What is VoIP - XBLUE phone system
advertisement

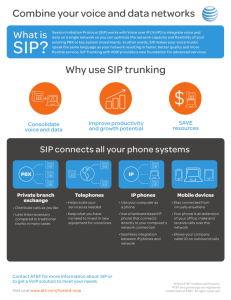
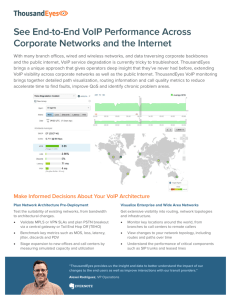
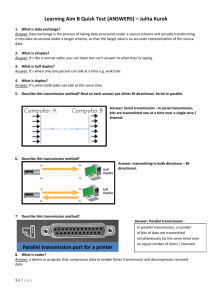
Agenda Evolution of Communications Digital vs VoIP How VoIP works as a transport layer What is “The Cloud”? Common Applications Advantages of VoIP Misconceptions about VoIP Evolution of Communications Scream at your Neighbor IP PBX Phone Guy Gets Yelled at! 2 Cans and a String CPE PBX using IC Chips Central Office Digital vs VoIP Digital -Like a Subway or a Train Goes Point to Point Lots of people in the same car! Predetermined stops Not Very Flexible VoIP – Like a Taxi Dynamic in direction Single Occupant Goes to one address Very Flexible Telephone Systems Telephones are directly connected to the system Telephones - limited distance from the KSU Telephones are dumb terminals System Hardware controls the configuration size Communications is most often proprietary Use Pulse Code Modulation Use Time Division Multiplexing Pulse Code Modulation Encoder 0111 0110 0111 0110 0101 0101 0100 0100 0011 0011 0010 0010 0001 0001 0000 0000 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 Time Division Multiplexing is the distance between the samples Voice Conversation is transmitted in 0’s and 1’s Transport Layer 1401 Ext 401 Voice PBX 1 010001110101 010001110101 PBX Digitized Voice All 0’s and 1’s Transmitted Via T1/PRI PSTN T1/PRI transport E&M Emulation Ext Ext2407 407 Voice Voice Digitized Voice All 0’s and 1’s Transmitted Via T1/PRI PBX 2 What is VoIP Voice over Internet Protocol is the transmission of voice over a network – Not the Internet Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model: 7 = Application – processes applications 6 = Presentation – data representation and encryption 5 = Session – Inter-host communications 4 = Transport – End to end connections and reliability (TCP) 3 = Network – Path determination and logical addressing (IP) 2 = Data Line – Physical Addressing (MAC addresses & LLC) 1 = Physical – Medial, signal and binary transmission 19216 WEST Address Driven x x x x x x x OFFICE 3 x x 192.16 West 8.1st – Office 1 192.16 West 8.1st – Office 2 192.16 WestOFFICE 8.1st – Office 13 192.16 West 8.1st – Office 4 192.16 West 8.1st – Office 5 OFFICE 1 st – Office 6 192.16 West 8.1 x OFFICE 3 x x OFFICE 5 OFFICE 5 ST 81 IP Address x x OFFICE OFFICE 4 4 x x x x x x xx OFFICE 6 6 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.3 OFFICE 192.168.1.4 OFFICE 2 Server 192.168.1.5 Room 192.168.1.6 2 xx Transport Layer Ext 1401 Voice PBX 1 Ext 2401 Voice Digitized Voice All 0’s and 1’s Digitized Voice All 0’s and 1’s Gateway 62.203.3.1 67.203.5.1 PBX 2 Gateway Packets addressed and sent over the Internet Packets addressed and sent over the Internet Internet transports from one location to another using address Internet What is the Cloud? 66.210.10.1 127.107.7.2 62.203.3.1 127.107.7.1 64.201.100.4 65.25.2.2 66.210.10.2 66.166.1.4 61.200.2.3 65.16.200.5 127.107.7.3 66.166.1.12 62.2.200.4 168.68.2.6 Common Applications Remote Worker Unmanaged Network – Latency and jitter Bandwidth Limitations 192.168.100.1 Only need one static IP Address 67.28.190.127 WAN Internet 167.19.120.111 301 302 303 Common Applications 192.168.1.120 Remote Workers Gateway Registration WAN Port 192.168.100.1 125.105.90.201 67.28.190.127 Internet 167.19.120.111 112.47.99.98 301 302 303 192.168.22.199 Common Applications Creating a Voice Network Unmanaged Network – Latency and jitter Bandwidth Limitations Only need one static IP Address Internet 67.28.190.127 301 302 303 122.24.50.13 301 302 303 Common Applications Adding to the Voice Network 192.168.22.110 192.168.22.111 192.168.11.110 WAN LAN 192.168.11.111 LAN Internet 67.28.190.127 301 302 303 122.24.50.13 301 302 303 Common Applications Adding SIP trunks to the Voice Network 192.168.22.110 192.168.22.111 Internet 67.28.190.127 SIP Trunks 301 302 303 SIP Trunks Common Applications Two locations 192.168.22.110 192.168.22.111 192.168.11.110 192.168.11.111 Internet 67.28.190.127 301 302 303 122.24.50.13 SIP Trunks 301 302 303 Advantages to VoIP Standards of Interconnectivity Dynamic in Installation and Application Unlimited in Size – Global Network Remote workers Relatively easy to create a “Voice Network” Easy to do MAC Work Single Cable Runs (Maybe) Tree Topology Tree Topology 1 x x x x OFFICE 3 x OFFICE 1 192.168.1.5 192.168.1.3 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.6 192.168.1.4 192.168.1.2 x OFFICE 4 x x x OFFICE 6 Server Room OFFICE 2 x x OFFICE 5 x Tree Topology 2 x x x x OFFICE 3 x OFFICE 1 192.168.1.5 192.168.1.3 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.6 192.168.1.4 192.168.1.2 x OFFICE 4 x x x OFFICE 6 Server Room OFFICE 2 x x OFFICE 5 x Disadvantages of VoIP Remains Expensive for the Small Business Can be difficult to troubleshoot Standards are still evolving Quality of Voice over an Unmanaged Network Lags on Call Processing Functionality External Interfaces Line appearances and buttons Misconceptions about VoIP I am going to save Money! No more paying long distance toll charges When I use VoIP I only need one cable drop per office Using Remote workers will save me money because I can use a smaller office