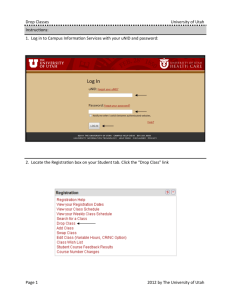
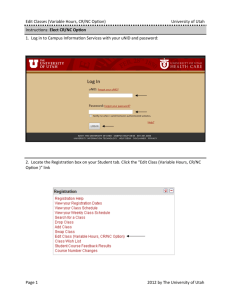
Review for Chapter 7
advertisement

Utah Native Tribes This is a no gum class. Please dispose of it properly! Take out all the work you have for this class. Chapter 3 Study Guide Survive! Hunters & Gatherers v. Farmers Skeletons Tell Tale (reading summary) We Shall Remain: The Ute Historic Indians organizer and map Anything else you have should have been turned in by now. Work on any incomplete questions, vocabulary, and the map in the study guide. Where should your backpack be? History Objective – We will prepare for tomorrow’s exam by reviewing the study guide. Language Objective – We will listen to, give answers and write the important details from the activity. Behavior Objective – Participation & Work Ethic: We will listen to each questions, answer the ones given to us, and write the important details in our notes. Use the map on page 194 to fill out your map. Then work on the geography map on page 8 of the study guide. Remembered history is history that was passed down either orally (in spoken words) or recorded in writing. Recovered history is history that was lost and found again, often through archaeology. Invented history is history that was made up by someone. ◦ All three of these give us valuable information. 38. What is a primary source? Examples: A primary source is a document/artifact created in the past that we can use to learn about that time. Sometimes a first hand account of an event. Diary, photo… 38. What is a secondary source? Examples: A secondary source is a document/artifact created by historians/archaeologists/etc who are explaining what they have learned about the past from primary sources. Textbook, documentary… 39. Give two examples of primary sources and two secondary sources from this unit (activity, readings, etc.) Primary – petroglyphs, tools, oral traditions of Native Americans Secondary – history books, movies, posters 36.In what ways are oral traditions important to modern Native Americans? People, like the Native Americans, who did not have writing had to memorize everything that was important to their tribe. Oral traditions were how they passed on their knowledge. 37.What types of information is passed down in oral traditions? History, language, culture Genealogy Knowledge of medicine, hunting, making items like clothes, baskets, pottery, etc. Religious stories 1) 2) 3) 35. Which tribe was Utah named after? Utes 34.Which tribe held rabbit and cricket drives to get meat? Goshute 33.This tribe, like the Ute, became very good at using the horse, eventually adopting teepees and a mobile lifestyle to follow large game like buffalo. Shoshone 32.This tribes territory covered much of eastern Utah and western Colorado, but eventually they were forced to move onto reservations, including the Uintah reservation. Utes 31.This tribe used over 100 different desert plants for food and medicine. Goshute 30.Sand painting, silver smithing, and weaving are all crafts this tribe is known for. Navajo 29.Which tribe was massacred at Bear River? Shoshone 28.Which tribe was the largest and most powerful in Utah when the Mormon settlers arrived? Utes 27.What tribe from Southwest Utah were hunters and gatherers, but also farmed on occasion? Paiutes 26.Which Indian tribe was sometimes called "RootDiggers"? Goshute 25.Which tribe got sheep from the Spanish and used the wool to weave beautiful rugs, blankets, & cloth? Navajo 24.Where did these people get the materials to build their dwellings (homes)? They found the things they used in nature, such as animal hides, wood, brush and grasses, clay, etc. 22.Name the five modern tribes that live in Utah today. Navajo, Goshute, Paiute, Ute, Shoshone 23.What type of dwelling (house) did each group live in? Utes – tepees Shoshone – tepees (at times wickiups) Goshute – wickiups Paiute – wickiups Navajo - hogans 20. What is the difference between a petroglyph and a pictogram? Petroglyphs are carved into rock with a stone; pictograms are painted onto rock. 21. What are some of the reasons they may have created this rock art? (3-5 reasons) History, good luck in hunting, religious rituals, graffiti- for fun, maps, warnings to other people 17.What type of dwelling (house) did the Fremont live in? Draw one. pithouse 18. Give five examples of artifacts made by the Fremont people. Coil grey pottery, jewelry, dolls, rock art, pithouses 19.Where could you go to see Fremont ruins in Utah today? Fremont State Park; Range Creek 14.What type of dwelling (house) did the Anasazi live in? Draw one. Pueblos, cliff dwellings, pithouses 15. Give five examples of artifacts made by the Anasazi people. Black and white pottery, jewelry, rock art, pueblos, mano and metate, kiva 16.Where could you go to see Anasazi ruins in Utah today? Hovenweep, Anasazi State Park 11. What is hunting and gathering? Describe how it works, who does what work, etc. A method for getting food used by people mostly in the past. Men typically hunted animals, women typically gathered plants. 