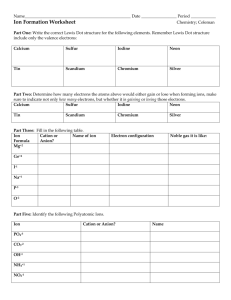
Reference Guide Ch 7: Compounds Naming and Writing Formulas These are your tabs on the bottom – label them. _________________________________ Metal to Non-metal Ionic Names_____ Metal to Non-metal Ionic Formulas___ Non-metal to Non-metal Molecular Names______ Non-metal to Non-metal Molecular Formulas____ Acids, Bases, and Salts Monatomic: 1. Positive Ions – use element name + ion. Ca2+ - Calcium ion 2. Negative Ions – drop ending and add “ide”. Br1- Bromide ion Binary: 1. Write the cation first, followed by the anion. 2. Metals that form more than one ion use Roman numerals to identify the charge of the ion. Fe 3+ : Iron (III) ion Cu2+ : Copper (II) ion 3. Add “ide” to the anion ending Polyatomic Ions: Use the chart Oxygen “ate” or “ite” Multiple – use parenthesis Metal to Non-metal Ionic Names Examples: Sodium Oxide Na2O Ammonium Sulfate (NH4)2SO4 Calcium Nitrite Ca(NO2)2 Strontium Phosphate Sr3(PO4)2 ________________________________ Binary Ionic Compounds: 1. Write the symbol of the cation first. 2. Charges of the ions are not included in the chemical formula. 3. Determine the ratio of ions by doing the “charge cross over” 1. - the absolute value of each ions’ charge as the subscript for the other ion. Ionic Formulas Examples: N2O dinitrogen monoxide SO2 sulfur dioxide N2O3 dinitrogen trioxide ________________________________ 1. Element with lower group number is first. If in the same group, greater period is first. 2. Second element is an anion (ide) 3. Greek prefixes determine number 1. *no mono on first Mono = 1 Di = 2 Tri = 3 Deca = 10 Tetra = 4 Penta = 5 Hexa = 6 Hepta = 7 Octa = 8 Nona = 9 Some compounds were discovered before the elements were known so some covalent compounds have names that don’t match their formulas. Ex. Water, ammonia, and methane. Molecular Names 1. The least electronegative element is written first. 2. Use prefixes to make the subscripts. If no prefix is present at the beginning, one atom is used. Molecular Formulas ___________________________________________ Acids – (begin with H and contain H+ ions) acids increase the concentration of H+ in aqueous solutions. 1. a. b. Binary – 2 elements – usually hydrogen and a halogen. Oxyacids – contain hydrogen, oxygen, and a third element. Bases – (contain OH- ion) – a substance that increases the concentration of OH- ions in aqueous solutions. 3. Salts – have a cation and an anion from an acid. Ex. HCO3- (hydrogen carbonate ion and Bicarbonate ion.) Acids, Bases, and Salts 2.