General Physical Science Semester #2 Unit 4: Force and Motion
advertisement

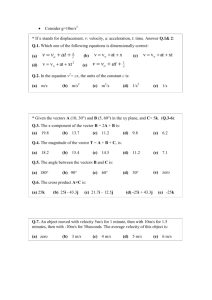
General Physical Science Semester #2 Unit 4: Force and Motion Exam Date: May 5 (A day classes), May 6 (B day Classes) Oregon State Content Standards H.2P.4 Apply the laws of motion and gravitation to describe the interaction of forces acting on an object and the resultant motion. Objectives: Meeting benchmark 1. I will be able to use the formula for speed to determine, speed, distance, and/or time. 2. Given an experiment, I will be able to identify the dependent variable and the independent variable. 3. I will be able to analyze a distance vs. time graph and accurately predict the speed of an object. 4. I will be able to analyze a speed vs. time graph and accurately describe the acceleration of an object. 5. I will be able to use the formula for acceleration to determine acceleration, change in speed, and change in time. 6. I will be able to identify the units for distance, speed, and acceleration. Exceeding benchmark 1. Given the formula for percent error, I will be able to calculate the percent error in a data set. 2. I will be able to convert speeds of one unit to speeds of a different unit. 3. To show my ability to exceed the benchmarks I will use words, drawing, mathematical relationships or other methods to further analyze patterns and/or relationships in the benchmarks. Vocabulary Speed: a description of the movement from one place to another over time. Acceleration: change in speed over time. Slope: change in steepness. (rise / run) or (change in Y value / change in X value) Dependent variable: the variable in an experiment which changes in response to choices made by the experimenter. The responding variable, which “depends” on the other one. Plotted on the Y-axis. (For example, if I wanted to see how turning up the heat in the room would affect student test scores, the test scores would be the dependent variable). Independent variable: the variable a researcher changes in an experiment. In the example above, the heat in the room is the independent variable. Controlled experiment: an experiment in which one variable is changed and all others stay the same. Percent error: how far a predicted result is from the actual result. Expressed in a percent. The lower the percentage, the closer the prediction to the actual result. Formulas and units Speed Speed = distance/time Time = distance/speed Distance = speed x time Acceleration Acceleration = Change in speed / Change in time Change in Time = Change in speed / Acceleration Change in Speed = Acceleration x Change in time Units for speed= meters/sec, miles/hour, cm/sec, etc. Units for acceleration = meters/sec2, meters/sec/sec, miles/hour/sec, etc. Formula for Percent error = (Predicted value – actual value) Actual value x 100 Homework for this unit: 1. Read Ch 1. Concept Rev #5-13 on pg 18 2. Read ch 2. Problems #7-13 on pg 41-42 3. Worksheet of practice problems 4. Practice on the back of this paper. Practice Problems: 1. What is the speed of a cheetah that travels 150 meters in 6 seconds? 2. How much time would it take for the sound to travel 1,000 m if sound travels at a speed of 330m/s? 3. How far would a school bus travel if it was going 50miles/hour for 4.5 hours? 4. A cyclist increases her speed from 2.0m/sec to 12.0 m/sec in 4.0 seconds. What is the acceleration? 5. A car slows its speed from 30 meters/sec to 5 meters/second. How long will it take to slow down if its rate of acceleration is 2 meters/second/second? 6. I did an experiment to see how eating vitamin D would affect my attitude. What is the independent variable- my attitude or the vitamin D? 7. What is a variable? 8. Explain why it is important to have a controlled experiment. 9. Which of the following is a unit for speed? Cm cm/sec cm/sec2 miles/hour miles 10. Draw a distance vs time graph which shows a car going slow and then fast. 11. Draw a speed vs time graph which shows a car going slow then fast. 12. A child measured her height to be 48 inches. Her actual height is 50 inches. What is her percent error? 13. Explain the difference in the motion of the car depicted in the two graphs below. s p e e d . D i s t Time Time Solutions: 1. Speed = distance / time. 150m/6s = 25m/s 2. Time = distance/speed. 1,000m / 330 m/s = 3.0 seconds 3. Distance = speed x time 50mile/hour x 4.5 hours = 225 miles 4. Acceleration = change in speed/change in time 12.0m/sec-2.0m/sec = 2.5 m/s/s 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 4 30m/sec – 5 m/sec = 12.5 seconds 2 The vitamin D is the independent variable. My attitude is the dependent variable because it is responding to the vitamin D (we are testing to see if it depends on the vitamin D). A variable is something that is changed which may affect the outcome of an experiment. In a controlled experiment, all variables stay the same except for the one you are testing. It is important to control variables so that you may learn what it is which is affecting the outcome. Cm/sec and miles/hour are units for speed. Change in time = change in speed/acceleration 11. 12. 48 in – 50 in x 100 = -4.2% 50 in 13. In the distance vs time graph the car is moving at a constant speed (cruise control). In the speed vs. time graph the car is speeding up (accelerating).