Chapter 11 Presentation
advertisement

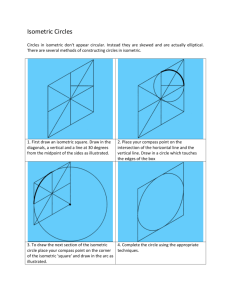
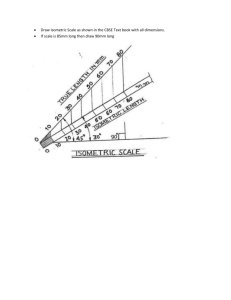
Chapter 11 Axonometric & Oblique Drawings Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Pictorial Drawings Show several faces of an object at once Uses? Selling- Sales Literature Manufacturing- (CNC paths exported or CAM) Installation (IKEA step by step instructions) Maintenance- Maintenance manuals Design- Visualization to untrained eye What is someone’s passion? (Add on Google) Axonometric Projection: Greek term Axon = Axis Greek term metric = measure Axonometric means: parallel projection around an axis or axes All 3 actual measurements are visible in one view Width, height, depth 4 projection types: Isometric vs. Non-isometric lines/ planes True length/ size & shape represented Isometric Planes vs. Non-Isometric Planes Exercise Sketch This in Isometric View Up to this point we have used Axonometric synonymously with Isometric, but there are actually three division of Axonometric projections Classified by angles between the lines comprising the axonometric axes Dimetric DrawingAngle between 2 axes same for 2 Surfaces Other Surface is Foreshortened Trimetric DrawingAngle between 2 axes different for all Surfaces Isometric DrawingAngle between all axes equal No Surface has more emphasis than any other Steps involved in rotating about 2 axes to get Isometric Projection Isometric Plane- contains isometric lines (any line parallel to one of legs of isometric axes) Rotation about 2 axis results in foreshortened projection of lines and faces and therefore we must increase the projection by approximately 20% to get full scale Standards for Isometric Drawings: •Hidden lines omitted unless absolutely necessary to completely describe part and not show in multi-view projection (where only isometric is being shown) •Centerlines omitted unless showing symmetry or for dimensioning (where only isometric is being shown) Section Views in Isometric Drawings: Only used when necessary to clearly define internal features 2 Types __________ and ____________ Oblique Drawing- 3D Axonometric representation Where front is show in true size and shape Common for Illustration purposes for furniture Oblique Drawing and scales: 3 Types: Cavalier- Full scale in height and depth Cabinet- Half scale in depth, full scale in height General- >half & < full scale in depth, full in height Oblique Rules: Longest Dimension parallel to frontal plane Cylinder Rule- Overrides dimensional rule for clarity Dimensioning Oblique Drawings: Where only oblique drawing is given for illustration purposes •Everything on frontal plan and limited dimensions in profile plane •Dimension only in true shape or Cavalier projection Summary: 3 classifications of Pictorials •Axonometric •Oblique •Perspective 3 Classifications of Axonometric •Isometric •Dimetric •Trimetric If you do not create your part on the right plane and you have to rotate it to where it is close to isometric view what are you really portraying? Homework Figure 11.75 (66) Create a solid model of the part in solid works and place in one of the axonometric projections that show the most detail