Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms, and Ions
advertisement

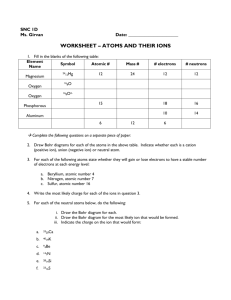
Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms, and Ions Atoms and Ions Atoms and Ions Objectives: 1. Students will be able to describe the formation of ions from their respective atoms and be able to name them. 2. Students will be able to relate the charge of an ion to the number of protons and electrons. 3. Students will be able to predict which ion a given element forms. Class Warmup Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in each of the following isotopes: 3 1 H 65 30 Zn 56 Fe Protons have (a) ________ charge. Electrons have (a) _______ charge Neutrons have (a) _______ charge Atoms and Ions What is an Ion? • An atom that has gained or lost electrons and, as a result has a negative or positive charge. How does an atom become an ion? • by gaining or losing electrons. • Metals form + ions by losing electrons • Nonmetals form - ions by gaining electrons Atoms and Ions Cation – a positively charged ion; formed when an atom loses one or more electrons 1+ Na has ______ protons and _____ electrons • Cations are named using the element name Examples: Fe3+ iron ion Na+ sodium ion Atoms and Ions Anion – a negatively charged ion; formed when an atom gains one or more electrons 2O has _______ protons and _______ electrons • Anions are named by dropping the element name ending and replacing it with “ide”. Examples: O2- oxide Ffluoride N3- nitride Practice Problems Find the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in each of the following ions. 19 9 F 24 12 Mg 2 23 11 Na 17 8 2 14 O N 3 Ion Charges and the Periodic Table Ions and their Compounds Formation of an Ionic Compound - YouTube