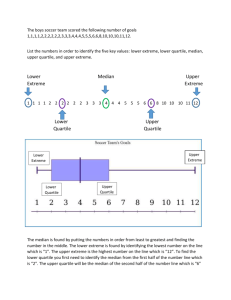
Economic Freedom of the World
advertisement

Prof. Edward Peter Stringham Hackley Distinguished Professor for the Study of Capitalism and Free Enterprise Fayetteville State University North Carolina, United States 1 What Explains Growth? Is it Resources? Location? Democracy? Or …… North Korea vs. South Korea Per Capita Income = $1,800 Per Capita Income = $24,200 Adam Smith’s Question: Why Are Some Countries Rich and Others Poor? An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations (1776) Policies and the system of economic organization (e.g., capitalism) matter more than things such as resources, geography, education, democracy, etc. Economic Freedom Economic Freedom means that people are free to trade with others, compete in markets, buy what they want, earn a living in a job they choose, keep what they earn, and own things privately. Measuring Economic Freedom • Economic freedom is complex and multidimensional, but it can be measured: • Personal choice • Freedom to trade, domestically and abroad. • Freedom to enter and compete in markets. • Security of Property/Rule of Law Motivation The key to changing policy in the world is changing the climate of opinion about what works and what does not work in encouraging world development The key to changing the climate of opinion is providing the widest possible audience with good information about the causes of development and under-development Economic Freedom of the World Project Objective: find a way to measure economic freedom and explore the connection between it and other indicators 20 year project Led by the late Milton Friedman, Rose Friedman and Michael Walker Involved 60 of the world’s top scholars, including three Nobel Laureates: Milton Friedman, Douglass North, and Gary Becker What is the Economic Freedom of the World Index? An annual compilation of data representing factors which make a country economically free Authors: James Gwartney, Robert Lawson, and Walter Block A compendium of 42 government policies affecting economic freedom based on objective data or independent surveys A ranking of 141 countries representing 95% of the world’s population according to the extent to which they permit their citizens to be economically free Now a collaboration of Institutes in 76 different nations and territories Components of the Economic Freedom of the World Index Size of government and taxation Private property and the rule of law Soundness of money Trade regulation and tariffs Regulation of business, labour and capital markets 5 Areas of Economic Freedom of the World (EFW) Index 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Size of Government: Expenditures, Taxes, and Enterprises Legal Structure and Security of Property Rights Access to Sound Money Freedom to Trade Internationally Regulation of Credit, Labor, and Business Photos are compiled by Russel Sobel, Ph.D. Example 1 A country with VERY LOW economic freedom Families in Guinea-Myanmar Relief efforts in Guinea-Myanmar 26 Example 2 A country with LOW economic freedom Romania Families in Romania Families in Romania Families in Romania Families in Romania Families in Romania Families in Romania Families in Romania Families in Romania Families in Romania Example 3 A Country with MEDIUM Economic Freedom India Families in India Families in India Example 4 Another Country with Medium Economic Freedom Mexico Families in Mexico Families in Mexico Example 5 A Country with HIGH Economic Freedom Hong Kong Families in Hong Kong Families in Hong Kong Families in Hong Kong Overall Economic Freedom Index and the Top 10 Hong Kong Singapore New Zealand Average of top 10 Switzerland United Kingdom Chile Canada Australia United States Ireland 0 2 4 6 Score (out of 10) Source: The Fraser Institute. 