Motion Study Guide
advertisement

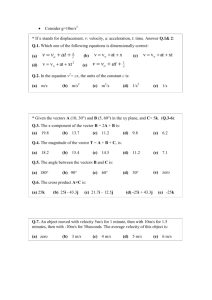
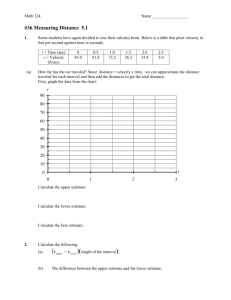
Motion Name: _____________________________ Study Guide Date: ________________ Per: _______ 1. What is motion? ________________________________________________________________________ 2. How do you know that motion has occurred? _________________________________________________ 3. What is the difference between distance and displacement? ______________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 4. A car travels 30 miles south, 10 miles east, 50 miles north, 10 miles west, and 10 miles south. What is its distance? ___________________ What is its displacement? ____________________ 5. How is instantaneous speed different than average speed? ________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 6. How is speed different than velocity? _________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 7. What is the formula for speed? _______________________ 8. How can velocity change? (there are 2 ways) - ____________________________________ - ____________________________________ 9. What is the difference between positive and negative acceleration? ________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 10. What is the formula for acceleration? ________________________________ 11. There are two ways to accelerate an object. What are they? (hint: speeding up and slowing down is only ONE way) ___________________________________________________________________________ 12. By looking at the units of each of the following values, label it as: distance (d), time (t), speed (s), velocity (v), acceleration (a), mass (m), or Force (F) . 80 g ______ 180 mph _______ 3.4 m/s _______ 10 N ______ 18 m/s/s _______ 180 mph west _______ 3.4 m/s2 ______ 30 m ______ 45 kg ______ 14 mph/s ______ 10 s ______ 13. Newton’s Laws: Law of Inertia: ____________________________________________________________________ Real – World Example: _________________________________________________ F = ma: _________________________________________________________________________ Real – World Example: _________________________________________________ Law of Action/Reaction: _____________________________________________________________ Real – World Example: __________________________________________________ 14. Which of Newton’s laws apply to each example? (name AND number) When I punch a wall, it punches me back. __________________________________ When I push a tennis ball and a bowling ball, the tennis ball has more acceleration. __________ When a glass is thrown against a wall, it shatters. _____________________________ When I hit the gas pedal, it throws me back against my seat. __________________________ 15. When I slam on the brakes, why does my drink splatter all over the radio? __________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ Which of Newton’s Laws is demonstrated? ________________________________________________ 16. What is acceleration due to gravity? (include the units) ____________________ 17. What does the law of universal gravitation basically say? _______________________________________ 18. If I have more mass, will exert more or less gravity on another object? __________________ 19. If two objects are close together, will they exert more or less gravity on each other? _______________ 20. What is the difference between mass and weight? ____________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 21. Are kilograms the units for mass or weight? ____________ What is the SI unit for weight? ____________ 22. Explain why the pilot of a plane must have precise measurements of velocity. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 23. You are riding on a train going north and you see a car traveling north parallel to the train. Yet the car seems to be going backward. Explain this occurrence. ________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ Use the following formulas to solve the practice problems: a = (vf – vi ) / t s=d/t d = ½ a t2 F=ma 1. A student practicing for a track meet ran 240 m in 30 sec. a. What was her average speed? b. If on the following day she ran 300 m in 30 sec, by how much did her speed increase? 2. A car traveled 1025 km from Chicago to New Orleans in 13.5 hrs. What was its average velocity? 3. How fast was a plane flying if it traveled 400 km in 30 min? 4. A student walks 10 blocks to a computer store (Assume all the blocks are equal length.) a. How long will it take him to reach the computer store if he walks 3 blocks in 2 min? b. What is his average velocity? 5. If the average speed a car is 45 km/hr, how far can it travel in 2 hours? 6. A driver starts his parked car and within 5 sec reaches a velocity of 54 km/hr as he travels east. What is his acceleration? 7. Falling objects drop with an average acceleration of 9.8 m/sec/sec/ or 9.8 m/sec 2. If an object falls from a tall building, how long will it take before it reaches a speed of 49 m/sec? 8. What is the force of gravity acting on a 40-kg object? Challenge: If the average speed a car is 45 km/hr, how far can it travel in 45 min?