Literacy Practice Powerpoint

Literacy Practice: Promoting
Content Area Reading
Designed by
Brenda Stephenson
The University of Tennessee
At the end of this presentation students should:
Define the concepts for promoting reading comprehension through content area reading materials.
Identify ways of using content area reading materials to promote reading comprehension in the classroom.
List materials and resources available to accomplish this practice.
Content Area Reading
…refers to the challenge of reading in the academic areas such as science, social studies, mathematics, literature, and the arts.
Content Area Reading
Scaffolding provides a systematic approach to address the challenges of
Content Area
Reading.
Content Area Reading: Scaffolding
instructional technique using teacher modeling to introduce the desired learning strategy or task, then gradually shifts responsibility to the students
Scaffolding Graph
Content Area Reading: Scaffolding
supports students before , during , and after they read.
enables students to accomplish what is normally beyond their abilities .
provides enough help so students can succeed with a task that otherwise would be impossible .
(Graves & Graves, 1994)
Video Clip
Biology Content Video
Content Area Reading: Scaffolding
Temporary
Task-oriented
Support to extend reach
Steps to Teaching:
• Preparation • Assistance • Reflection •
Teacher
Analyzes
Text
Prior to Lesson
Assesses Readability
Modifies text if necessary
Identifies Key Vocabulary & Concepts
Identifies Expository Text Structures
Identifies Relation to Prior Knowledge
Teacher Text:
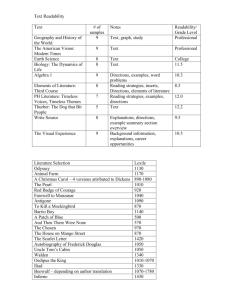
Readability
Prepare students to read the material by considering readability factors
interest & motivation of the reader legibility of the print & illustrations
complexity of words and sentences in relation to the reading ability of the reader
Teacher Text:
Readability
Analyze Word & Sentence Complexity
run a readability analysis at intervention central.org using the OKAPl! Reading Probe
Generator
use Microsoft Word spell & grammar check with the readability tool option turned ‘on’
Teacher Student:
Reading
Level
Assess Student Reading Levels:
Running Records
–
– readinga-z.com
Tutorial
Informal Reading Inventories
Teacher Text:
Modify
If…
Text Level is higher than Instructional
Level
Then…
Paraphrase (rewrite)
Many textbooks now have companion readers/study guides developed specifically as content area reading supplements. These are often ordered by schools for the ELL students. Check. It will save you a lot of time and work!
Teacher Text:
Vocabulary
Limit the number of words introduced…
Choose words
– critical to understanding the main ideas
– not likely to be learned independently
Teacher Text:
Text Structures
Analyze Word & Sentence Complexity
Researchers have found that instruction in expository text structure has a positive effect on recall and comprehension.
(Armbruster, Anderson, & Ostertag, 1987; Roller & Schreimer, 1985; Taylor
& Beach, 1984).
Teacher Text:
Text Structures
Patterns
Science
problem-solving classification experimental cause and effect definition/explanation
Social Studies
chronological events definition/ explanation cause and effect compare/contrast question & answer
Teacher Text:
Text Structures
Patterns
Math
key words graphic relationships evidence & reasoning symbolic relationships
& operations
Literature
character development
settings
plot
moral & message
symbolism
genre
Student Text:
Skills
Literacy Skills needed in content areas are:
Identifying the main idea
Locating facts and specific details
Organizing material mentally
Vocabulary comprehension
Adjusting
Reading Rate &
Focus
Summarizing
Graphic Organizer Video
Content Writing Clip
Content Reading:
Teaching
Teacher Text Student
Before Reading
• Building Vocabulary • Activating Prior Knowledge • Setting a Purpose • Previewing • Brainstorming • Predicting •
During Reading
• Scanning • Visualizing • Context Clues • Inferring •
Questioning • Clarifying •
After Reading
• Summarizing • Drawing Conclusions • Reflecting • Critical
Thinking • Review • Synthesis • Writing to Learn •
Content Reading: Teaching
Teach Strategies Using:
– Established programs & techniques which
address before, during, after
utilize graphic organizers
provide modeling of desired skills
offer variety to address varying learning styles
Content Reading:
Techniques
(More links from Reading Quest Check out the Print
Charts!)
Writing to Learn
Directed Reading Activity (DRA)
Directed Reading Thinking
Activity (DRTA)
Guided Reading Procedure (GRP)
SQR3
Listen-Read-Discuss (L-R-D)
Content Reading:
Techniques
(Click the links below for information from Reading
Quest on each strategy. Check out the Print Charts!)
ABC brainstorm history frames
carousel inquiry chart
clock buddies
K - W - L
opinion-proof
column notes
power thinking
comparisoncontrast
Content Reading:
Techniques
(More links from Reading Quest Check out the Print
Charts!)
questioning the author
RAFT papers
reciprocal teaching
underlining
semantic feature
analysis story maps
summarizing
thesis-proof
think-pair-share
Content Reading:
Techniques
(More links from
Reading Quest )
3-minute pause
3 - 2 – 1
venn diagrams word maps
QARs
(Links to other successful programs & techniques)
word splash
word sorts
anticipation guide
Materials and Media
http://www.timetabler.com/reading.html
http://www.gopdg.com/plainlanguage/readability.html
http://www.ncrel.org/sdrs/areas/issues/students/learning/lr2grap.htm
Bibliography
Mora, Jill Kerper. “Content Area Reading for English Language
Learners” March 16, 2006. http://coe.sdsu.edu/people/jmora/ContentReadMM/ >
“Reading in the Content Areas: Strategies for Success” March 21,
2006.
http://www.glencoe.com/sec/teachingtoday/educationupclose.phtml/12
“Literacy Strategies” March 21, 2006 http://www.litandlearn.lpb.org/strategies.html