Feudalism & Manorial System
advertisement

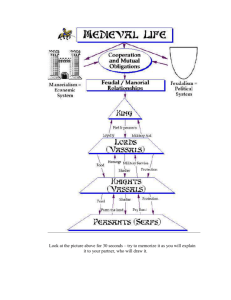
Feudalism & Manorial System I. Invaders Attack W. Euro. 800-1000: invasions helped destroy Carolingian Emp. – Muslims – Magyar – Vikings A. The Vikings From Scandinavia “Northman” or the “Norse” (Germanic) Farmers, fishermen, hunters, traders, & explorers “a-Viking” we will go! (summer months) 800s = food shortage in Scan. Viking ships Sailed across Atlantic to Iceland, Greenland, & N. Amer. (Leif Ericson) Also, England, Ireland, & Fr. – Normandy Traded w/strong, pillaged weak Enjoyed battle (large axes, swords, & wooden shields) Followed pagan beliefs 1000: Vikings faded – Gradually accepted Christianity – Euro. climate warmed…ag. improved B. Magyars & Muslims Attack Magyars: nomads from east (late 800s) – Tactics similar to Huns – Become the “Hungarians” – Overran Italy, reached Rhineland & Burgundy – Did not settle conquered land, only took slaves – Settled in what is now Hungary Muslims: attacked from south (Italy & Spain) – Terrorized Med. coast—took Sicily, Sardinia, & Corsica Invasions = disorder & suffering – Euros. were in constant danger – Turned to local rulers for security II. Feudalism Govt. disappeared after Char’s. death 814 Continent of small, independent local govts. Feudalism: kings granted land to other nobles in return for loyalty & military assistance – Kings = gave grants of land (fief) to nobles Lord = person who granted land Vassal = person who received land – Fief = grant of land, contract betw. lord & vassal A. Feudal Pyramid Hierarchical Pyramid – King – Vassals (nobles & bishops) – Knights (defended lord’s land) – Peasants (landless) B. Social Classes Three groups: – 1. those who fought – 2. those who prayed – 3. those who worked Vast majority of pop. Serfs (bound to place of birth) Majority of pop. = peasants (serfs) – Could not leave the land w/out the lord’s permission Church = part of the feudal system – 900s: owned vast amounts of land granted some as fiefs to nobles for military protection C. Feudal Relationships Three facts: – 1. it was an honorable relationship betw. equals – 2. same man could be both vassal & lord – 3. the relationship was a personal one D. Obligations of Feudalism Vassals had more obligations than the lord – Provide lord w/cavalry & infantry – Had to cover extraordinary expenses – Served on the lord’s court E. Feudal Justice Court trials were decided: – 1. trial by battle (duel) – 2. compurgation (oath taking) – 3. trial by ordeal F. Warfare Fights betw. feudal lords or betw. lords & vassals Knights: – Iron helmet, shirt of chain mail, sword, shield, lance Later, metal plates replaced chain mail (Why?) *For nobles, war = opps. for glory & wealth! III. The Manorial System Feudalism = govt. & military system Manorial System = economic structure – Large estate Manor = lord’s estate Lord gave serfs housing, farmland, & protection Serfs tended land, animals, & performed maintenance Peasant women shared farmwork No central authority or trade existed – Manors were self-sufficient Lord & peasants shared land – Lord = 1/3 of land (demesne) – Peasants = 2/3 of land Usually located on a stream for its mill Covered a few square miles Had lord’s house, church, & workshops Cultivated land was divided into 3 large fields – 2 of 3 planted each year (1 lied fallow) A. Peasant Life peasants = serfs Some free people rented land – Skilled workers (millers, blacksmiths, carpenters) Priests Life on manor = very hard – Meager diet – Rarely ate meat Life expectancy = 30 years (disease, starvation, war) B. The Life of Nobility Nobles did not lead luxurious lives Castle – Fortified home of lord – Served as base from which to protect the surrounding countryside – Early castles = relatively simple built of wood & earth – Later = stone – Located in hills or easily defendable areas (had moats)