File
advertisement

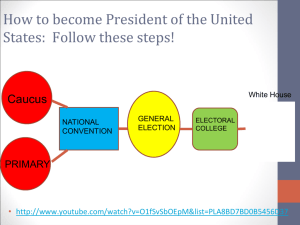
The Electoral Process Chapter 7 Section 1 THE NOMINATING PROCESS First Steps • Nomination – the naming of those who will seek office. – One of the primary functions of political parties – Reason for the decentralized nature of the two major parties. • Since two major parties dominate politics, the nomination process is very important. • Nominations are made by self-announcement, caucus, convention, direct primary, and petition in the United States. Self-Announcement • A person who wants to run for office simply announces that fact. – Usually someone unable to win their party’s nomination and is unhappy with their party’s choice. The Caucus • A caucus is a group of like-minded people who meet to select the candidates they will support in an upcoming election. • Caucus’ are used today mainly at the local level to make nominations of candidates and are typically open to all party members. The Petition • Often used at the local level for non-partisan posts and municipal offices. – Usually the higher the office the higher number of signatures required for nomination by petition. The Convention • Since 1832 all major political party candidates have been chosen by conventions. – Parties meet in local caucuses to select local candidates and choose delegates to county conventions. – At county conventions delegates select candidates for county offices and choose delegates to state conventions. – At state conventions, delegates select candidates for state offices and choose delegates to national conventions. – At national conventions, delegates select presidential and vice presidential candidates and electors. The Direct Primary • A direct primary is an intraparty election. – It is held within a party to pick that party’s candidates for the general election. – The state closely oversees direct primary elections despite the fact that they are party processes. – Way to combat the party bosses and prevent corruption. Primaries Today • Typically caucus/convention or direct primaries today or a combination of the two. • Primary elections are set by the State parties. • There are two main types. – Open Primaries • Anybody can vote in any primary – Closed Primaries • Only party members can vote – Colorado has closed Primaries – Some states use blanket primaries • All candidates for every party are listed on the ballot. Caucus vs. Ballot Primary Caucus • Encourages discussion and debate. • Very time consuming – Colorado has this system. Ballot Primary • Votes are straightforward • Takes very little time. Runoff Primary • In some cases where more than two candidates are successful in early primaries later in the process a runoff may occur where only the two most successful candidates are on the ballot. Presidential Primaries • Presidential primaries are primary elections held as one part of the process by which presidential candidates are chosen. – It is a process in which a party’s voters elect some or all of a State party organization’s delegates to that party’s nation convention – And/or it is a preference election in which voters can choose among various contenders for the party’s presidential nomination. Evaluating Primaries • Many people criticize the complexity and difficulty of participating in primary elections. • Financial aspects of primaries keep many qualified candidates out of the running. • Voters are usually very uninformed so it becomes a name-recognition process often. • Very few voters participate in primary elections.