8 10 Overall Economic Freedom Index and the Bottom Ten Chad Central Afr. Rep. Guinea-Bissau Congo, Dem. R. Venezuela Niger Congo, Rep. Of Myanmar Angola Zimbabwe 0 2 4 6 Score (out of 10) Source: The Fraser Institute. 8 10 Why is Economic Freedom Important? Economic rights are fundamental rights in the sense that without them there can be no political or civil freedoms They are a prerequisite for growth and development They are a prerequisite for broader human development The impact on economic growth and development Income (per person) of the Bottom Ten Venezuela Angola Congo, Rep. Of Chad Myanmar Central Afr. Rep. Niger Guinea-Bissau Congo, Dem. R. 0 10,000 20,000 30,000 40,000 GDP per Capita, 2006 (ppp) Sources: The Fraser Institute; The World Bank, World Development Indicators, 2008. 50,000 Income (per person) of the Top 10 Singapore United States Ireland Hong Kong Switzerland Canada Australia United Kingdom New Zealand Chile $0 $10,000 $20,000 $30,000 $40,000 $50,000 GDP per Capita, 2006 (ppp) Sources: The Fraser Institute; The World Bank, World Development Indicators, 2008. Per Capita Income and Economic Freedom Quartile GDP Per Capita (ppp), 2006 $35,000 $30,000 $25,000 $20,000 $15,000 $10,000 $5,000 $0 Least Free Quartile 3rd Quartile 2nd Quartile Most Free Quartile Least Free ………………... Most Free Sources: The Fraser Institute; The World Bank, World Development Indicators, 2008. Foreign direct investment, net inflows (% of GDP), 1990-2006 Foreign Direct Investment and Economic Freedom Quartile 5.0% 4.0% 3.0% 2.0% 1.0% 0.0% Least Free Quartile 3rd Quartile 2nd Quartile Most Free Quartile Least Free ……………...…... Most Free Sources: The Fraser Institute; The World Bank, World Development Indicators, 2008. Economic freedom and economic growth have bestowed benefits across all levels of society 59 Our Homes Percent of homes with Heating & Air Conditioning 1956 = 6% 1996 = 81% Percent of homes with only one bathroom 1956 = 71% 1996 = 9% And They are Better: Our Showers Our Cars We now have DVD players, Air Conditioning, Anti- lock Brakes, Power windows Our Phones Our Entertainment Our Science Our Computers Our Medicine Our Music But what about the poor? 69 Income Share of the Poorest 10% and Income Share Held by Lowest 10%, 1990-2006 Economic Freedom 3.0% 2.5% 2.0% 1.5% 1.0% 0.5% 0.0% Least Free Quartile 3rd Quartile 2nd Quartile Most Free Quartile Least Free …………….. Most Free Sources: The Fraser Institute; The World Bank, World Development Indicators, 2008. Income Level of the Poorest 10% and Income Level of the Poorest 10%, 1990-2006 Economic Freedom $9,000 $8,000 $7,000 $6,000 $5,000 $4,000 $3,000 $2,000 $1,000 $0 Least Free Quartile 3rd Quartile 2nd Quartile Most Free Quartile Least Free …………….. Most Free Sources: The Fraser Institute; The World Bank, World Development Indicators, 2008. 73 A free society also has no barriers to getting rich University of Michigan Panel Survey on Income Dynamics data show that of Americans in the bottom 20 percent income bracket in 1975, only 5.1 percent of them remained in that lowest income bracket by 1991. In fact, 29 percent of the lowest fifth of income earners in 1975 had moved to the top 20 percent of income earners in 1991. 74 The impact of Economic Freedom on the UN’s Human Development Index and other indicators of well-being Human Development Index and Economic Freedom Quartiles United Nations Human Development Index Higher ratings indicate higher levels of development 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 Least Free Quartile 3rd Quartile 2nd Quartile Most Free Quartile Least Free ……………. Most Free Sources: The Fraser Institute; United Nations Development Programmme, Human Development Indicators 2008, available at http://hdr.undp.org/. Life Expectancy at Birth and Economic Freedom Quartiles 80 Years 60 40 20 0 Least Free Quartile 3rd Quartile 2nd Quartile Most Free Quartile Least Free ……………. Most Free Sources: The Fraser Institute; The World Bank, World Development Indicators, 2008. Per 1,000 live births, 2006 Infant Mortality and Economic Freedom Quartile 80 60 40 20 0 Least Free Quartile 3rd Quartile 2nd Quartile Most Free Quartile Least Free ………..