Chapter 15 - Stress and Health
advertisement

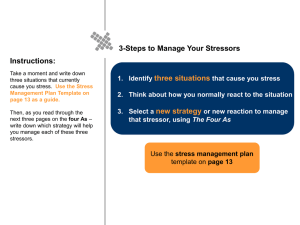
Advanced Psychology Ch. 15 Notes – Stress Mr. Slocomb Name:__________________________________ Period:_________ Section 1-Sources of Stress __________________- a person’s ________________ to his or her inability to cope with a certain tense ______ or situation. Components of Stress _________________- a stress-________________ event or situation Stress ____________________- the __________________ response to a stressor ____________________- stress that stems from acute anxiety or ________________ Eustress- __________________ stress, which results from _________________ strivings and challenges. Conflict Situations _________________ __________________- when a person must choose between two or more options that tend to result from opposing motives _____________________________ – choose between two attractive options _____________________________ – choose between two bad options _____________________________ – one option (yes or no) with good and bad either way _____________________________ – multiple options with good and bad for all Appraising a situation _____________________Appraisal – immediate ______________ of a situation – irrelevant, positive, negative _____________________ Appraisal – pick _____________ _______________ __________________________ stressors - an external form of a stressor that you are exposed to Life changes and stress – see first graphic, study on stressful events in life _____________________ - small annoyances that if isolated will not produce __________________ stress Section 2- Reactions to Stress Stress will be reacted to if __________________ and/or _________________ ____________________ vs. _________________ Varies by _______________ and ________________ _____________________– the bodies default response to a perceived threat or danger Autonomic Nervous System – controls this Sympathetic (speeds up) Parasympathetic – slows down __________________________________________ 1. _____________________ – first reaction to stressor. Resistance diminished 2. _____________________– if the body or individual adapts to the stressor(s), increased resistance occurs. Alarm reactions disappear. 3. _____________________– Long-continued exposure wears down body’s resistance; adaptation energy is exhausted. Alarm reaction signs reappear. Individual can eventually die. Emotional and Cognitive responses _____________________- a vague, generalized, apprehension or feelings of _____________________ _____________________- the irate reaction likely to result from _____________________ _____________________- the usual reaction when a stressor involves real or imagined danger Behavioral Reactions _____________________– behaviors such as using alcohol and drugs to _____________________ problems. _____________________– involves _________ ____________of problems, realistic appraisals, recognizing and modifying unhealthy responses Physical Reactions _____________________ - _____________________ Factors influencing reactions to stress Personality differences Type A vs. Type B personality Emotional Expressiveness Perceived Control over Stressors _____________________ Stress better than _____________________ _____________________- employees need to believe they _____________________in what is going on _____________________– What is perceived as real is real in its _____________________ Social Support _____________________ – concerned listening/affection _____________________– Interactive, sort out (Socratic Method) _____________________ – stressed person responds/solutions _____________________ – direct help (money, bed, car, etc…) Sections 3-Coping with Stress Psychological Coping Strategies _____________________- the interpretation of an event that helps determine its ________________________. _____________________ Coping Strategies _____________________- a coping mechanism in which a person decides that the event is not really a _______ _____________________ - a coping mechanism in which the person analyzes a situation from an ___________ detached viewpoint. _____________________ Coping Strategies _____________________to fix, deal with or _____________________a stressful situation (Adaptive Coping if positive, maladaptive coping if negative) _____________________ – ability to not give up -- Traits Control, Commitment, Challenge Controlling Stressful Situations _____________________ Controlling Exposure to Stressors Problem solving _____________________ situation head on/rational analysis Leads to __________________________________________ _____________________ Style _____________________ - people who see the circumstances they are in positively _____________________ - people who see the circumstances they are in negatively Seligman Baseball Players - analyzed post game comments, coded them optimists lived ______________ _____________________ - Control Physiological Responses to Stress _____________________- lying down comfortably and tensing and releasing the tension in each major muscle group in turn. Meditation- a focusing of _____________________ with the goal of clearing one’s mind and producing an ‘inner peace” _____________________- the process of learning to control bodily states by monitoring the states to be controlled. Humor/Exercise – helps regulate hormone release (______________ and ______________) – Fight or flight Support Groups and Professional Help _____________________ - Practicing speaking, playing golf, mock interviews Improving _____________________ Skills Section 4- Stress in Your Life _____________________- ability to take care of oneself and make one’s own decisions Choosing College - “_____________________” Peter Madison (1969) College students __________________________________________expectations initially Sources of change __________________________________________- friends force on another to _____________________ their basic assumptions and perhaps adopt new ideas and beliefs. _____________________- Focusing on goals, work harder through doubt; going through ________________ _____________________- combining old ideas with new ones and reorganizing feelings in order to renew one’s identity. Working - Variety of Challenges, Rewards in Working Work Satisfaction and Dissatisfaction 5 Major Sources of Work _____________________ 1. Resources – tools to do the job _____________________ 2. $$$ - includes income, benefits, _____________________ 3. _____________________ 4. Relations with _____________________ 5. _____________________ (conditions, commute, physical aspects) Changing _____________________ Retire then start new career Good economy = __________________________________________= more change Bad economy = __________________________________________= less change Career- a _____________________ in which a person works at least a _____________________. Comparable Worth _____________________- the concept that women and men (and all people) should receive _____________________for jobs calling for comparable skill and _____________________. People (consciously or unconsciously) compare their career to others Can be a source of great _____________________