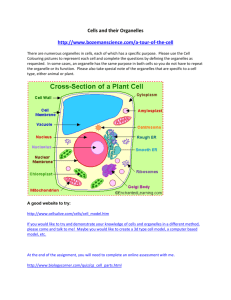
Cell Organelle Notes Cells & Organelles 2014 KRS
advertisement

Cells & Organelles Cells Definition •Cell: the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms •There are different types of cells… Examples: Eukaryotic Animal cells Plant cells Prokaryotic Bacterial cells Cell Theory • The Cell Theory has 3 main points: KNOW THESE!!! Characteristics of Cells: 1. All living things are composed of cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things 3. All cells are produced from other existing cells Organelles Definition: • Organelle: a tiny structure in a cell that carries out a specific function within a cell Organelles Characteristics: • The organelles work together to create a properly functioning system (the cell)… • • just like all the parts of a factory work together to make a properly functioning factory! If one organelle is removed or missing, the cell will not function properly! The 5 Functions of Cells KNOW THESE!!! (STIPE) • Structure • Transport • Information storage & commands • Production system (making materials) • Energy Organelles • Some organelles are part of a system to provide structure & support to cells Organelles: Plasma / Cell Membrane • Function: • “Baggie” that holds the cell together and provides a barrier to the outside environment Organelles: Plasma / Cell Membrane • Feature 1: found around outside of cell • Feature 2: Selectively permeable: only allows certain substances in and out of cell • Feature 3: made of a phospholipid bilayer Organelles: Plasma / Cell Membrane • The phospholipid bilayer Organelles: Cytoskeleton • Function: Gives support & shape to the cell and provides movement for objects inside cell Organelles: Cytoskeleton • Features: • Made of protein fibers in the cell • Can be dis- and reassembled to change shape of cell • Acts like a monorail system for transport using “motor proteins” Organelles: Cytoplasm • • Functions: • Site of chemical reactions; holds organelles in place (like pieces of fruit in jello) Features: • • Jelly-like fluid that fills the cell 70-90% water Organelles: Cytoplasm Organelles • Some organelles provide information storage and instructions for cells Organelles: Nucleus • Functions: • Controls the normal activities of the cell • Feature: • Contains DNA (the instruction manual for the entire cell / organism) Organelles, cont. • Some organelles are part of a system to make proteins (protein synthesis), carbs and lipids • Assembly • Transport • Storage Organelles: Nucleolus • Function: makes ribosomes (which make proteins) • Feature: inside the nucleus Organelles: Ribosome • • Function: Makes proteins for the cell to use Feature: • some attached to the endoplasmic reticulum & some floating free in the cytoplasm Organelles: Rough ER Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) • Function: Location where proteins are made and transported from • Features: • Attached to nucleus & made of membrane • Has ribosomes attached Organelles: Golgi Complex (aka the Golgi Apparatus or Golgi Body) • • • Functions: • Processes, packages, and delivers products made at ER (proteins, carbs & fats) Makes membranes, creates some products for secretion Feature: Has many layers of membranes (looks like stacks of pancakes) Organelles: Vesicles • Function: Carry finished products to other parts of the cell or leave the cell to deliver products to other cells • • “UPS trucks” Feature: made of membranes formed from Golgi Organelles: Smooth ER • Function: Location where fats & carbohydrates are made • Features: No ribosomes attached (hence being smooth), has tubes and canals of membranes Organelles: Lysosome • • • Functions: Cleans and breaks down unused or unwanted materials in the cell Breaks down / destroys: worn out parts of the cell, bacteria, foreign particles, toxic wastes Organelles: Lysosome • Features: • Baggies of enzymes • About 40 types • Mostly found in animals, but can exist in plants Organelles • Some organelles provide energy for cells Organelles: Mitochondria • Functions: • Site of cell respiration: Converts glucose from food into usable energy (ATP) which is used by cells to do work • The “powerhouse” of the cell • Feature: • Has own DNA Organelles: Mitochondria Organelles: Chloroplast • • Functions: • Site of photosynthesis: Converts light energy into food (carbs, such as glucose) and oxygen gas (O2) Features: • 1: contain pigments (like chlorophyll) that help capture light energy • • 2: Have own DNA Plants only! Organelles • Back to organelles that provide structure & support to cells… These are for plants!!! Organelles: Vacuole • Functions: • Stores, digests and releases nutrients and wastes • Prevents plant from wilting (think of water balloons) Organelles: Vacuole • Features: • 1: Takes up a large portion of plant cells • 2: Can “deflate” when a plant isn’t watered enough → wilting plant! Or give fruits/veggies its crispiness if full • Large in plants, sometimes present but small in animals Organelles: Cell Wall • Function: • • Features: • • • Provides rigid support and structure to plant cells 1: Found outside the cell membrane. 