America: A Narrative History (Ninth Edition)
advertisement

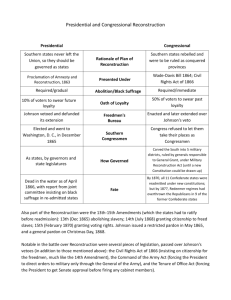
America: A Narrative History (Ninth Edition) Chapter 17 - Reconstruction: North and South I. America after the Civil War o A. Effects of the war on the nation 1. Questions facing the nation after the war 2. Development in the North a. Morrill Tariff b. National Banking Act c. Subsidies for transcontinental railroad d. Homestead Act of 1862 e. Morrill Land Grant Act of 1862 3. Impact on the South a. Property destroyed b. Confederate currency and bonds worthless c. Loss of $4 billion that had been invested in labor—the slaves d. Problems of postwar agriculture e. Transformation of southern society o B. Special problems of the freedmen 1. Freedmen and the confusion over citizenship 2. Hardships 3. The Freedmen’s Bureau II. Lincoln and Reconstruction o A. Lincoln’s lenient 10 percent plan o B. Loyal governments not recognized by Congress o C. Arguments over Reconstruction o D. The Wade-Davis Bill o E. Lincoln’s philosophy of Reconstruction o F. Lincoln’s assassination III. Johnson’s plan for Reconstruction o A. Johnson’s background and personality o B. Johnson’s philosophy of Reconstruction o C. Johnson’s plan 1. Comparable to Lincoln’s 2. The wealthy excluded from Johnson’s amnesty proclamation 3. Additional requirements for southern states o D. Southern states’ response to Johnson’s requirements IV. Southern intransigence o A. Southern states had elected many ex-Confederates o B. Southern states had passed “black codes“ o C. In reaction, Radical Republican strength grows in North V. Radical Republican ascendance o A. Partisan interests of Radical Republican Reconstruction 1. Support of African American suffrage 2. Disenfranchisement of former Confederates 3. Forfeited rights of southern states o B. Johnson’s battle with Congress 1. Johnson’s waning power and influence 2. Johnson’s first veto of Freedmen’s Bureau bill upheld 3. Johnson’s veto of Civil Rights Acts of 1866 overridden 4. Johnson’s veto of revised Freedmen’s Bureau bill overridden 5. The Fourteenth Amendment a. Citizenship rights for all Americans, including African Americans b. Guarantees of due process and equal protection under the law c. Tennessee ratifies first d. Race riots in Memphis and New Orleans VI. Congressional Reconstruction o A. Johnson’s loss of public support 1. Midwest speaking tour 2. Huge veto-proof Republican gains in 1866 election o B. Congress moves to limit Johnson’s power 1. Command of the Army Act 2. Tenure of Office Act o C. Other measures of Congressional Reconstruction 1. Military Reconstruction Act 2. Second Reconstruction Act Tindall/Shi America: A Narrative History (Ninth Edition) 3. Congress protects its program from Supreme Court VII. Impeachment and trial of Johnson o A. Johnson’s removal of secretary of war Edwin Stanton 1. Violation of Tenure of Office Act o B. House of Representatives impeaches Johnson o C. Senate trial fails to convict o D. Effects on Radicals and Johnson VIII. Republican rule in the South o A. New governments established in southern states o B. Georgia’s readmission rescinded o C. Fifteenth Amendment protects right to vote o D. The Union League o E. Blacks in the Reconstructed South 1. Faced animosity from white southerners as well as northerners 2. Effects of military service 3. Separate churches 4. Black families 5. Black schools 6. African Americans in southern politics a. Blacks in high positions b. Extent of black influence in Reconstruction governments o F. White Republicans in the South 1. Carpetbaggers 2. Scalawags o G. The Republican record 1. Achievements 2. Corruption IX. Religion and Reconstruction o A. Christians for racial justice o B. “Apostles of forgiveness“ o C. Differing religious perspectives X. Grant administration o A. Positions of parties in the 1868 election o B. Grant’s unwise cabinet appointments o C. The government’s debt 1. Debate over monetary expansion versus monetary restriction 2. Public Credit Act (1869) a. Greenbacks withdrawn from circulation b. Debt to be paid with gold o D. Scandals in Grant’s administration 1. Jay Gould and Jim Fisk and the gold market 2. The Crédit Mobilier scandal 3. Other scandals XI. Further challenges to the Grant administration o A. Southern resistance to “Radical rule“ o B. Formation of Ku Klux Klan o B. Terrorist activities of Klan and similar groups o C. Prosecution of such groups under new federal laws o D. Republican reformers and the election of 1872 o E. Conservative resurgence 1. Ku Klux Klan weakened black and Republican morale 2. Diminished northern commitment to ideals of Reconstruction 3. Collapse of Republican control and Radical Republican regimes o F. The beginning of the panic of 1873 o G. The Specie Resumption Act of 1875 XII. The election of 1876 o A. Republicans nominate Rutherford B. Hayes o B. Democrats nominate Samuel J. Tilden o C. Tone of the campaigns o D. Disputed electoral vote count 1. Congress forms special Electoral Commission to resolve o E. The Compromise of 1877 1. Election goes to Hayes 2. Reconstruction ends with last federal troops withdrawn from South o F. The legacy of Reconstruction Tindall/Shi