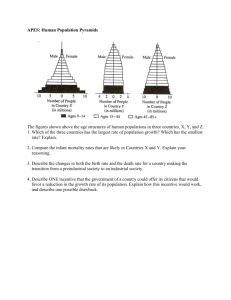
Berridge-Banbury-2007
advertisement

Berridge Unconscious emotion components What is an unconscious emotion? “Our feeling … IS the emotion.” William James What is an emotion? (1894) “So for emotions, feelings and affects to be unconscious would be quite out of the question.” Sigmund Freud The Unconscious (1915) Unconscious emotion? Zajonc Öhman Wilson Damasio LeDoux Winkielman Analogous to nonconscious blindsight or implicit memory … Components? Affective building blocks Even simplest emotion contains affective building blocks Dissociate Conscious Emotion Core Building Blocks Positive affect (reward) ‘Like’ ‘Want’ Construct Fear Desire ? What causes hedonic ‘liking’? Brain hedonic hotspots Generating pleasure ‘liking’ via a network of opioid islands Hedonic hotspots: Peciña, Smith, Berridge (2006) ‘Liking’ & ‘Disliking’ expressions to taste Reflect palatability of physiological hunger, learning, & brain hedonics Neural hierarchy: forebrain hedonics control brainstem reactions Brain hedonic hotspot network Generating pleasure ‘liking’ for incentives Nucleus Accumbens hotspot Opioid DAMGO microinjections in hedonic hotspots (nucleus accumbens shell or ventral pallidum). Increases ‘liking’ reactions to sweetness Hedonic hotspots: Peciña, Smith, Berridge (2006) Dopamine: Breaking apart simple reward Rewards activate dopamine & nucleus accumbens Liking, Predicting or Wanting? Win money! Positive Emotions Expect reward Meta-analysis O’Doherty et al 2004 Knutson et al 2004 Social (trusted face) reward Weger et al 2003 McLure et al 2004 Singer et al 2004 Hippocampus DA Amplifies CS+ Incentive Code Thalamus Orbitomedial Frontal Cortex Amygdala Nucleus Accumbens Ventral Tegmental Area Ventral Pallidum SNc/SNr Hypothalamus CS Trained brain normally fires to first cue US incentive salience Then to 2nd and to sugar reward pursuit Decision Utility CS+1 CS+2 Predicted utility SugarUCS Time Incentive cue Tindell, Berridge, Zhang, Peciña, Aldridge, 2005 Hippocampus DA Amplifies CS+ Incentive Code Thalamus Orbitomedial Frontal Cortex Amygdala Nucleus Accumbens Ventral Tegmental Area Ventral Pallidum SNc/SNr Hypothalamus CS Drug sensitization magnifies impact of second incentive cue US incentive salience pursuit Decision Utility Decision utility ‘wanting’ CS+1 CS+2 SugarUCS Time Incentive cue Tindell, Berridge, Zhang, Peciña, Aldridge, 2005 Hippocampus DA Amplifies CS+ Incentive Code Thalamus Orbitomedial Frontal Cortex Amygdala Nucleus Accumbens Ventral Tegmental Area Ventral Pallidum SNc/SNr Hypothalamus CS Amphetamine on board also magnifies impact of second incentive cue US incentive salience pursuit Decision Utility Decision utility ‘wanting’ CS+1 CS+2 SugarUCS Time Incentive cue Tindell, Berridge, Zhang, Peciña, Aldridge, 2005 Hippocampus DA Amplifies CS+ Incentive Code Thalamus Orbitomedial Frontal Cortex Amygdala Cue-triggered firing by VP neurons Nucleus Accumbens Ventral Tegmental Area Ventral Pallidum SNc/SNr Hypothalamus CS Combination especially magnifies impact of second incentive cue US incentive salience pursuit Decision Utility Decision utility ‘wanting’ CS+1 CS+2 SugarUCS Time Incentive cue Tindell, Berridge, Zhang, Peciña, Aldridge, 2005 Implications of ‘liking’ vs ‘wanting’? Incentive-Sensitization theory of Addiction Terry Robinson Addiction Relative Effect Initial Use Incentive Value Subjective Pleasure Time Positive affect (reward) Neural Sensitization of mesolimbic dopamine systems: Hyper-excitable Caused by amphetamine, cocaine, heroin, alcohol, nicotine… Lasts years… ‘want’ ‘like’ ‘Wanting’ is triggered by cues: Images & imagery