Diffusion & Osmosis - Barnstable Academy
advertisement

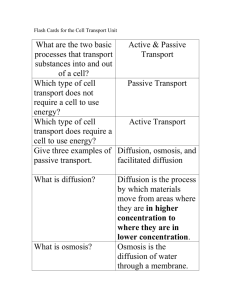
Weekly Announcements Chapter 7 Test Friday 10/4/13 9/30/13 Diffusion & Osmosis Types of transport in Cells Passive transport - movement of substances through a membrane from a region of high to a region of low concentration - no energy needed (ATP) - diffusion and osmosis are examples of this Active transport - movement of substances through a membrane from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration requires cellular energy (ATP) Whether passive or active transport is needed depends on the CONCENTRATION GRADIENT The concentration gradient is the difference in the concentration of a substance in two different spaces Concentration - the amount of a particular substance in a contained area compared with the amount of the same substance in another area Translation: Amount of PROCESSES OF THE PLASMA MEMBRANE There are two types of passive transport: Diffusion and Osmosis The goal of both diffusion and osmosis is to reach EQUILIBRIUM within the cell Equilibrium is a condition in which the movement in one direction is equal to the movement in another direction Diffusion the tendency of molecules to move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration (concentration gradient- diff in conc. between 2 regions) Osmosis movement of water through a membrane from a region of higher to lower con. Solute - substance being dissolved in a liquid (ex. salt) Solvent - substance doing the dissolving (ex. water) Permeability - the extent to which a membrane will allow particular sized molecules to pass Semi-permeable membrane (selectively permeable)-allows some molecules to pass but not others So, describe how “Kool-Aid”® is made with regard to the terms “solute” and “solvent”. What is the “universal solvent”? When comparing two solutions there are three possible relationships, We Identify the relationships by determining what would happen if a cell were placed in the solution. Hypertonic- A solution that causes a cell to shrink because of osmosis. Meaning water leaves the cell. Hypotonic- A solution that causes a cell to swell because of osmosis meaning water rushes into the cell. Isotonic-A solution that causes no change in cell size. Meaning there is no movement of water. If the fluid outside the cell has… …less water than is present inside the cell …more water than is present inside the cell …same amount of water as inside the cell Then the outside fluid is… Water moves… Effect on the cell? So, answer this question…. Why do “establishments” offer free popcorn, peanuts, and pretzels to their patrons if they are serving beverages? What changes are taking place in the body to initiate the need for more beverages? 10/1/13 Do Now: Name the two types of passive transport and describe how they are different from each other. HW: Read pages 212 – 213 and complete the questions in the 7.3 Assessment Active Transportthe movement of a substance against the concentration gradient. (uphill) Active transport requires cell to USE ENERGY Sodium pump - transports three sodium ions out of the cell and two potassium ions into the cell Both are against the concentration gradient The energy needed to perform this activity is supplied by ATP (adenosine tri-phosphate) ATP is a unit of energy made by the cell Endocytosis- the movement of a substance into the cell by a vesicle. A vesicle is a form of packaging that is used by cells. Exocytosis- the movement of a substance out of the cell by a vesicle. Phagocytosis- cytoplasm of cell surrounds and engulfs particle--ex. ameba and white blood cell Pinocytosis- plasma membrane "pinches in" to permit entry of molecules too large to diffuse through Passive Vs. Active Transport Writing Activity Compare the two types of transport in no more than 2 paragraphs (3-4 sentences each paragraph). Make sure to describe in detail the differences between both types of transport. Diffusion The movement of molecules from an area in which they are highly concentrated to an area in which they are less concentrated. Diffusion Osmosis The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane. Osmosis is a type of Passive Transport. Osmosis requires NO ENERGY. Osmosis Hypertonic- a solution that causes a cell to shrink because of Osmosis. Hypotonic- a solution that causes a cell to swell because of Osmosis. Isotonic- a solution that causes no change in the size of the cell Osmosis In this picture a red blood cell is put in a glass of distilled water. Because there is a higher concentration of water outside the cell, water enters the cell by OSMOSIS. In this case too much water enters and the cell swells to the point of bursting open. Selectively Permeable A membrane that allows only certain materials to cross it Materials pass through pores in the membrane Summary Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lesser concentration. Osmosis is the movement of water thru a semi permeable membrane. Active transport requires energy. (molecules move from an area of lesser to higher concentration) Passive transport needs NO ENERGY! (molecules move from an area of higher to lesser concentration). Why are osmosis & diffusion important? All living things have certain requirements they must satisfy in order to remain alive – maintain homeostasis These include exchanging gases (usually CO2 and O2), taking in water, minerals, and food, and eliminating wastes. These tasks happen at the cellular level. Molecules move through the cell membrane by diffusion A balance, or EQUILIBRIUM, must be maintained. 10/2/13 Do Now: What is homeostasis and how do cells maintain it? HW: Review 7.4 – Chapter 7 Test Friday 10/3/13 Do Now: Clear your desks! Today is your review day for tomorrow’s chapter 7 test. HW: Study for Chapter 7 Test tomorrow 10/4/13 Do Now: Clear your desks! Today is your Chapter 7 Test!