RENAL SYSTEM
advertisement

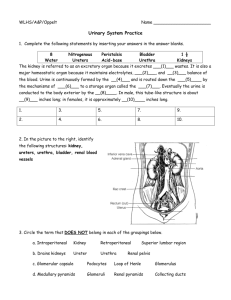
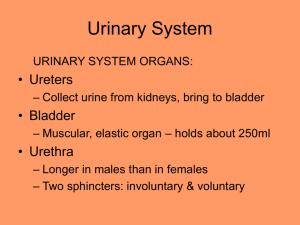
Renal system Learning objectives To outline the renal system; To describe the structure and function of nephron,processes of urine formation; To describe briefly the processes of urine formation; To describe the renin-angiotensin system; To describe the regulationofpotassium, calcium and pH. RENAL SYSTEM EXCRETION ~ removal of toxic waste productions of metabolism from the body WASTE ~ nitrogenous waste (urea & ammonia), CO2, bile pigment RENAL SYSTEM OSMOREGULATION ~ the process maintaining constant osmotic equilibrium between the internal & external environment of an organism Mammalian renal system I KIDNEY paired organs in abdominal cavity held firmly by peritoneum embedded in fat solid, dark red & bean shape below stomach renal artery vs renal vein Structure of kidney Mammalian renal system II URETERS narrow tubes passing urine from kidneys to bladder valves prevent back flow of urine stop bacteria from going into kidney Diaphragm Kidney Ureter Bladder Urethra Mammalian renal system III URINARY BLADDER muscular bag stores urine temporarily 300 cm3 of urine sensation of urination contraction of bladder + relaxation of sphincter muscle forces urine out Ureter Ureteral opening Urethra Urethral orifice Mammalian renal system IV URETHRA muscular tube carries ONLY URINE in female carries URINE & SEMEN in male A nephron unit FLOW OF GLOMERULAR FILTRATE Glomerulus Bowman’s space in Bowman’s capsule Descending limb of Henle’s loop Ascending limb of Henle’s loop Renal pelvis Proximal convoluted tubule Distal convoluted tubule Collecting duct NEPHRON 1,000,000 nephrons / kidney structural & functional units Cortical nephron ~ in cortex, short Loop of Henle, osmoregulation under NORMAL condition Juxtamedullary nephron ~ at junction of cortex & medulla, long Loop of Henle, osmoregulation when SHORT OF WATER Nephron Renal corouscle Glomerulus: knot of blood capillaries Bowman’s capsule Proximal convoluted tubule Descending limb of loop of Henle Ascending limb of loop of Henle Distal convoluted tubule Collecting duct Functions of kidney Excretion ~ remove nitrogenous waste i.e. urea, salts, water, heat, toxic substance Osmoregulation ~ controlling amount of water in body ~ maintain osmotic potential Urine Formation Pressure filtration (ultrafiltration) Reabsorption Tubular secretion Ultrafiltration Occur at Malpighian body Glomerular filtrate: all substances in blood except RBCs & plasma protein Blood pressure: Diameter of afferent arteriole > Diameter of efferent arteriole Glomerular filtrate rate 180l/ day Adaptation large area, great pressure, thin ,membrane Reabsorption 99% of the glomerular filtrate are reabsorbed matter reabsorbed: all glucose, amino acid mineral salts other useful substances SELECTIVE REABSORPTION Method of reabsorption diffusion active transport Sites of reabsorption Proximal convoluted tubule ~ major site of reabsorption (80%) ~ microvilli surface area ~ numerous mitochondria ~ surrounded by pertubular capillaries Sites of reabsorption Loop of Henle ~ conserve water in terrestrial mammal ~ creates & maintain an increasing osmotic gradient in the medulla ~ Na+ in medulla vigorous osmotic extraction of water from collecting ducts hypertonic urine Formation of hypertonic urine Sites of reabsorption Vasa recta ~ narrow capillaries situated close to loop of Henle ~ freely permeable to ions, urea & water ~ Counter current exchanger system Counter current exchange system Sites of reabsorption Distal convoluted tubule ~ fine control of salt, water & pH balance of the blood Collecting duct ~ water is extracted by osmosis conc. hypertonic urine Tubular secretion Takes place in distal convoluted tubule absorption of unnecessary: ammonia, potassium & drug from capillary network & secrete them into lumen of tubule Regulation of urine composition Anti-diuretic hormone(ADH) Aldosterone Renin-angiotensin system ADH ADH ADH Aldosterone Renin angiotensin system Potassium content most abundant intracellular ion reabsorbed by proximal convoluted tubule & loop of Henle, secreted by collecting ducts K secretion aldosterone secretion of K Calcium content Ca excitability of nerve & muscle cell membranes hypocalcemic tetany Ca cardiac arrthythmias most reabsorbed, no secretion pH level Metabolic reactions are highly sensitive to H+ Sources of H+ gain or loss Gain ~ from CO2, metabolism of protein etc, loss of CO3 2- in diarrhea & urine Loss ~ in vomitus & urine