Co-dominance
advertisement

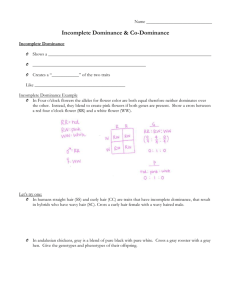
Warm ups: 1. What is a sex linked disorder? 2. What chromosome are these genes usually on? ( X or Y) 3. If you were a male, what two chromosomes would you have? a. XX B. YY C. XY Incomplete dominance and Codominance in Genetics Lets look at Incomplete Dominance first!!! Incomplete dominance is like the genes sharing the dominance. You get a mixing or blending of the dominant trait. Incomplete dominance 1. Incomplete dominance – when there are two dominant traits that don’t have dominance over each other. This results in a combined phenotype. 2.It’s like a “blending” of the two dominant genes, both traits are expressed. (sharing dominance) + White = Red Pink Incomplete dominance 3. Examples: a. Red flower color (R) and White flower color (W) = Pink flowers (RW) + = b. Red flowers (R) and Blue flower color (B) = Purple flower color (RB) + = c. When you have a purebred red; the genotype is RR d. When you have a purebred white; the genotype is WW e. When you have hybrid flower (RW) the resulting color is PINK!! (both share dominance) Examples of Incomplete Dominance • • • • Skin color Flower color Fur color Short fur or long fur INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE PUNNETT SQUARES PRACTICE PROBLEMS 1. A red flowered is crossed with a white flowered . (R = red, W = white) R RR Red flower = _____ WW White flower = ____ 0 ____ % white 0 ____ % red 100 ____ % pink 100 ____ % heterozygous 0 ____ % homozygous R W WR WR W WR WR 2. A blue flowered rose is crossed with a purple flowered rose. (B = blue, R = red) B BB Blue flower = _____ BR purple flower = ____ 50 ____ % blue 0 ____ % red 50 ____ % purple 50 ____ % heterozygous 50 ____ % homozygous B B B B BB R B R B R Now lets talk about Codominance in Genetics In Co-dominance, you see both dominance traits. Co-Dominance 1. Co-dominance – when two dominant traits are shown in the offspring. 2. Both traits appear at the same time, but not mixed or blended together. + White = Red + = Red and white Co - dominance 3. Examples: a. Example: Red flower color (R) and White flower color (W) = Red and White flowers (RW) + = b. Example: Yellow flowers (Y) and Blue flower color (B) = Yellow and Blue flower color (YB) + = Co - DOMINANCE PUNNETT SQUARES PRACTICE PROBLEMS 1. A red flowered is crossed with a white flowered . (R = red, W = white) R RR Red flower = _____ WW White flower = ____ 0 ____ % white 0 ____ % red 100 ____ % red and white 100 ____ % heterozygous 0 ____ % homozygous R W WR WR W WR WR Exit slip 1. What type of dominance creates in a blending or sharing of the genes? 2. What type of dominance creates an offspring that shows both dominant traits.