………. Most Free Sources: The Fraser Institute; The World Bank, World Development Indicators, 2008. % of Population Using Improved Water Sources 100 Percentage 80 60 40 20 0 Least Free Quartile 3rd Quartile 2nd Quartile Most Free Quartile Least Free ………………... Most Free Sources: The Fraser Institute; The World Bank, World Development Indicators, 2008. Environmental Performance and Economic Freedom Quartile Higher ratings indicate higher levels of environmental performance Index (out of 100) 100 80 60 40 20 0 Least Free Quartile 3rd Quartile 2nd Quartile Most Free Quartile Least Free ………..……….. Most Free Sources: The Fraser Institute; The World Bank, World Development Indicators, 2008. Can a nation improve their level of economic freedom? 81 Economic Freedom Over Time Economic Freedom Score 10 8 6 6.1 5.5 5.4 5.5 5.7 6.0 6.4 6.4 6.4 6.4 6.4 6.6 6.6 4 2 0 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 Source: The Fraser Institute. Case Study: Zimbabwe • Legal Structure/Property 10 • 6 4 • 2 • 05 20 00 20 95 19 90 19 85 19 80 0 19 EFW Rating 8 • Rights rating has fallen to 3.7 from 5.5. Annual inflation has increased to 349% from 6.5%. Foreign currency bank accounts are illegal. Tariff rates increased to 16.7% from 8.7%. Price control rating = 0.0! GDP per capita growth, 1995-2005 = -3.43% Case Study: Venezuela • Government 10 • 6 • 4 • 2 • 05 20 00 20 95 19 90 19 85 19 80 19 75 19 70 0 19 EFW Rating 8 consumption increased to 20.3% from 14.4%. Transfers & subsidies increased to 15% from 2%. Inflation remains high at 16%. Foreign currency accounts restricted. Military interference rating fallen to 0.8 from 5.6. GDP per capita growth, 1995-2005 = -0.36% Case Study: Ireland 10 • Transfers & Subsidies fell to 11.7% from 21.8%. • Top marginal tax rates fell to 42% from 65%. • Tariff rate fell to 2.7% from 8.8 %. • Sound Money rating increased to 9.7 from 5.8. 6 4 2 05 20 00 20 95 19 90 19 85 19 80 19 75 19 70 0 19 EFW Rating 8 GDP per capita growth, 1995-2005 = 5.97% Case Study: Estonia 10 • Transfers & Subsidies fell 6 4 2 05 to 11.7% from 15.3%. • Inflation fell to 1.6% from 33.7%. • Credit market regulation rating increased to 9.7 from 4.3. • Legal Structure/Property Rights rating increased to 7.7 from 6.5. 20 00 20 95 0 19 EFW Rating 8 GDP per capita growth, 1995-2005 = 7.27% Case Study: Chile 10 • Top marginal tax rates fell to 40% from 58%. • Tariff rate fell to 4.9% from 30%. • Inflation rate fell to 6 4 3.1% from 30.7%. • Capital market controls lifted. 2 05 20 00 20 95 19 90 19 85 19 80 19 75 19 70 0 19 EFW Rating 8 GDP per capita growth, 1995-2005 = 2.99% Case Study: China 10 • Freer trade: tariffs reduced to 9.2% from 49.5%. • Capital market deregulation: rating improved to 6.5 from 6 4 2 05 20 00 20 95 19 90 19 85 19 80 0 19 EFW Rating 8 0.0. • Note: China varies tremendously internally. GDP per capita growth, 1995-2005 = 8.21% Case Study: India 10 • Government investment and SOEs are less important: The rating in this area increased to 8 from 0. • Tariffs have fallen to 6 4 2 05 20 00 20 95 19 90 19 85 19 80 19 75 19 70 0 19 EFW Rating 8 17%. from 98.8% • Many capital market controls have been lifted. GDP per capita growth, 1995-2005 = 4.68% Case Study: Botswana 10 • Improved monetary stability: 5.3 to 9.0 rating. • Fewer regulations: 5.9 to 7.6 rating. • Improved legal structure rating: 6.3 to 7.4 rating. 