Plant Hormones: Control of Growth & Flowering
advertisement

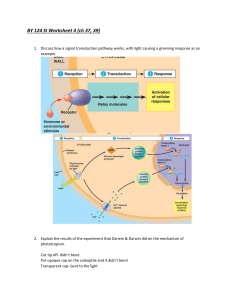
Plant Hormones: Control of Growth & Flowering DP Biology 2009 Plant Hormones Many aspects of plant function are controlled and regulated through the action of hormones. What hormones have we already discussed? Plant Hormones Many aspects of plant function are controlled and regulated through the action of hormones. Abscisic acid: closes guard cells Gibberellin: stimulates embryo growth and production of amylase. Plant Hormones Many aspects of plant function are controlled and regulated through the action of hormones. Abscisic acid: closes guard cells Gibberellin: stimulates embryo growth and production of amylase. Just one other one you need to know for IB … Auxin: stimulates stem & fruit growth, root formation, and phototropism. Other Plant Hormones (FYI) Brassinosteroids: growth of stem & pollen tubule, vascular tissue differentiation Cytokinins: work with auxin, promote growth & inhibit senescence Ethylenes: promotes fruit ripening and leaf abscission Jasmonates / Oligosaccharins / Salicylic Acid : stimulates protection against herbivores and/or pathogens Auxin & Plant Growth Auxin promotes the elongation of cells. (Not the formation of new cells … why?) Auxin & Plant Growth Auxin promotes the elongation of cells. Plant cell elongation is usually prevented by …? Auxin & Plant Growth Auxin promotes the elongation of cells. Plant cell elongation is usually prevented by the cell wall. Auxin & Plant Growth Auxin promotes the elongation of cells. Plant cell elongation is usually prevented by the cell wall. Auxin loosens the cell wall of plants, allowing the central vacuole to take up more water and stretch the cell by tugor pressure. Auxin & Plant Growth Auxin promotes the elongation of cells. Plant cell elongation is usually prevented by the cell wall. Auxin loosens the cell wall of plants, allowing the central vacuole to take up more water and stretch the cell by tugor pressure. The cell wall can be re-strengthened by the addition of more cellulose fibers. Auxin & Plant Growth How does auxin ‘loosen’ cell walls? Auxin increases the H+ concentration in cell wall (with what effect on pH?) Auxin & Plant Growth How does auxin ‘loosen’ cell walls? Auxin increases the H+ concentration in cell wall (lowering the pH) Auxin & Plant Growth How does auxin ‘loosen’ cell walls? Auxin increases the H+ concentration in cell wall (lowering the pH) H+ triggers proteins called expansions to break up hydrogen bonds between cellulose fibers, allowing them to slide past each other. See animation: http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/content/chp38/3802003 .html Auxin & Phototropism Tropisms are directional growth responses. Auxin mediates phototropism -- the growth of the stem towards light. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Auxin & Phototropism Photoreceptors in shoot tip absorb light. Detection of light causes proteins that redistribute auxin to be produced. Auxin is moved from the tip (where it is produced) down through the stem. photoreceptors QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Auxin & Phototropism Auxin is concentrated in the shady side of the stem, promoting greater elongation there. Uneven elongation promotes curving of stem towards light. See animation: http://trc.ucdavis.edu/ biosci10v/bis10v/media/ ch19/auxin_phototropism.html photoreceptors QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Other Tropisms (FYI) Can you think of any other plant tropisms? Other Tropisms (FYI) Geotropism: Growth towards or away from gravity. Thigmotropism: Growth towards touch. Time lapse videos for fun … http://plantsinmotion.bio.indiana.edu/plantmotion /movements/tropism/tropisms.html Control of Flowering Flowering in many plants is seasonal, and closely related to day-length. “Long-day” plants flower in the summer, whereas “Short-day” plants flower in the winter. Control of Flowering Flowering in many plants is seasonal, and closely related to day-length. “Long-day” plants flower in the summer, whereas “Short-day” plants flower in the autumn. Experiments have shown that it is not the length of the day that matter, but rather the length of the night. Control of Flowering Plants have a critical night length that determines the timing of flowering. What does this mean? Control of Flowering Plants have a critical night length that determines the timing of flowering. Long-day plants flower if the night is shorter than critical value. Short-day plants flower if night is longer than critical value. Control of Flowering How can we tell that it is night length that matters? Control of Flowering Experimenters interrupted dark and light periods with a flash of light or a brief period of dark. What do their results suggest? QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. D Control of Flowering A flash of light during night affects flowering Dark spell during day does not affect flowering. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. D Measuring “dark” Pigments in leaves called phytochromes absorb light. PR absorbs red light (660 nm) and converts to PFR PFR absorbs far-red light (730nm) and converts to PR PFR slowly degrades into PR QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Measuring “dark” Sunlight contains far more red light than far-red light, so while exposed to sunlight, most of phytochrome is in PFR state. At the end of the night, much of the PFR has converted back to PR. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. Measuring “dark” The amount of PFR in the leaves at the start of the day determines whether plants flower. How does the response differ in short- and longday plants? Flowering is inhibited by PFR in short-day plants Flowering is promoted by PFR in long-day plants Measuring “dark” Experiments support the role of PFR in determining timing of flowering. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. ‘Florigen’ discussion Phytochromes are found in leaves, but their effects are seen elsewhere in a plant. A single leaf is enough to control flowering in a large plant -- even several plants grafted together. ‘Florigen’ discussion Scientists have long suspected that a hormone is involved in controlling this response -- its even been given a name: florigen. Yet, despite decades of intense research, no one has been able to isolate and identify this hormone. ‘Florigen’ discussion Scientists have long suspected that a hormone is involved in controlling this response -- its even been given a name: florigen. Yet, despite decades of intense research, no one has been able to isolate and identify this hormone. ‘Florigen’ discussion Why would the theory persist, even though scientists have failed to identify the hormone? Does a failure to identify the hormone indicate a lack of evidence for its existence? ‘Florigen’ discussion Most scientists agree that a theory is not ‘scientific’ unless it is falsifiable. What does this mean? What do you think of the following quote from the 1970s: “"Flowering is a religion based on the totally unfounded dogma of florigen." ‘Florigen’ discussion What would a scientist have to do to show that florigen doesn’t exist? Can you think of any other non-falsifiable ‘theories’ in science? Recent Florigen Developments Recently a few molecules (proteins & RNAs) have been discovered that either are the elusive florigen -- or are otherwise involved in generating the signal.