Simultaneous synergy: Reward cue & brain dopamine activation Ordinary desires differ chiefly in degree of brain activation? Shared affective building block for positive & negative emotion? Dissociate Emotion Building Blocks Positive affect (reward) ‘Like’ ‘Want’ Construct Fear Desire ? Nucleus Accumbens shell Bivalent emotion from corticolimbic tweaks (Glutamate AMPA blockade by shell DNQX) •Positive front , Negative back •No neutral center •Ambivalent middle: +/- both together Appetitive positive Aversive fear (eat, prefer, ‘like’) (bite, distress, ‘dislike’) Anterior Front Reynolds & Berridge, 2003 Back Posterior Natural ‘dread reaction’ Fearful defensive treading (from Donald Owings & Richard Coss) 0 Natural ‘dread reaction’ Fearful defensive treading (from Donald Owings & Richard Coss) 0 Affective building blocks & Fear versus Desire • What do ‘ambivalent sites’ in the middle mean? • Simultaneous desire/dread fixed valence channels? • Or flexible limbic block built into opposite emotions? Emotion Affective Building Blocks Fear Desire ? Construct But does valence overlap actually reflect flexibility of affective building block? • Can same limbic block be used to build desire or fear ? Fear Desire ? ? Test using situational appraisal: Can same building block be used for both desire & fear? 3 situations for test • Comfortable Home – • Dark, quiet, familiar Regular Lab – • Standard test Aversively noisy & bright – – Iggy Pop music: loud discordant Bright lights Reynolds & Berridge Place Conditioning Self-administration choice • Iggy Pop ? ? Home sweet home But rats avoid Iggy Pop Home vs. Lab 1000 Home Lab 800 Home 600 )e c s ( e m Ti 400 ** 200 ** ** ** Lab 0 12 3 15-min Time Bin 4 Lab vs. Iggy Pop 1000 Lab Iggy Lab 800 600 )c e s ( e m Ti 400 ** 200 0 ** 12 ** 3 15-min Time Bin ** 4 Iggy Place Conditioning Self-administration choice • Iggy Pop ? ? Home sweet home But rats avoid Iggy Pop Home vs. Lab 1000 Home Lab 800 Home 600 )e c s ( e m Ti 400 ** 200 ** ** ** Lab 0 12 3 15-min Time Bin 4 Lab vs. Iggy Pop 1000 Lab Iggy Lab 800 600 )c e s ( e m Ti 400 ** 200 0 ** 12 ** 3 15-min Time Bin ** 4 Iggy Causation maps for motivation valence Home comfort converts fear into desire Anterior Iggy Pop converts desire into fear Anterior Posterior Posterior Flexible building blocks? Suggests the same limbic building block can construct opposite emotions Fear Desire ? ? Conclusions Counterintuitive emotion components Emotions Conscious Unconscious Components Positive affect (reward) ‘Like’ ‘Want’ Fear Desire ? Types of Miswanting • Conventional miswanting • Gilbert, Wilson, Kahneman Choosing what one wrongly expects to like Kahneman Reward utilities: (Decision U = Predicted U) > Experienced U • Affective forecasting • Distorted predicted utility • More irrational ‘miswanting’ • • Choosing what one does NOT expect to like • Decision U > (Predicted U = Experienced U) Today’s thesis: Brain mesolimbic dopamine activation may elevate decision utility alone Humans ‘want without like’? Ex: False ‘pleasure electrodes’ • Rat LH stimulation – Food ‘wanting’ without ‘liking’ • Famous 1960s human studies – Neurologists implanted patients • Robert Heath, M.D. • Patient B-19 - 20-yr man –MFB electrode – Stimulated electrode 1500 times in a session, protested whenever stimulator taken away (p. 6, Heath, 1972) – “feelings of pleasure, alertness, and warmth (goodwill); he had feelings of sexual arousal and described a compulsion to masturbate.” Positive affect (reward) But really pleasure? – No exclamations of pleasure – And electrode did not substitute for sex – Electrode only made him want sex more… ‘want’ ‘like’