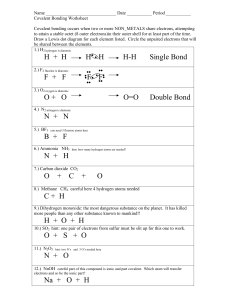
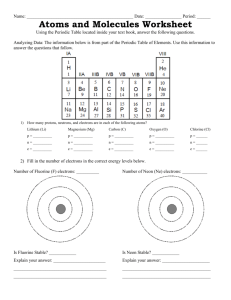
Covalent Bonds
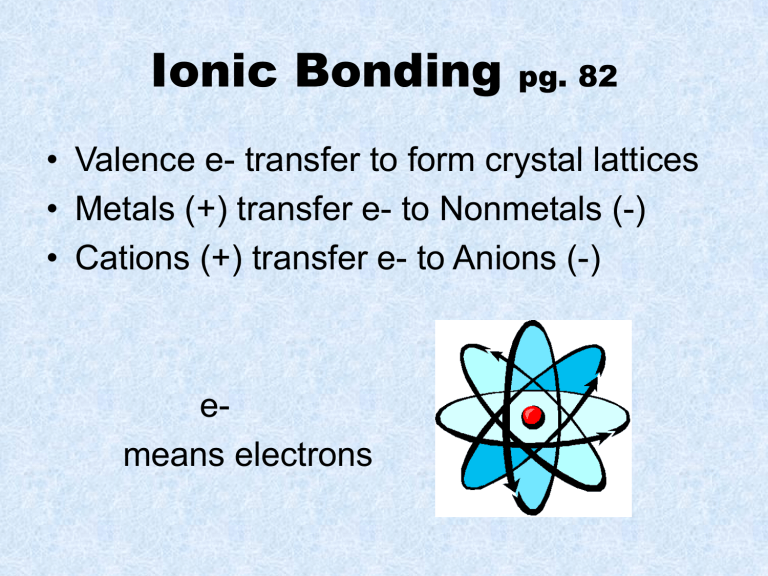
Ionic Bonding pg. 82
• Valence e- transfer to form crystal lattices
• Metals (+) transfer e- to Nonmetals (-)
• Cations (+) transfer e- to Anions (-) emeans electrons
Binary Ionic Compounds pg. 82
Made from two elements
Cation keeps its name
Ex: Magnesium (+2)
Anion adds suffix –ide
Ex: Fluoride (-1)
…becomes Magnesium Fluoride MgF ₂
Polyatomic Ions pg. 82
• Covalently bonded group of atoms acting as one unit that can bond with other ions.
• Positive or Negative
Ex: Ammonium NH
4
+
Hydroxide OH -
Nitrate NO
3
-
Sulfate SO
4
2-
What is the correct formula for a compound containing sodium and sulfur?
• a. NaS
• b. Na
2
S c. NaS
2 d. NaS
3
What is the correct formula for a compound containing sodium and sulfur?
• a. NaS
• b. Na
2
S
• Answer: b c. NaS
2 d. NaS
3
Oxidation numbers are used to
• a. keep track of the neutrons lost or gained by each atom.
• b. keep track of the protons lost or gained by each atom.
• c. keep track of the electrons lost or gained by each atom.
• d. keep track of the quarks lost or gained by each atom.
Oxidation numbers are used to
• a. keep track of the neutrons lost or gained by each atom.
• b. keep track of the protons lost or gained by each atom.
• c. keep track of the electrons lost or gained by each atom.
• d. keep track of the quarks lost or gained by each atom.
• Answer: c
The formation of an ionic bond involves the
• a.transfer of electrons.
• b.transfer of protons.
• c. transfer of neutrons.
• d.none of the above.
The formation of an ionic bond involves the
• a. transfer of electrons.
• b. transfer of protons.
• c. transfer of neutrons.
• d. none of the above.
• Answer: a
• Valence e- from metal to nonmetal
Fluorine, F, forms a binary ionic compound with lithium, Li. What is the name of this compound?
• a.fluorine lithide
• b.lithium fluorine
• c. lithium fluoride
• d.fluorine lithium
Fluorine, F, forms a binary ionic compound with lithium, Li. What is the name of this compound?
• a. fluorine lithide
• b. lithium fluorine
• c. lithium fluoride
• d. fluorine lithium
• Answer: c
• Metal/Cation first, add ide to nonmetal/anion
Covalent Bonds page 85
Two or more elements
(nonmetals) share valence electrons to have a more stable outer electron structure.
What is a Molecule? Pg. 85
• Only compounds formed from covalent bonds are called molecules.
Metals bonded to nonmetals form ionic crystals not molecules!
Circle the molecules and put an X on the compounds that are not molecules.
NaCl CO
2
CH
4
Al
2
O
3
CaCl
2
Br
2
NaOH H
2
O C
6
H
12
O
6
N
2
KI C
4
H
10
3 Types of Bonding pg. 85
• Ionic Bonds – Metal ions bond to nonmetal ions
• Covalent Bonds – Nonmetal atoms bond with each other
• Metallic Bonds – Metals bond with each other
Properties of Covalent Compounds
• Share electrons between nonmetal atoms
(elements on right side of the periodic table)
• Low melting and boiling points
• Brittle
• Do not conduct electricity well