AP:Lattice Energy
advertisement

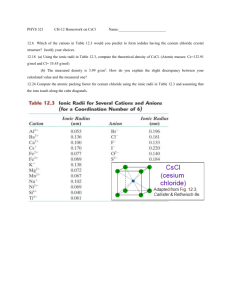
AP:Lattice Energy Consider Ionic Compounds Consider Ionic Compounds • Not molecules Consider Ionic Compounds • Not molecules • Have an arrangement of several ions all interacting with each other. Consider Ionic Compounds • Not molecules • Have an arrangement of several ions all interacting with each other. • The solid is a regular arranged pattern of ions called a crystal lattice. LiF…….An ionic compound between lithium and fluorine LiF…….An ionic compound between lithium and fluorine Li (s) + ½ F2 (g) LiF (s) Li must be converted to a gas 1. Li (s) Li (g) kJ/mol +161 LiF…….An ionic compound between lithium and fluorine Li (s) + ½ F2 (g) LiF (s) Li must be converted to a gas Li must be ionized (ionization energy) 1. Li (s) Li (g) kJ/mol +161 2. Li (g) Li+ (g)+e- +520kJ/mol LiF…….An ionic compound between lithium and fluorine Li (s) + ½ F2 (g) LiF (s) Li must be converted to a gas 1. Li (s) Li (g) kJ/mol +161 Li must be ionized (ionization energy) F molecules need to be broken into atoms 2. Li (g) Li+ (g)+e- +520kJ/mol 3. 1/2F2 (g) F (g) kJ/mol +77 LiF…….An ionic compound between lithium and fluorine Li (s) + ½ F2 (g) LiF (s) Li must be converted to a gas Li must be ionized (ionization energy) F molecules need to be broken into atoms Form F ions 1. Li (s) Li (g) kJ/mol +161 2. Li (g) Li+ (g)+e- +520kJ/mol 3. 1/2F2 (g) F (g) kJ/mol 4. F (g) + e- F- (g) +77 -328 kJ/mol LiF…….An ionic compound between lithium and fluorine Li (s) + ½ F2 (g) LiF (s) 1. Li (s) Li must be ionized (ionization energy) 2. Li (g) Li+ (g)+e- +520kJ/mol Li must be converted to a gas F molecules need to be broken into atoms Form F ions (electron affinity) The ions are highly attracted to each other…Lattice energy Li (g) +161 kJ/mol 3. 1/2F2 (g) F (g) +77 kJ/mol 4. F (g) + e- F- (g) -328 kJ/mol 5. Li+ + F- LiF -1047kJ/mol An ionic compound forms between a metal and a nonmetal • Net change: kj/mol An ionic compound forms between a metal and a nonmetal • Net change: kj/mol • • • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 161 520 77 -328 -1047 - 617 kJ/mol of LiF formed An ionic compound forms between a metal and a nonmetal • The solid formed is a regular arranged pattern of ions called a crystal lattice • Net change: kj/mol • • • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 161 520 77 -328 -1047 - 617 kJ/mol of LiF formed An ionic compound forms between a metal and a nonmetal • The solid formed is a regular arranged pattern of ions called a crystal lattice • Lattice energy of LiF is 1047 kJ/mol • Net change: kj/mol • • • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 161 520 77 -328 -1047 - 617 kJ/mol of LiF formed Born-Haber Cycle As LiF (or another ionic compound dissolves in water…………. As LiF (or another ionic compound dissolves in water…………. • Energy must be released to pull ions apart As LiF (or another ionic compound dissolves in water…………. • Energy must be released to pull ions apart • The quantity of energy released must be > or = to the lattice energy As LiF (or another ionic compound dissolves in water…………. • Energy must be released to pull ions apart • The quantity of energy released must be > or = to the lattice energy • Energy of hydration Hydration of ion..dissolving Requires and interaction with the polar water molecule General rule of solubility…”Like dissolves like” Nonpolar molecules require nonpolar solvents Lattice Energies of Alkali Metals Halides (kJ/mol) FCl- Br- I Li+ 1047 853 807 757 Na+ 923 787 747 704 K+ 821 715 682 649 Rb+ 785 689 660 630 Cs+ 740 659 631 604 • Lattice energy for LiF is - Lattice Energies of Alkali 1047 kJ/mol….it Metals Halides (kJ/mol) dissolves in water FCl- Br- I Li+ 1047 853 807 757 Na+ 923 787 747 704 K+ 821 715 682 649 Rb+ 785 689 660 630 Cs+ 740 659 631 604 • Lattice energy for LiF is - Lattice Energies of Alkali 1047 kJ/mol….it Metals Halides (kJ/mol) dissolves in water FCl- Br- I Li+ 1047 853 807 757 + 923 Na 787 747 704 • Lattice energy for MgO + 821 K 715 682 649 is -3916 kJ/mol… it + 785 Rb 689 660 630 does not dissolve in + 740 Cs 659 631 604 water Lattice energy for LiF is Lattice Energies of Alkali -1047 kJ/mol….it Metals Halides (kJ/mol) dissolves in water FCl- Br- I Li+ 1047 853 807 757 Lattice energy for MgO Na+ 923 787 747 704 is -3916 kJ/mol… it K+ 821 715 682 649 does not dissolve in Rb+ 785 689 660 630 water Cs+ 740 659 631 604 Lattice energy for NaF -923kJ/mol Size of Ions Ion-Ion Interactions • Coulomb’s law states that the energy (E) of the interaction between two ions is directly proportional to the product of the charges of the two ions (Q1 and Q2) and inversely proportional to the distance (d) between them. (Q1Q 2 ) E d Predicting Forces of Attraction • Coulombs Law indicates the increases in the charges of ions will cause an increase in the force of attraction between a cation and an anion. • Increases in the distance between ions will decrease the force of attraction between them. Lattice Energy • The lattice energy (U) of an ionic compound is the energy released when one mole of the ionic compound forms from its free ions in the gas phase. M+(g) + X-(g) ---> MX(s) k(Q1Q2 ) U= d Comparing Lattice Energies Lattice Energies of Common Ionic Compounds Compound U(kJ/mol) LiF -1047 LiCl -864 NaCl -790 KCl -720 KBr -691 MgCl2 -2540 MgO -3791