Genetic Transformation

Genetic
Transformation
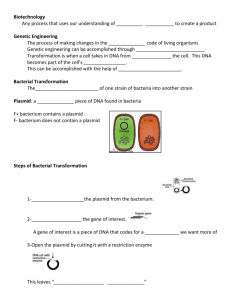
What is transformation?
When a cell takes up and expresses a new piece of genetic material—DNA— in order to change the organism ’ s traits
A gene is a piece of DNA which provides the instructions for making (coding for) a particular protein
DNA Protein Trait
History of Transformation
1928 – Fredrick Griffth first described transformation
Pneumococcus bacteria
(pneumonia) and mice
1944 – Oswald Avery , Colin
MacLeod , Maclyn McCarty identified the “ transforming principle ” as DNA
History of Transformation
1952 – Alfred Hershey and
Martha Chase provided final proof that DNA was the molecule of heredity
1970 – Morton Mandel and
Akiko Higa developed a protocol for transforming E.
coli bacteria
What is transformation used for?
Agricultural
Genes coding for traits such as frost, pest or drought resistance can be genetically transformed into plants
What is transformation used for?
Environmental
Bacteria can be genetically transformed with genes enabling them to digest oil spills or remove pollutants from the environment
What is transformation used for?
Medical
Production of human proteins to treat genetic diseases
Protein
Human insulin
Human Growth Hormone
Disease/Disorder
Diabetes mellitus
Deficiency in children
Erythropoietin
DNase I
Human antibody blocker
Anemia
Cystic fibrosis
Asthma
What are we doing?
We will transform bacteria ( E. coli ), giving it the ability to make green fluorescent proteins
Green Fluorescent Protein
Used in science as a visual marker …
Biological processes (protein production)
Localization and regulation of gene expression
Cell movement
Cell fate during development
Formation of different organs
Marker to identify transgenic organisms
How does it work?
Cell membrane
Bacterial chromosomal
DNA
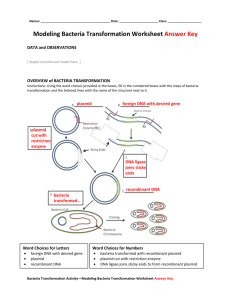
*plasmids*
Making Plasmids
Plasmid
+
Gene
=
pGLO Plasmid
GFP
To make green fluorescent proteins araC
To survive with
Ampicillin (antibiotic)