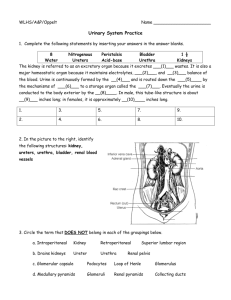
File
advertisement
THE URINARY SYSTEM PHYSIOLOGY 2 PHL-226 اعداد : دينا عالم عبد المقصود استاذ مشارك The Urinary System The urinary system is a group of organs that are responsible for excretion of excess fluid and other substances from blood stream in the form of urine. Organs of the Urinary system : Paired kidneys A ureter for each kidney Urinary bladder Urethra 2 THE KIDNEY Kidneys are retroperitoneal organs that is located in the superior lumbar region of the posterior abdominal wall The lateral surface of the kidney is convex The medial surface of the kidney is concave Hilum is cleft in the medial surface of the kidney where vessels, ureters and nerves enter and leave through it Adrenal gland lies superior to each kidney * * 3 4 Kidney has two regions: Cortex: outer It lies under the capsule and contains: a. Cortical tissue b. Renal columns which divide the medulla into “pyramids c. Nephron” Medulla: inner Darker, cone-shaped medullary or renal pyramids Parallel bundles of urine-collecting tubules 5 The human kidney has lobes Each lobes formed from renal pyramid and cortical tissue surrounding it There are 5-11 lobes per kidney Renal pelvis (=basin) It is the expanded, funnel shaped and superior part of ureter Branches to form two or three major calyces (plural of calyx ) Each of these divides again, to form minor calyces: collect urine from papillae of pyramids NB; Renal calyx(minor and major calyces and Renal pelvis are called (renal cavities) 6 Uriniferous tubule is the main structural and functional unit of the urinary system A uriniferous tubule is the main structural and functional unit of the urinary system Each kidney contains : 1- More than a million of uriniferous tubules are present in each kidney and act together to form the urine 2- The urine is formed by three main mechanisms: a. Glomerular filtration b. Tubular reabsorption c. Tubular secretion 3- A uriniferous tubule has two major parts: 1. A urine-forming nephron 2. A collecting duct which concentrates urine by removing water from it 7 Uriniferous tubule Uriniferous tubule (anatomical unit for forming urine) consists of Nephron which is formed of : Renal corpuscle (in cortex) which consists of: – Glomerulus (tuft of capillaries) – Glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule Tubular section that consists of : – Proximal convoluted tubule – Loop of Henle – Distal convoluted tubule Collecting duct 8 function of uriniferous tubule a. Glomerular filtration Fluid is squeezed out of the glomerular capillary bed b. Tubular reabsorption Most nutrients, water and essential ions are returned to the blood of the peritubular capillaries. c. Tubular secretion Moves additional undesirable molecules into tubule from blood of peritubular capillaries 9 Nephron Uriniferous tubule (anatomical unit for forming urine) Nephron Renal corpuscle (in cortex) Glomerulus (tuft of capillaries) Glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule Tubular section Proximal convoluted tubule Loop of Henle Distal convoluted tubule Collecting duct 1) Renal corpuscle: Present only in the renal cortex It consists of : Tuft of capillaries called glomerulus Surrounded by cup-shaped, hollow glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule 10 Classes of nephrons 1) Cortical nephrons 85% of all nephrons Almost entirely within cortex 2) Juxtamedullary nephrons Renal corpuscles near cortexmedulla junction 11 Glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule: Bowman‘ s capsule consists of two layers:1.Parietal layer of the capsule: which is the outer layer . 2.Visceral layer of capsule which has podocytes WHAT IS PODOCYTES? They are unusual branching epithelial cells They have foot processes with slit processes between them WHAT IS THE BOWMANS SPACE? It is the space between two layers of the 12 bowman‘s capsule GLOMERULAR FILTERATION BARRIER 1) The capillary endothelial cells which contain slits (fenestrations) FUNCTION: They restrict the passage of the largest elements such as blood cells and most protein 2) The basement membrane which is the main filtration barrier that FUNCTION: 1. it prevents any large molecules from being filtered. 2. it contain heparin sulphate proteoglycans which repels negatively charged protein such as albumin 3) Slit diaphragm ( filtration slits or processes ) between processes of podocytes which hold back large molecules and proteins while letting through small molecules such as water, ions, glucose, amino acids, and urea 13 Uriniferous tubule (anatomical unit for forming urine) Tubular section of the Nephron 1. the tubular section consists of Proximal convoluted tubule Loop of Henle Distal convoluted tubule Nephron Renal corpuscle (in cortex) Glomerulus (tuft of capillaries) Glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule Tubular section Proximal convoluted tubule Loop of Henle Distal convoluted tubule Collecting duct 2. The tubular section ends by joining collecting duct. FUNCTION : It is responsible for reabsorption and secretion of solutes 14 Uriniferous tubule (anatomical unit for forming urine) Proximal convoluted tubule Confined to renal cortex FUNCTION: Reabsorption