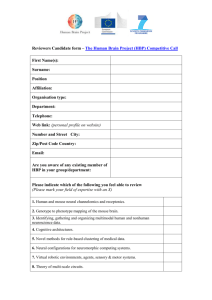
Cardiovascular Meds

Cardiovascular Meds
Arrhythmias
• Heart attacks sometimes cause damage to the myocardium (heart muscles)
• Irregular heart beats may develop post MI’s
• Atrial flutter, palpitations, premature ventricular contractions (PVC’s) are all common types of arrhythmias
• Goals of meds is to reduce over sensitive heart muscle tissue to contract spastically by reducing cell membrane permeability hence reduced excitability of the myocardium.
Membrane stabilizers for arrhythmias
• Norpace
• Lidocaine by IV only to stabilize irreg. hearts right after an MI in the ER
• Procainamide (pronestyl) and quinidine orally for long term use
Anti-Arrhythmics which prevent neurotransmitter release
• Cordarone and Betapace, orally, can cause dizziness, low blood pressure
Anti arrhythmics which are Calcium blockers
• Calcium ions needed to move across membranes to allow the heart to contract
• Blocking Calcium blocks overly excited hearts post MI’s
• Cardizem and Verapamil, norvasc, procardia,
• Can cause hypotension, bradycardia
CHF (congestive heart failure)
• Heart regular BUT too weak for a large body and is failing. Accumulating too much blood but can’t pump it out. Swollen ankles, fatigue, bloating, weakness, dyspnea
• Lanoxin (digitalis) increases the force of heart contractions which helps weak hearts.
• Patients might see green blue halos!!!
ACE inhibitors
• These block the release of a certain enzyme in the kidneys. Angiotensin is the pre-enzyme that it blocks which then blocks renin release hence
ACE/angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors
• Vasotec, monopril,capoten, accupril, Altace,
• Side effects; low BP, dizziness, cough,
• They do not cause patient to lose potassium and in fact may cause hyperkaliumia, and they interact with Lithium taking depressive patients
Beta Blockers for MI’s
• Reduce overly sensitive and over active hearts trying too hard to compensate for overload s like edema, obesity, smoking, arryhthmias,
• Heart attack damage, etc.
• Block adrenalin receptors in the heart tissue to relax hearts showing HBP
• Toprol, lopressor, tenormin,coreg,Inderal, corgard:all very commonly used for first line tx of
HBP. All cause bradycardia, depression,impotence
Angina care
• No O2 getting to heart tissue therefore heart pain due to poor coronary circulation
• Nitroglycerine:sublingual, spray, patch powerful vasodilator, red in the face as well and dizziness, it’s flammable and protect from sunlight and always taper it off!
• Imdur and Isodil both sublingual and safer to use
Meds for HBP
• Diuretics: increase fluid excretion thus reducing load on sick heart
• Side effect: hypokalium
• Don’t take at bedtime or get nocturia
• Diuril (Chlorthiazide), Lasi (furosemide),
Hydrodiuril (hydrochlorthiazide), Aldactone
(spironolactone), Diazide, Maxide
• All cause hypokalemia EXCEPT spironlactone so take with bananas/OJ
CNS blockers for HBP
• Block adrenalin output by blocking CNS causing its release from the adrenal medulla
• Catapres (clonidine),Aldomet
• Dizziness, depression
Peripheral nervous system blockers for HBP
• Allow peripheral vasodilation due to blocking sympathetic nerves
• Cardua, Minipress, Hytrin
Peripheral vasodilators for HBP
• Apresoline (hydralazine)
• Minoxidil (Rogaine) also grows hair!
• Both block smooth muscle in arterioles hence lower BP
Combination HBP meds
• Advantage; fewer side effects for they reduce the total dose of each component so safer
• Hyzaar: beta blocker PLUS a diuretic