Tissues
advertisement

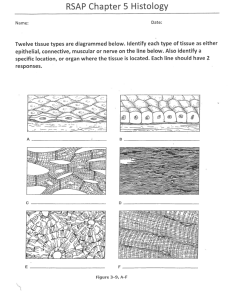
Muscle Tissue Types: Skeletal-connected to skeleton Cardiac-heart (pump blood) Smooth-in digestive system (move food), uterus Function: contract to provide motion Involuntary muscles-cardiac and smooth-cannot control Voluntary muscles-skeletal, pull on bones, produce movement Nervous Tissue FXN: neurons receive and conduct electrochemical impulses from one part of body to another Location: Brain, spinal cord, nerves Connective Tissue FXN: protect, support, bind together other body tissues Characteristics: variation in blood supply, extracellular matrix Types/Location: -Bone -Cartilage-ear and spinal cord(discs) -Dense connective tissue-lower layer of skin -Loose connective tissue-protects organs, fat -Reticular Connective Tissue-lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow -Blood-connective tissue because it is cells surrounded by non-living fluid matrix Important facts: 1. connects all body parts 2. most abundant tissue type in body 3. consists of living cells surrounded by non-living matrix Epithelial Tissue: FXN: protection, absorption, filtration, secretion Location: covers all body surfaces, other layer of skin and inside body to line cavities (digestive system) Characteristics: -close together -at least one exposed surface -lower surface rests on basement membrane (connective tissue) -no blood supply of their own, rely on diffusion -regenerate easily on their own if well nourished Tissue Repair: Types-Regeneration, replacement of damaged tissue. Fibrosis-repair by dense connective tissue What happens- 1. Capillaries become permeable-increases blood flow, formation of clot, holds edges together. 2. Granuation tissue forms-delicate tissue composed of new capillaries, phagocytes dispose of clot, builds scar tissue 3. Surface epithelium regenerates-beneath scab, scab detaches, fully regenerated tissue, scar may be visible Exercise 5 pg. 49-54, use book and manual pg. 37-48 as reference.