of water, ions and solutes Nephron Renal corpuscle (in cortex) Glomerulus (tuft of capillaries Glomerular (Bowman’s) capsu Tubular section Proximal convoluted tubule Loop of Henle Distal convoluted tubule Collecting duct * 15 Uriniferous tubule (anatomical unit for forming urine) Nephron Loop of Henle 1. Confined to renal medulla 2. It consists of : Descending limb Ascending limb Renal corpuscle (in cortex) Glomerulus (tuft of capillaries) Glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule Tubular section Proximal convoluted tubule Loop of Henle Distal convoluted tubule Collecting duct 16 Uriniferous tubule (anatomical unit for forming urine) Nephron Renal corpuscle (in cortex) Glomerulus (tuft of capillaries) Glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule Tubular section Proximal convoluted tubule Loop of Henle Distal convoluted tubule Collecting duct Distal convoluted tubule It is confined to the renal cortex FUNCTION: It is responsible for selective secretion and reabsorption of ions 17 Uriniferous tubule (anatomical unit for forming urine) Nephron Renal corpuscle (in cortex) Glomerulus (tuft of capillaries) Glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule Tubular section Proximal convoluted tubule Loop of Henle Distal convoluted tubule Collecting duct Collecting Ducts Collecting Duct Each receives urine from several DCT of nephrons Run straight through cortex into the deep medulla 18 Uriniferous tubules 1. Nephron 2. Collecting ducts Collecting Ducts * At papilla of pyramid, collecting ducts join to form larger papillary ducts Empty into minor calices Role: conserve body 19 fluids The collecting ducts Role of ADH in maintaining the volume of urine: The most important role of ADH is to conserve body fluids. 1- When the body must conserve water, the posterior pituitary gland secretes ADH (antidiuretic hormone). 2- ADH increases the permeability of the collecting tubules and distal tubules to water so more water is reabsorbed into blood. 3- This decreases the total volume of urine. 4- Alcohol inhibits the release of ADH, so less water is reabsorbed producing copious amounts of dilute urine (can cause dehydration). 20 Vessels Afferent and efferent arterioles associated with glomerular capillaries Allows high pressure for forcing filtrate out of blood About 20% of renal plasma flow is filtered each minute (125 ml/min): this is the glomerular filtration rate (GFR), an important clinical measure of renal function This is about one liter every 8 minutes (only 1% ends up as urine) Peritubular capillaries arise from efferent arterioles Absorb solutes and water from tubule cells 21 (vascular supply of the kidney ) 1- Aorta gives off right and left renal arteries 2- Renal arteries divides into 5 segmental arteries as enters hilus of kidney 3- Segmental arteries branch into lobar arteries. 4- Lobar artery divide into interlobar arteries 5- Interlobars give rise arcuate artery at the junction between medulla and cortex 6- Arcuate arteries send interlobular arteries into cortex. 7Cortical interlobular arteries give rise to 22 glomerular arterioles Vasculature of the kidney The glomerular capillary bed is unusual in having arterioles going both to it and away from it (afferent and efferent arteriole), instead of a vein going away as most 23 24 (vessels, continued) The Vasa recta 1)The Vasa recta is a portion of the peritubular capillary system which enters the medulla where the solute concentration in the interstitium is high. 2) It acts with the loop of Henle to concentrate the urine by a complex mechanism of counter current exchange using urea. If the vasa recta did not exist, the high concentration of solutes in the medullary interstitium would be washed out. ____vasa recta 25 Juxtaglomerular apparatus Juxtaglomerular apparatus is formed of : 1) Mesangial cells 2) Macula densa cells:3) Juxtaglomerular cells (granular cells) FUNCTION : Regulation of blood pressure. 26 Juxtaglomerular apparatus 1) Mesangial cells:- that are located between glomerular capillaries. They are supportive cells. 2) Macula densa cells:- which line the wall of distal convoluted tubule facing the glomerular capillaries afferent and efferent arteriole FUNCTION: It act as chemoreceptors by monitor salts (Na Cl) concentration in the distal convoluted tubule. 27 Juxtaglomerular apparatus The macula densa cell response to the drop of blood pressure by 2 mechanisms: 1) It dilates the afferent arteriole of the glomeruli to increase the volume of blood and pressure inside the glomeruli 2) Releases prostaglandin from adrenal glands which stimulate the juxtaglomerular cells to release renin in the blood stream 28 Juxtaglomerular apparatus 3) Juxtaglomerular cells (granular cells) : – Juxtaglomerular cell is a modified smooth muscle cell Function : 1) They act as mechanooreceptor which monitor the change in blood pressure in the arteriole 2) They secrete renin in response to falling blood pressure in afferent arteriole. 29 Juxtaglomerular apparatus Juxtaglomerular cells secrete renin in response to : 1) A decrease in the blood pressure in afferent arteriole. 2) Signals from macula densa. 3) Sympathetic nervous system activity 30