Chapter 19 Auxin: the growth hormone Animal hormones

Chapter 19 Auxin : the growth hormone
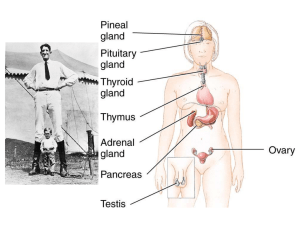
Animal hormones: are synthesized and secreted in one part of the body and are transferred to specific target sites in another part of the body via the blood stream. endocrine and paracrine hormones kinds: proteins, small peptides, amino acid derivatives, and steroids.
Plant hormones: have profound effects on development at vanishingly low concentration
(
1 mM).
kinds: auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, ethylene, abscisic acid brassinosteroids, jasmonic acid, salicylic acid, polypeptide systemin
Plant growth regulators: promoters and inhibitors
Auxin:
the first growth hormone to be discovered in plants
¤
Plant cell expansion
¤
Viability
¤
Stem elongation
¤
Apical dominance
¤
Root initiation
¤
Fruit development
¤
Oriented, tropic growth or phototropism
6 mm
Cell elongation
The active growth-promoting substance can diffuse into gelatin block;
Bioassay: a measurement of the effect of a known or suspected biological active substance on living material .
Auxin:
to increase or to grow
H
2
O + auxin the elongation of oat coleoptile sections
Natural vs. synthetic auxins
Active auxins: a negatively charged carboxyl group a fractional positive charge on aromatic ring
1930 indole herbicide
The definition of auxins:
the compounds with biological activities similar to those of IAA, including the ability to promote cell elongation in coleoptile and stem sections, cell division in callus cultures in the presence of cytokinins, formation of adventitious roots on detached leaves and stems, and other developmental phenomena associated with IAA action.
Adventitious roots: roots that arise from structures other than roots, such as stems or leaves.
Promote lateral and adventitious root formation
– even though auxin inhibit the primary root elongation
Lateral roots: above the elongation and root hair zone and originate from small groups of cells in the pericycle.
Adventitious roots: originating from non-root tissue via their cell division activity
Quantitative auxins:
¤
Bioassay
¤
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
¤
Mass spectrometry – gas chromatography: ~ pg
Auxin synthesis sites:
The shoot and root apical meristems , young leaves , developing (young) fruits and seeds (06?)
The margins of young leaves
Hydathodes: the special pores associated with vein endings at the leaf margin
A synthetic auxin-sensitive DR5 promoter + a GUS reporter a differentiating vascular strand
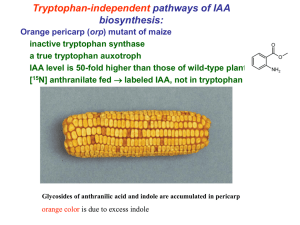
Tryptophan -dependent pathways of IAA biosynthesis: bacteria
Brassicaceae,
Poaceae,
Musaceae multiple pathways
important for development