BOT-2: Gross Motor Bruininks-Oserentsky Test of Motor Proficiency
advertisement

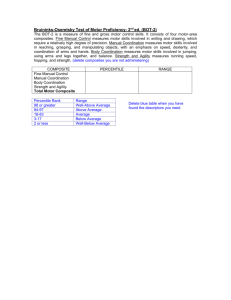
BOT-2: Gross Motor Bruininks-Oserentsky Test of Motor Proficiency- 2nd Edition Key characteristics Purpose Evaluate proficiency of motor skills Support diagnoses, screening (short form), educational placement (physical education), etc. Most widely used motor proficiency test Age 4yrs -21yrs 11 months Time Complete form= 40-60 minutes Short Form= 15-20 minutes Cost Gross motor kit- $515.00 Gross motor Body coordination Strength & Agility Bilateral coordination Running speed and agility Balance Strength Gross Motor Domains Gross motor composite total: 26 items Body coordination: motor skills used with balance & coordination of the upper and lower extremities Strength & agility: large muscle strength, motor speed, and motor skills for maintaining body position for walking and running Procedures Testing procedures Standardized test: administered & scored according to specific procedures Gross motor should be performed in an area 60 feet long 12 feet wide Determine hand preference: set a tennis ball on the table and ask the examinee to pick up the ball and throw to you. Foot preference: place tennis ball on floor and instruct the examinee to kick the ball Within each subtest the entire item set should be administered regardless of the child’s age Procedures • Administration procedures • • • • Structured Can teach the item using pictures, physical demonstration, or verbal instruction Establish rapport Administrative options: • • • Complete form: most reliable measure of overall motor proficiency Short form: quick and easy overall measure & also used to determine the need for further assessment Select composites & select subtest: can administer only subtests or composites that are relevant to the client’s need but the complete form should be used for qualifying a client for special-education services or diagnosis such as DCD Examples of test items Gross motor Body coordination Bilateral coordination Jumping jacks, tapping foot and finger Balance Walking forward on a line, standing on one leg on a balance beam Strength & Agility Running speed & agility Shuttle run, one-legged side hop Strength Standing long jump, sit-ups, push-ups Standardization •Scores identify motor-skill deficits in individuals with mild to moderate motor control problems Sample: N=1520 12 groups of 4-21 year olds Sample tested in 239 sites within 38 states Based on the Current Population Survey (Bureau of the Census, 2001) & the Twentysixth Annual Report to Congress (U.S. Department of Education, 2004) Sampling goal to match US population: Sex Race/ethnicity (closely matched US population) Socioeconomic status Geographic region Development Started out as the BOTMP in 1978 2002 product survey identified less effective items within the test New content focused on improving measurement among 4 & 5 year olds, and expanding coverage of fine and gross motor skills Secondary goal Subtest more homogenous collection of activities 2005 final publication of the BOT-2 Psychometric Properties Internal consistency Test-retest Reliability Interrater Reliability Domains (0.86-0.92) Test-retest study N=134 Interrater reliability: Manual coordination, body coordination, and strength & agility 0.98-0.99 Sub-domains (0.770.86) Mean re-test interval 7-42 days Fine motor: 0.92 Total BOT-2 Score (0.95-0.96) Age 4-7=0.81 Age 8-12=0.80 Age 13-21= 0.75 Psychometric Properties Continued Validity Content Validated through logical & empirical procedures that were used to select items during development Construct Used a composite structure that distinguishes motor skills by limbs and musculature involved in relationship to functional activities in areas of postural control, locomotion, and object manipulation Clinical group difference Supports diagnosis of motor performance deficits Criterion BOTMP, PDMS-2, TVMS-R Scoring & Recording Results Converting raw scores to point scores Compute subtest total point scores Convert scale scores to composite standard scores Interpretation •Well below average •Below average •Average •Above average •Well above average Test characteristics Areas of occupation Education (physical education) Play Assessment approach Bottom-up approach Frame of Reference Developmental Where would this tool be used? Private practice School system Performed in a gymnasium Area should be 60 feet long and 12 feet wide, low distractions Measurement concerns Normative data did not represent for populations outside of the US Cost: Complete form test kit= $837.00 Area, size, requirements, special equipment Examinee dependent Assessment time