Bacteria Notes
advertisement

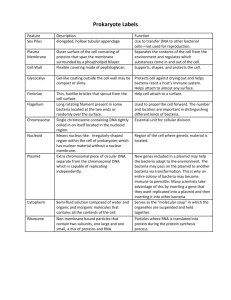
They Are Everywhere An introduction to bacteria Prokaryotes Prokaryote: Single-celled organism that lacks a true nucleus (also called bacteria) DNA is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane, have no membrane bound organelles. Cover almost every cm2 of earth! Size Matters Prokaryotes = 1-5 micrometers Eukaryotes = 10-100 micrometers Vs. Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells. One to Two *Until recently all prokaryotes were one kingdom, Monera Monera is now split into 2 kingdoms: Eubacteria, Archaebacteria Now three domains 1)Eubacteria/Bacteria 2)Archaea 3)Eukaryota/Eukarya Archaebacteria! A hot springs in Yellowstone National park! Archaeabacteria Lack peptidoglycan walls and have different membrane lipids than Eubacteria DNA sequences are closer to Eukaryotes than Bacteria Extremophiles – ‘phileo’ in Greek means love Extremophiles: – Live in extreme environments! Halophilic: salt loving Thermophilic: heat loving Methanogens – produce methane gas Live in the gut of mammals, sewage disposal plants and swamps Eubacteria Largest of prokaryote groups *Have cell walls that contain peptidoglycan (carbohydrate) Find everywhere on earth. Shapes Three Shapes 1) Bacilli 3) Spirilla (rod-shaped) (spiral or corkscrew) 2) Cocci (spherical) “Strep” throat Shapes Streptococci Streptobacilli Form chains or strings Staphylococci Staphylobacilli Form clumps like grapes Streptospirilla SSSS S Staphylospirilla Round = Cocci Rod shaped = Bacilli Spiral shaped = spirilla Ribosome Flagella Pili Capsule Cell wall Cell membrane DNA Plasmid Cytoplasm Plasmid – piece of DNA , plays role during conjugation Pili Help with conjugation – transferring of genetic material p.558, Stick to host’s cells Cytoplasm Contains DNA, Proteins and plasmid Capsule – Protects against drying out, chemicals and host’s white blood cells. Flagella: Movement Ribosomes- Making proteins Cell wall - Protects, gives cell shape Eubacteria–has peptidoglycan DNA - Carries the genetic material Cell membrane – Regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell Conjugation Pili – forming conjugation bridge Cell Walls Two Types of Eubacteria: – Gram-Positive Thick peptidoglycan walls Turn dark purple when stained – Gram-Negative Much thinner walls inside an outer lipid layer Appear pink or light red Energy Heterotrophs Parasitic – Cause diseases (pathogens) Saprophytic – Feed on dead tissues Decomposers Autotrophs Photoautotrophs: – Use light energy to convert CO2 and H2O to food (like plants) – Ex: cyanobacteria Chemoautotrophs: – Use chemical energy to convert CO2 and H2O to food Releasing Energy Obligate Aerobes: – Require constant supply of oxygen Obligate Anaerobes: – Do not require oxygen . . . It kills them Facultative Anaerobes: – Do not require oxygen, but can live with it – Ex: E. coli *Growth and Reproduction Some bacteria can divide every 20 minutes – If there was unlimited resources 1 bacteria could grow into a mass 4000 times the mass of earth in just 48 hours!!! Reproduction Binary fission 1) Binary Fission Binary Fission: – Asexual reproduction where organism replicates DNA and divides in half – Produces two identical daughter cells 2) Conjugation Conjugation: (“Sexual” reproduction) A type of sexual reproduction where organism exchange genetic information 3. Forming Endospores • Help survive unfavorable conditions. Anthrax spores Some are BAD and make us ill Streptococcus Strep throat Pneumonia Tetanus (lock jaw) Affects nervous system E. coli Some in our intestines … others are pathogens that can cause kidney failure Bacteria Can be bad … but can be good Make vitamins that we cannot make ourselves Decomposers *Help breakdown sewage treatment water Feel better with?? Nitrogen Fixation Converting nitrogen gas into a form plants can use (nitrates – NO3) – Plants use the nitrates to make proteins. For example Rhizobium living in the roots of legumes such as soybean plants. Other Uses Oil digestion/ Clean up of pollutants (Bioremediation) Are living: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Made up of cells Have DNA Grow and develop Use energy Homeostasis Reproduction Respond to stimuli Evolve/Show adaptations – resistant bacteria Show some type of organization – Flagella, pili, ribosomes, cell wall