math 4a chapter 10 powerpoint presentation trigonometry
advertisement

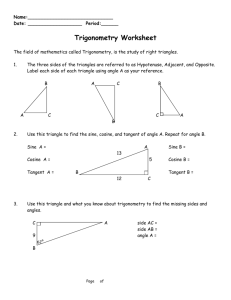
FUNDAMENTALS OF ALGEBRA 2A CHAPTER 10 POWERPOINT PRESENTATION TRIGONOMETRY TRIGONOMETRY LEARNING TARGETS • AFTER YOU COMPLETE THIS CHAPTER, YOU WILL BE ABLE TO: • DEFINE TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS • CHANGE MEDIAN MEASURE TO DEGREE MEASURE • DEFINE AND NAME TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS IN SPECIAL TRIANGLES • IDENTIFY GRAPHS OF SINE, COSINE, & TANGENT • USE THE LAW OF SINES AND COSINES TRIGONOMETRY RATIOS • Trigonometry: Comes from the Greek word, “trigonon” or triangle and “metron” to measure. The main part of trigonometry is the right triangle. There are several special names that define the ratios. • Cosine, Sine, and Tangent. • They also have reciprocals (or the opposite) Here is a chart of the ratios….. Here is a list of reciprocal ratios… Chapter Vocabulary • • • • • • • • Degree: 1/360 of a full circle – symbol = ⁰ Minute: 1/60 of a degree, so 1⁰ = 60’ Second: 1/60 of a minute, so 1’ = 60” Quadrant – four parts of a circle, using Roman Numerals and numbers counter-clockwise. Quadrant I = 0⁰ to 90⁰ Quadrant II = 90⁰ to 180⁰ Quadrant III = 180⁰ to 270⁰ Quadrant IV = 270⁰ to 360⁰ What does this look like? • Radians – the angle between two radii of a circle, which is cut off on the circumference by an arc equal in length to the radius. A 360⁰ Circle Special Triangles • 30 – 60 – 90 Triangle • 45 – 45 – 90 Triangle • There is a unique relationship to the sides in these triangles: Basic Identities • • • • Reciprocal – opposites Pythagorean – using Pythagorean Theorem Quotient – using division Cofunction – one ratio working with another Reciprocal Identities Pythagorean Identities Quotient Identities Cofunction Identities Other Identities The Unit Circle • In the unit circle – the radius is 1. The right triangle for each quadrant is determined by the reference angle, the angle with the initial side at 0⁰. Inverse Trigonometric Functions • A quick look at the graph for cosine, sine, and tangent shows that there is one x and y value. They can pass the vertical line test. The inverse or opposite function cannot. • Principal value: The value of a function in a restricted range. • Arcsin, Arccos, Arctan are the inverse functions. COSINE CURVE SINE CURVE TANGENT CURVE COFUNTCIONS AND COMPLEMENTARY ANGLES • COFUNCTIONS OF COMPLETMENTARY ANGLES ARE EQUAL. • COFUNTCION PAIRS: SOLVING THE TRIANGLE • Solving the triangle: the process to find the missing sides and angles. • Law of Sines: Law of Cosines – Arbitrary Triangles