6 4 2 05 20 00 20 95 19 90 19 85 19 80 0 19 EFW Rating 8 GDP per capita growth, 1995-2005 = 6.14% GDP per capita by country 91 Economic Freedom by Country 92 Conclusions Economic Freedom is associated with Lower rates of homicide Reduced poverty Increased prosperity for rich and poor Prof. Edward Peter Stringham Lloyd Hackley Endowed Professor of Capitalism and Free Enterprise Studies Fayetteville State University 94 Latest research Economic freedom and crime 95 The Encyclopedia of Murder and Violent Crime states, “Killing and violent behavior has permeated the development of America,” attributing this in large part to “the inevitable clash of capitalism” (Hickey, 2003, pp.xxxi-xxxii). “The only source of crime is capitalism” (Lynch and Groves, 2000, p.336). 96 Crime and Capitalism (Greenberg, 1993) contains thirty chapters arguing how markets cause crime. Wenger and Bonomo (1993, p.420) “[T]he relationship between crime and the terminal crisis of capitalism has become the subject of considerable debate….[But] the debate does not concern the role of capitalism in producing crime—to all but the reactionary or the naïve, such questions have long been settled.” 97 (homicide rate) = 1 + 2(economic freedom) + 3(incarceration rate) + 4(death penalty) + 5(gini) + 6 (literacy rate) + , 98 Table 1: Summary Statistics Variable Obs Mean Std. Dev. Homicide rate (per 100k) 63 6.64 9.33 Economic Freedom (Fraser) 115 6.00 1.23 Economic Freedom (Heritage) 61 2.65 0.71 Incarceration rate (per 100k) 63 202.76 145.95 Death penalty 63 0.52 0.50 Gini index 58 35.50 8.72 Literacy rate 55 96.25 5.54 Ethnic fractionalization 61 0.34 0.20 English legal origin 56 0.14 0.35 Unemployment rate 58 9.07 6.54 Percent rural 61 32.36 16.76 GDP per capita 62 11623 12097 Min 0.5 3.44 1.56 58 0 23.2 67.5 0.00 0 0.72 0 160 Max 61.6 9.08 4.28 714 1 59.7 100 0.71 1 46.24 75 44440 99 TABLE 3: Baseline Regressions Dependent Variable: Homicides Per 100,000 People (1) (2) Economic Freedom (Fraser) -3.699 *** (0.00) Economic Freedom (Heritage) 4.659 ** (0.02) Incarceration rate 0.005 0.006 (0.66) (0.57) Death Penalty -2.484 0.013 (0.45) (1.00) Gini index 0.61 *** 0.512 *** (0.00) (0.01) Literacy rate 0.11 0.094 (0.71) (0.75) Constant -2.093 -34.116 (0.95) (0.31) Observations 41 50 R-squared 0.432 0.332 Notes: p-values are in parentheses; * is significant at 10% ** significant at 5%; *** significant at 1% 100 -20 0 20 40 60 FIGURE 1: Partial Regression Plot for Regression 1 (dependent variable: homicide rate) with Economic Freedom data from Fraser (higher scores indicate more economic freedom) -4 -2 0 e( freedom | X ) 2 4 coef = -3.6992051, se = 1.1085175, t = -3.34 101 Case studies 102 5 4.5 4 10 20 30 40 Economic Freedom (Fraser) 5.5 50 Venezuela 1990 1995 2000 year Homicide rates per 100k 2005 2010 Economic Freedom (Fraser) 103 5.6 5.4 5.2 18 20 22 24 26 Economic Freedom (Fraser) 28 5.8 Colombia 1990 1995 2000 2005 year Homicide rates per 100k Economic Freedom (Fraser) 104 7 6.5 6 6 5.5 8 10 Economic Freedom (Fraser) 12 7.5 Latvia 1990 1995 2000 year Homicide rates per 100k 2005 2010 Economic Freedom (Fraser) 105 7 6.5 6 5.5 5 8 10 12 Economic Freedom (Fraser) 14 7.5 Lithuania 1990 1995 2000 year Homicide rates per 100k 2005 2010 Economic Freedom (Fraser) 106 7 6.5 6 5.5 40 50 60 Economic Freedom (Fraser) 70 7.5 South Africa 1990 1995 2000 year Homicide rates per 100k 2005 2010 Economic Freedom (Fraser) 107 Moving forward 108 109 Economic Freedom of the World www.freetheworld.com 110 Economic Freedom of the World www.freetheworld.com 111 Prof. Edward Peter Stringham Lloyd Hackley Endowed Professor of Capitalism and Free Enterprise Studies Fayetteville State University 112