Modeling Plasmid Selection - Biology2020
advertisement

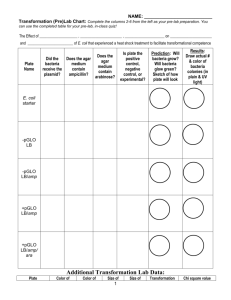
Modeling Plasmid Selection And Authentic Assessment 6-2010 http://biology2020.wikispaces.com/ 2 With the pGlo Plasmid Bacteria are very useful organisms in genetic engineering. They are able to bring in plasmids. Into which DNA of interest may be added. The Problem? • Finding the bacteria that have taken in the modified plasmids. • You can see the bacteria, but not the plasmid. • Must look for some visible effect of the plasmid. What to look for? • Growing in the presence of antibiotic. • The effect of a gene, like the glow of pGLO Cut Four Paper Ovals (or…draw 4 ovals on a large sheet of paper.) • Each represents a bacterial cell Make Four Chromosomes • Out of four chenille stems • Bacterial • Circular • Give a little twist to prevent confusion with a nucleus. • Add to “cells.” • (Or just draw this chromosome in on paper) Form your plasmids Use 1/2 a chenille stem each. Make two plasmids as below. Twist into ring but leave tails Regulatory Gene bla Ara C Antibiotic Resistance Ara B Ara A AraD Structural Genes GFP Bla codes for beta lactamase, a protein which confers antibiotic resistance. By the way…great place to teach the operon. Reserve Restriction Enzymes • Plasmids are cut with the same restriction enzyme used to cut the DNA to be inserted. A restriction enzyme which leaves overhanging sticky ends is needed for this this procedure. This provides the free base pairs needed to combine the plasmid DNA with the source DNA. Restriction Enzyme Cut from EcoRI ✤ Procedure: • • Open the plasmids you prepared by untwisting the ½ chenille stem. • This represents the recognition site for the restriction enzyme. Remove ara B, araA, and araD (last 4 beads). • Add a green bead to represent the GFP (gene of interest). Modeling pGlo LB -pGLO LB/AMP -pGLO LB/AMP +pGLO LB/AMP/ARA +pGLO Bacteria Lives? LB Yes -pGLO LB/AMP No -pGLO LB/AMP LB/AMP/ARA Yes Yes +pGLO +pGLO Bacteria Glows? LB No -pGLO LB/AMP LB/AMP LB/AMP/ARA No No Yes -pGLO +pGLO +pGLO Great Lab for Authentic Assessment Let’s try it. More Authentic Assessment 1. Is this gel in the chamber correctly? 2. How do you know? 2nd block may get this! Provide a ruler and some semi-log paper. Ask: How big is fragment X? Which is larger , X or Y? 17 Micropipettor • Have out a micropipettor and a microtube. • Instructions: – Pipet 50 µL of water into the microtube. – Close and write your initials on the top with the permanent marker. – Place in the box by clicker number. – Set the micropipettor to the day of the month you were born on. 18 Osmosis • Provide a scale and weigh boat. Just use water…but ask… • This bag has been in this beaker of distilled water for 30 minutes. • The initial mass of the bag was 30 g. • Is the bag hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic to the beaker? • Which way did water move? 19 Fruit Flies Give sex and eye type. 20 Mitosis Identify the stage of mitosis at the tip of the pointer. 21 Respiration Read the pipette. 22 References • Biotechnology Explorer, pGLO Bacterial Transformation Kit. BioRad. http://www3.bio-rad.com/images/pglomap2.gif 24