12. What is farming/agriculture? Describe how it work, who does the work, etc. Planting seeds and harvesting plants to provide food for a community. Lots more work to do in farming so families are very large and everyone helps. 13. What are some the benefits of each system, and some of the problems they can create? (at – Hunting/Gathering Problems: Can’t have lots of kids Small population May not get enough food Benefit: People healthier More equality Less disease 13. What are some the benefits of each system, and some of the problems they can create? (at – Farming Problems: Benefit: Diseases Bigger population Poor nutrition/shorter life Complex society Rich/poor – less equality Food surplus 10. How did the atlatl make hunting easier? It is faster, easier to throw, more accurate at hitting things, can take down smaller targets, and uses less resources. 9.Why did early groups of people move from place to place? They moved to find food because they were hunters and gatherers. 8.How did most prehistoric Indians spend their time? Traveling looking for food, hunting and gathering, making tools, telling stories that taught their family about their history, religion, and how to survive. 6.What are the names of the two earliest groups of prehistoric people? Paleo-Indians; Archaic Indians/Desert Gatherers 7.Which prehistoric Indian group was the earliest to live in Utah? Paleo-Indians 5.What is one of the greatest challenges archaeologists face today in Utah? Vandals who destroy archaeological sites and looters who steal artifacts from archaeological sites. 4.What types of items have helped them learn about PaleoIndians? Mostly stone tools like Clovis points, but also some preserved bones, animal remains, and trash left at camp sites. 3.How do archaeologists learn about the past? Mostly by studying artifacts they find from conducting digs. 2.When do archaeologists think humans arrive in Utah? 13,000 – 20,000 years ago at least 1.In what ways did the earliest people adapt to climate change? They changed what animals they hunted and how they hunted, they adapted their use of plants as the climate became drier, they changed their clothing styles, etc. This is a no gum class. Please dispose of it properly! Take out your Chapter 3 Study Guide packet (study guide, maps). Only the packet and something to write with can be on your desk! Start working on the essay brainstorms (You must do all three!) Where should your backpack be? Question #1 Choose one of the groups of people you learned about in Chapter 3. Describe how they lived and the contributions they made to the people who came after them and/or to us today. (Paleo-Indians, Archaic, Fremont, Anazazi, Ute, Paiute, Goshute, Shoshone, etc.) Question #2 What contributions (3 things that 1st detail 2nd detail were changed, learned or discovered because of them gifts, history, heritage, knowledge ) have Native Question #3 What were some of the advantages and disadvantages of hunting and gathering and/or farming? Americans made to Utah? 1st detail 1st detail 2nd detail 3rd detail 2nd detail 3rd detail 3rd detail These questions are not at easy to turn into topic sentences as the ones in previous chapters. Follow this pattern to create a good topic sentence: ◦ Subject – Who are you writing about? ◦ Object – What did they do that you are writing about? Choose one of the groups of people you learned about in Chapter 3. Describe how they lived and the contributions they made to the people who came after them and/or to us today. What contributions (3 things that were changed, learned or discovered because of them - gifts, history, heritage, knowledge ) have Native Americans made to Utah? What were some of the advantages and disadvantages of hunting and gathering and/or farming? This is a no gum class. Please dispose of it properly! Take out all the work you have for this chapter. Chapter 3 Study Guide Survive! Hunters & Gatherers v. Farmers Skeletons Tell Tale (reading summary) We Shall Remain: The Ute (blue) Historic Indians organizer (white) Anything else you have should have been turned in by now. Work on your essay outline and final draft. There should be nothing on your desk except your papers and a pencil! Where should your backpack be? First: Finish your essay outline. Second: Write your final draft of the essay using your best handwriting, spelling, punctuation, and grammar. Third: Pick up the computer that matches your box number. Log into Canvas, go to quizzes, and take the Chapter 3 test. Fourth: Make sure your name is on all of your papers. Turn in everything except the blue Ute video guide and the white map. Put away your computer Finally: Finish writing your paragraphs about the Ute (blue paper). If there is time at the end of the hour, you may read, draw or do something quiet. First: Get an ipad and log into Canvas. ◦ Log in name: s# + @s.loganschools.org Second: Choose the chapter 3 test and complete it. Put your ipad back on the charging cord. Finally: Complete the essay.