Central Nervous System
advertisement

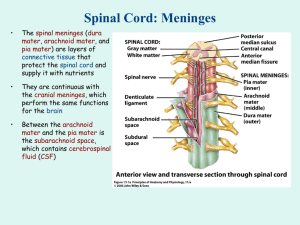
Central Nervous System Nervous tissue Axon Dendrite Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Schwann cells Motor neuron Interneurons Somatic Sensory neuron A nerve fiber with thorn like spines that conducts an impulse towards the cell body Substance of Schwann cell composed of lipoprotein Transmits impulse from sensory to motor neuron within CNS Unmyelinated axon between Schwann cells on neurons of the peripheral nervous system Transmits impulse into brain or spinal cord from receptors A nerve fiber; conducts impulse away from a neuron cell body A myelinating cell that surrounds a fiber on a peripheral nerve Pertaining to the body Transmits impulse out of the brain or spinal cord to effectors Interneurons Meninges and Spinal Cord Arachnoid mater Outermost layer of meninges Dura mater Contains cerebrospinal fluid Pia mater Thin, weblike middle membrane Epidural space Inner delicate membrane CSF Protective fluid, the brain floats in it 5 Word box 1 6 Midbrain Pons 7 2 3 4 Spinal cord 8 Sulci Thalamus Cerebellum Cerebrum 9 10 Gyri Corpus callosum Diencephalon Hypothalamus Medulla oblongata 11 12 L A B E L Sheep’s Brain Gyrus-noodles Diencephalon Transverse fissure Sulcus- deep grooves Cerebrum Corpus callosum CerebellumArbor vitae Olfactory bulb Optic chiasma Spinal cord Medulla oblongata Red arrows = brainstem Midbrain Pons Lobes of Cerebrum, Motor, Sensory, Association areas of Left Cerebral Cortex Parietal lobe, sensory perception of all the body, (feel itchy toe) • Lobes in Black Motor areas involved with the control • Frontal of voluntary muscles (moves to itch • Parietal toe) • Temporal • Occipital Motor speech area (Broca’s • Insula area) Occipital lobe, vision from retina Sensory, motor, association areas in purple Interpretation of sensory experiences, auditory patterns Temporal lobe auditory perception Cerebellum, motor coordination Cranial Nerves (Auditory) On old Olympus towering top a Fin and German viewed a hops. Reflex Arch What are the five steps? 1. Receptor organ receives stimulus at dendrite end of a sensory (afferent) neuron 2. Sensory neuron leads into the CNS and communicates with interneurons 3. Interneurons communicate with motor (efferent) neurons 4. Axons of those efferent neurons lead outward to effectors 5. Effector organ responds Hypothalamus Pineal gland Pituitary White matter Gray matter Ventricles CSF fluid Spinal cord Central canal Fissure Afferent Efferent Thalamus Diencephalons convolutions Corpus callosum Connects hemispheres Tube within the spinal cord Seperates hemispheres, seperates cerebrum from cerebellum Impulse sent away from CNS, motor impulse Impulse sent to the CNS, sensory Sense of smell doesn’t pass through here Part of the CNS, provides 2-way communication Looks like a butterfly in the spinal cord Surrounds gray matter Spaces within the central canal, left and right hemispheres of the brain and are filled with CSF fluid Occupies the ventricles of the brain, arachnoid space of meninges, and the central canal Maintains homeostasis, regulates body temperature Gyrus A mass of gray matter at the base of the cerebrum A small structure within the diencephalons that secretes melatonin Lies under the hypothalamus