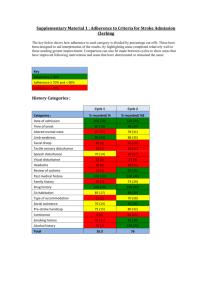
Brain and Cranial Nerves

Chapter 13
Brain and Cranial Nerves
13-1
Formation of the Neural Tube
• Brain and spinal cord develop from the neural plate under the influence of the notochord.
• Neural folds elevate to form the neural crest and a neural groove.
• Neural crest cells become the peripheral nerves.
• Ventricles and central canal develop from the lumen of the neural tube
13-2
Development of Brain Segments and Ventricles
13-3
13-4
Brain and Cranial Nerves
• Brain
– Part of CNS contained in cranial cavity
– Control center for many of body’s functions
• Structures of the Brain
–
Brainstem
• Includes the Medulla Oblongata, Pons and Midbrain
–
Cerebellum
– Diencephalon
•
Includes the Thalamus, Subthalamus, Epithalamus and
Hypothalamus
– Cerebrum and basal nuclei
• Cranial nerves
– Part of PNS arise directly from brain
13-5
13-6
Brainstem
• Connects spinal cord to brain
• Parts
– Medulla oblongata
–
Pons
– Midbrain
13-7
Brainstem
• Medulla oblongata
– Functions:
• Regulates: Heart rate, blood vessel diameter, respiration, swallowing, vomiting, hiccupping, coughing, and sneezing
• Contains ascending and descending fiber tracts.
–
Pyramids:
• Function: Controls voluntary muscle movement
•
Fiber tracts Decussate at the lower pyramid
– Olives
• Function: equilbrium, coordination and modulation of sound in inner ear.
• Contains Nuclei for many cranial nerves
13-8
Brainstem
•
Pons
–
Function
• Contains Ascending and
Descending nerve tracks and Pontine nuclei
• Contains Sleep and respiratory center
– Pontine Nuclei
• Anterior nuclei: relay information from cerebrum to cerebellum
•
Posterior Nuclei: Cranial nerves V – IX.
• Respiratory and Sleep
Nuclei
13-9
Brainstem
• Midbrain
– Contains:
• Cranial nerve nuclei III, IV, V
• Tectum
– Corpora Quadrigemina
» Superior Colliculus – visual reflexes
» Inferior Colliculus – auditory reflexes.
• Tegmentum
– Ascending tracts and Red nucleus
• Cerebral Peduncles
– Major descending motor pathways
• Substantia Nigra
– Muscle tone and movement
• Reticular Formation
– Sleep wake cycle and arousal.
13-10
Brainstem and Diencephalon
13-11
Cerebellum
• Involved in control of: balance, posture, locomotion, and fine motor coordination producing smooth flowing movements
13-12
Diencephalon
• Components
–
Thalamus, Subthalamus, Epithalamus, Hypothalamus
13-13
Diencephalon
• Thalamus
– Largest part of diencephalon
–
Most sensory input projects to here
–
Influences mood and actions as fear or rage
• Subthalamus
– Involved in controlling motor functions
• Epithalamus
– Pineal gland may influence sleep-wake cycle
• Hypothalamus
– Functions
• ANS control
• Endocrine control
• Muscle control
• Temperature regulation
• Regulation of food and water intake
• Emotions
• Urine production
• Regulation of sleep-wake cycle
• Regulation of reproductive behavior
13-14
Cerebrum
• Functions: sensation, perception, voluntary movement, learning, speech and cognition.
• Divisions
– Right
– Left
• Lobes: Frontal, parietal, occipital, temporal, insula
• Cortex: Outer surface
• Medulla: Center
13-15
Basal Nuclei
• Structure:
– Corpus Striatum
• Lentiform Nucleus
(Putamen)
• Caudate Nucleus
– Subthalamic nucleus
– Substantia Nigra
– Motor function control
•
Function: Facilitate the initiation of willed movements
• Basal Ganglian Disorders lead to Diskinesias.
– Hypokinesia -paucity of movement caused by over inhibition.
– Hyperkinesia -excess movement.
13-16
•Hypokinesia – Parkinson’s Disease
•Affects 1% of people over 50
•Difficult to initiate willed movements
•Leads to Akinesea, rigidity and tremors of hands and jaw
•Due to degeneration of substantia nigra and dopamine circuits.
•Hyperkinesia- Huntington’s Disease
•Hereditary, progressive and lethal syndrome
•Characterized by: demetia, chorea (uncontrolled movements) and ballistic movements
•Due to Damage in the basal nuclei
13-17
Limbic System
•Basic survival functions such as:
• Memory
• Reproduction
• Nutrition
• Emotions
13-18
Meninges
• Connective tissue membranes
– Dura mater: Superficial
–
Arachnoid mater
–
Pia mater: Bound tightly to brain
–
Spaces
• Subdural: Serous fluid
• Subarachnoid: CSF
13-19
Ventricles
• Ventricles: Lateral ventricles (2), third ventricle, fourth ventricle
• Choroid plexuses produce CSF which fills ventricles and other parts of brain and spinal cord
– Blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier: Substances do not pass between cells but through due to tight junctions of blood endothelial cells 13-20
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
• Similar to serum with most of proteins removed
• Bathes brain and spinal cord
• Provides a protective cushion around CNS
• Provides some nutrients to CNS tissues
• Produced by ependymal cells
13-21
Flow of CSF
13-22
Brain Blood Supply
• Brain
– Requires tremendous amount of blood
–
Receives 15-20% of blood pumped by heart
– Interruption can cause unconsciousness and irreversible brain damage
–
High metabolic rate and dependence on constant supply of oxygen and glucose
– Receives blood through arteries
• Blood-Brain barrier
– Capillary endothelial cells along with astrocytes and basement membrane
–
To be considered when developing drugs
13-23
Cranial Nerves
• Indicated by Roman numerals I-XII from anterior to posterior
• May have one or more of
3 functions
– Sensory (special or general)
– Somatic motor (skeletal muscles)
– Parasympathetic (regulation of glands, smooth muscles, cardiac muscle)
13-24
Cranial Nerves
• Olfactory (I)
• Optic (II)
• Oculomotor (III)
• Trochlear (IV)
• Trigeminal (V)
• Abducens (VI)
• Facial (VII)
• Vestibulocochlear (VIII)
• Glossopharyngeal (IX)
• Vagus (X)
• Accessory (XI)
• Hypoglossal (XII)
13-25
13-26
13-27
13-28
13-29
13-30
13-31
13-32
13-33
13-34
13-35
13-36
13-37