Force Theory of State Formation
advertisement
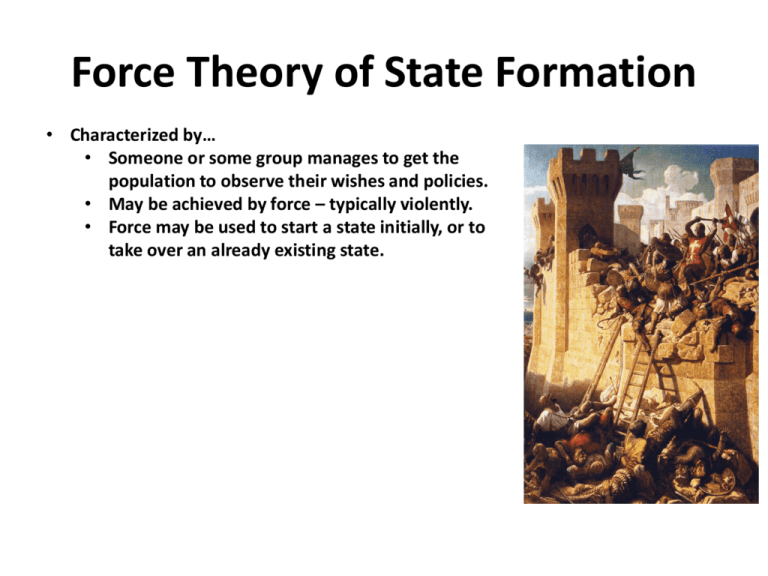
Force Theory of State Formation • Characterized by… • Someone or some group manages to get the population to observe their wishes and policies. • May be achieved by force – typically violently. • Force may be used to start a state initially, or to take over an already existing state. Evolutionary Theory of State Formation • Characterized by… • Origins in family/kinship • Develop links to a defined area through growth of clans, and then development of permanent agriculture, tying you to a defined area. Divine Right Theory of State Formation • Characterized by… • Unique tie to a defined territory and the government of it, is inspired and/or given by a higher power. • Single leader (king) who claims that God ordained to rule. King Charles II of England (1660) Social Contract Theory of State Formation • Characterized by… • Government formed by the will of the population in a territory. • The “contract” is that the people “allow” the government to serve in their name; they may overthrow an unresponsive and tyrannical government if they are able to organize such a transition. • Typically associated with what emerges as democratic, non-monarchical states.