Introduction to Digestion
advertisement

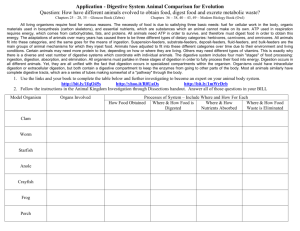
Do Now: After you eat your food, how does it get into the cells of your body? Aim: What is digestion and how does it take place in different organisms? I. Digestion - The process by which food is converted into substances that can be absorbed and assimilated by the body. A. Different types of digestion 1. Intracellular – when food particles are broken down within the cell. 2. Extracellular – when food particles are broken down outside the cell. Usually involves digestive enzymes. 3. Mechanical digestion – when food is physically broken down into smaller particles (increase the surface area) so it can be digested easier. 4. Chemical digestion – when food is broken down and turned into a different substance by the use of digestive enzymes. Example: Starch is broken down into disaccharides. B. Digestion in different organisms 1. One -cell (Unicellular) Organisms (ex: Ameba, paramecium) Ameba Paramecium a. Ingest food – Ameba ingests (takes it into the cell) food by the process of phagocytosis (surrounds and engulfs food). b. Food vacuole – temporarily stores food until it is digested by the lysosome which releases digestive enzymes to break down food. Intracellular Chemical Digestion!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! 2. Digestion in the Hydra a. Paralyzes its prey with stinging cells located in tentacles. b. Ingests food through mouth c. Both intracellular and extracellular digestion occurs within the hydra. d. Wastes are released through the mouth (2-way digestive tract). 3. Digestion in the Earthworm a. Ingests food through mouth b. Food is temporarily stored in the crop c. Food is mechanically broken down (grinded) by the gizzard. d. Nutrients are chemically digested and absorbed in the intestine. i. Typhlosole – fold in intestine that increases surface area for both digestion and absorption. e. Anus – where undigested material passes out of Earthworm. One – way digestive tract!!!!! 4. Digestion in the Grasshopper a. Food is ingested through mouth and sucked through the pharynx. b. Food passes through esophagus. c. Food is mechanically broken down by mouth parts (mandible) d. Food is temporarily stored in the crop. e. Has digestive glands (gastric caeca) outside of intestine to help in chemical digestion. f. Wastes temporarily stored in rectum and eventually egested through anus.