2: Made mostly of cellulose Plants & bacteria only! Similarities between plant cells and animal cells • Shape: • Size: • Chloroplasts? Mitochondria?? • 4 characteristics that are unique to animals Similarities between plant cells and animal cells Both have a cell membrane surrounding the cytoplasm Both have a nucleus Both contain mitochondria Both eukaryotic cells What else?? Differences between plant cells and animal cells Plant Cells Size Shape Nucleus location Cell wall Cell membrane Chloroplast Mitochondria Lysosomes Vacuole Food storage Animal Cells Plant vs. Animal Cells Plant vs. Animal Cells Create a chart indicating which organelles are found mostly in plant cells, mostly in animal cells and which organelles they have in common: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton Golgi complex Lysosome Mitochondria Nucleolus Nucleus Ribosome RER SER Vacuole Vesicle Differences between plant cells and animal cells Plant Cells Animal Cells Size Relatively larger Relatively smaller Shape Regular / geometric Irregular Nucleus location Near edge of cell Near center of cell Cell wall? Yes No Cell membrane? Yes Yes Chloroplast? Yes No Mitochondria? Yes Yes Lysosomes? Rarely Yes Vacuole? Large Small or absent Food storage Starch Glycogen Plant or animal or what?? • What organelles are found in plant cells only? • Which organelles are only in animal cells? • What organelles are found in both plant and animal cells? • • CC Plant Cells: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9UvlqAVCo qY&index=6&list=PL3EED4C1D684D3ADF Labeling a cell: http://www.welchclass.com/Biology/animalcell .swf Characteristics of Life • What are the 6 characteristics of living things? Characteristics of Life 1.Reproduce 2.Grow & develop 3.Respond to their environment 4.Convert energy 5.Made of chemicals 6.Made of cells The Cell as a Coordinated Unit • Cell ≠ Organelle • Why is a cell classified as the basic unit of structure & function in living things, but organelles are not? The Cell as a Coordinated Unit Coordinated Unit • Each organelle has a specific function • All organelles are dependent on each other to produce a properly-working cell • The sum is greater than its parts The Cell as a Coordinated Unit • Each organelle can carry out 1+ characteristic of living things, but not all of them • The organelles work together to create a properly functioning system (the cell) that fulfills all 6 characteristics of life • If one organelle is removed or missing, the cell will not function properly! Energy… • What are the 6 characteristics of living things? • What do organisms use energy for? • What types of organisms require usable energy? More fit??? • Compare the organelles found in plants vs. animals. Which type of cells would be more fit to survive without any outside source? WHY? • Provide an answer IN TERMS OF ENERGY. Compare & Contrast Compare & Contrast The 5 Functions of a Cell • The organelles within cells carry out at least one of 5 functions… • Allowing the cell, as a whole, to fulfill the 6 characteristics of living things and be classified as “the smallest unit of structure and function in living things” The 5 Functions of a Cell KNOW THESE!!! (STIPE) • Structure • Transport • Information storage & commands • Must contain DNA or RNA • Production system (making materials) • Energy conversions Back to the 5 functions of a cell… • What function does each organelle fit under best? • Place at least 3 organelles in each of the 5 essential cell function categories Plant vs. Animal Cells Create a chart indicating which organelles are found mostly in plant cells, mostly in animal cells and which organelles they have in common: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoplasm Cytoskeleton Golgi complex Lysosome Mitochondria Nucleolus Nucleus Ribosome RER SER Vacuole Vesicle Chemical Reactions • • • Many chemical reactions occur in the cell. A chemical reaction is the rearrangement of atoms to form new substances. The following organelles undergo reactions that we will discuss in the following slides: • • • • • • Mitochondria Rough ER Ribosomes Smooth ER Golgi Complex Cytoplasm Chemical Reaction: Mitochondria • What do mitochondria do?? • Chemical Reaction: Break covalent bonds in sugar (CHO) and oxygen to create usable energy Chemical Reaction: Ribosomes • Make proteins… which are made of a hundreds of amino acids • Chemical Reaction: Creates covalent bonds between amino acids Chemical Reaction: Rough ER • Chemical Reaction: Creates covalent bonds between amino acids Chemical Reaction: Smooth ER • Chemical Reaction: Creates covalent bonds between carbohydrates and fats Chemical Reaction: Golgi Complex • Chemical Reaction: Modifies covalent bonds between amino acids to adjust (fix) proteins Chemical Reaction: Cytoplasm • Chemical Reaction: • Form or break covalent bonds with enzymes Are Viruses Living? • We need to look at what makes something living… • What are the 6 characteristics of living things? Viruses • Evidence to Explore… • Characteristics of life 1.Made of cells 2.Made of chemicals 3.Use/obtain energy 4.Grow & develop 5.Reproduce 6.Respond to environment Viruses • Evidence for Life/Cells • Made of Chemicals • Viruses ARE made from CHO, etc. • Respond to Environment • Viruses ARE able to respond to their environment •They look alive so far… • Viruses Evidence Against Life/Cells • • • • Reproduce • • Kind of… They require the machinery of other organisms to reproduce, NOT on their own! Use/obtain energy • Do not metabolize Grow & develop • Not on their own Made of cells • •VIRUSES have SOME characteristics of living things, but not all… so they are NOT considered LIVING organisms No! because of all of the reasons mentioned above Various Viruses • How big is it? http://www.cellsalive.com/howbig.htm • How viruses invade… http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rpj0e mEGShQ