Document
advertisement

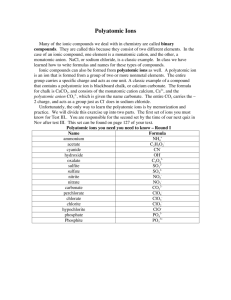
Compounds & Molecules NaCl, salt Buckyball, C60 Compounds & Molecules • COMPOUNDS are a combination of 2 or more elements in definite ratios by mass. • The character of each element is lost when forming a compound. • MOLECULES are the smallest unit of a compound that retains the characteristics of the compound. ELEMENTS THAT EXIST AS DIATOMIC MOLECULES ELEMENTS THAT EXIST AS MOLECULES Allotropes of C ELEMENTS THAT EXIST AS POLYATOMIC MOLECULES S8 sulfur molecules White P4 and polymeric red phosphorus Molecular Compounds Compounds without Ions CO2 Carbon dioxide CH4 methane BCl3 boron trichloride MOLECULAR FORMULAS • Formula for glycine is C2H5NO2 • In one molecule there are –2 C atoms –5 H atoms –1 N atom –2 O atoms STRUCTUAL FORMULAS • Can also write glycine formula as –H2NCH2COOH to show atom ordering • or in the form of a structural H H O H N C C O H H formula MOLECULAR MODELING H H O H N C C O H H Ball & stick Drawing of glycine Space-filling Naming Elements & Compounds Chapter 2 & 3: Chemical Equations Handbook molecules are formed from two or more nonmetals. CO2 Carbon dioxide BCl3 boron trichloride ammonium chloride, NH4Cl Ionic compounds have a cation and anion: generally involve a metal and nonmetal, NaCl IONS AND IONIC COMPOUNDS • IONS are atoms or groups of atoms with a positive or negative charge. • Taking away an electron from an atom gives a CATION with a positive charge • Adding an electron to an atom gives an ANION with a negative charge. Forming Cations & Anions A CATION forms when an atom loses one or more electrons. Mg --> Mg2+ + 2 e- An ANION forms when an atom gains one or more electrons F + e- --> F- COMPOUNDS FORMED FROM IONS CATION + ANION ---> COMPOUND Na+ + Cl- --> NaCl Are NEUTRAL. Compounds have EQUAL number of + and - charges. IONIC COMPOUNDS NH4 + Cl ammonium chloride, NH4Cl Properties of Ionic Compounds Forming NaCl from Na and Cl2 • A metal atom can transfer an electron to a nonmetal. • The resulting cation and anion are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces. Electrostatic Forces The oppositely charged ions in ionic compounds are attracted to one another by ELECTROSTATIC FORCES. These forces are governed by COULOMB’S LAW. Electrostatic Forces COULOMB’S LAW (charge on +)(charge on -) Force of attraction = (distance between ions)2 Direct relationship between charge and force: charges increase, the force increases. Inverse relationship between distance between ions and force: increase distance, decrease force. Importance of Coulomb’s Law NaCl, Na+ and Cl-, m.p. 804 oC MgO, Mg2+ and O2m.p. 2800 oC PREDICTING ION CHARGES In general • metals (Mg) lose electrons ---> cations • nonmetals (F) gain electrons ---> anions METALS M ---> n e- + Mn+ where n = periodic group Na+ sodium ion Mg2+ magnesium ion Al3+ aluminum ion Transition metals --> M2+ or M3+ are common Fe2+ iron(II) ion Fe3+ iron(III) ion NONMETALS NONMETAL + n e- ------> Xnwhere n = 8 - Group no. Group 4A Group 5A Group 6A Group 7A C4-,carbide N3-, nitride O2-, oxide F-, fluoride S2-, sulfide Cl-, chloride Br-, bromide I-, iodide Charges on Common Ions -4 -3 -2 -1 +1 +2 +3 By losing or gaining e-, atom has same number of e-’s as nearest Group 8A atom. Predicting Charges on Monatomic Ions Binary Ionic Compounds Mn2+ + O2- ----> MnO manganese (II) oxide Al3+ + S2- ----> Al2S3 aluminum sulfide Ca2+ + 2 F- ---> Sn4+ + Cl- ----> SnCl4 Tin (IV) chloride or Stannic chloride CaF2 calcium fluoride Practice Name & Formulas Ultimate Equation Handbook Only the binary compounds • Exercise 2-1 pg. 10 • Exercise 3-2 pg 17 Homework: Worksheets pgs 23-28 POLYATOMIC IONS Groups of atoms with a charge. MEMORIZE the names and formulas in Table 3.1, page 89. Polyatomic Ions NH4+ ammonium ion One of the few common polyatomic cations Polyatomic Ions HNO3 nitric acid NO3nitrate ion Polyatomic Ions CO32carbonate ion HCO3bicarbonate ion hydrogen carbonate Polyatomic Ions PO43phosphate ion CH3CO2acetate ion Polyatomic Ions SO42sulfate ion SO32sulfite ion Polyatomic Ions NO3nitrate ion NO2nitrite ion sheet pg #22 “ates” Practice Name & Formulas Ultimate Equation Handbook Add the polyatomic compounds • Exercise 2-1 pg. 10 • Exercise 3-2 pg 17 • Exercise 4-1 pg 20 • Exercise 4-3 pg 21 Homework: Worksheets pgs 23-28 –poly Pgs 29-33 Molecular & Ionic Compounds Heme NaCl