Knowledge Targets
advertisement

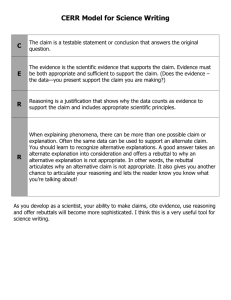
Deconstructing st 21 Century CSOs What Do We Expect Students to Learn? Title I School Improvement Coordinators Erin Sullivan & Gail Varney WVDE Title I Coordinators Session Goals Understand the change in the rigor and relevance of the revised CSOs. Participate in a process of deconstructing the CSOs that ensures teachers understand the depth of knowledge and what reasoning and skills students will be expected to master. Understand that the deconstructed CSOs form the basis of designing assessments and selecting appropriate instructional strategies. Three Ways to Improve Student Learning Raise the level of rigor in the content standards and objectives. Increase the skill and knowledge of teachers in teaching the content. Engage students in active learning designed around the standards for content, learning skills and technology tools. The Rigor/Relevance Framework K N T Evaluation O A Synthesis W X Analysis L O Application N E Understanding O D G M Awareness E Y 6 5 C Assimilation D Adaptation 4 3 2 1 A Acquisition 1 Knowledge 2 Apply in discipline B Application 3 Apply across disciplines APPLICATION MODEL 4 5 Apply to Apply to realreal world world predictable unpredictable situations situations RLA CSO Comparison – Grade 4 Previous Policy RLA.4.1.11 Summarize the author’s purpose (e.g., to persuade; to inform; to determine a specific viewpoint). Revised Policy RLA.O.4.1.09 Determine author’s purposes in literary and informational texts and use supporting material to justify author’s intent: To persuade To entertain To inform To determine a specific viewpoint Mathematics CSO Comparison - Grade 3 Previous Policy MA.3.1.6 Compare and order fractions with like and unlike denominators using concrete models. Revised Policy M.O.3.1.6 Create concrete models and pictorial representations to • compare and order fractions with like and unlike denominators, • add and subtract fractions with like denominators, and verify results. What is Depth of Knowledge? The degree of depth or complexity of knowledge reflected in the content standards and assessments How deeply a student needs to understand the content for a given response/assessment Depth of Knowledge Levels Level 1: Recall Recall, recognition; skill, behavior or sequence of behaviors learned through practice and easily performed Level 2: Skill/Concept Engagement of some mental processing beyond recalling; the use of information or conceptual knowledge; requires making some decisions regarding how to approach a question or problem Level 3: Strategic Thinking More sophisticated reasoning and analysis; deep understanding; students are required to solve problems & draw conclusions Level 4: Extended Thinking Requires integration of knowledge from multiple sources and ability to represent knowledge in a variety of ways; usually requires work over an extended period of time Understanding Depth of Knowledge DOK is about intended outcome, not difficulty. DOK is a reference to the complexity of mental processing that must occur to answer a question, perform a task, or generate a product. Understanding Depth of Knowledge Words like explain or analyze have to be considered in context. “Explain to me where you live” does not raise the DOK of a simple rote response. Even if the student has to use addresses or landmarks, the student is doing nothing more than recalling and reciting. Copyright © 2007 Mississippi Department of Education Understanding Depth of Knowledge Difficulty is a reference to how many students answer a question correctly: How many of you know the definition of exaggerate? DOK 1 - recall If all of you know the definition, this question is an easy question. How many of you know the definition of prescient? DOK 1 - recall If most of you do not know the definition, this question is a difficult question. Copyright © 2007 Mississippi Department of Education Activity: Determining DOK Level DOK ? Describe three characteristics of metamorphic rocks DOK ? Describe the difference between metamorphic and igneous rocks. DOK ? Describe a model that you might use to represent the relationships that exist within the rock cycle. Practice Activity: Sample One Locate and interpret key information in illustrations, titles, chapter headings, glossaries and maps to answer questions. Practice Activity: Sample Two Solve one-step linear equations and inequalities with one variable, interpret the solution or solutions in the context from which they arose, and verify the reasonableness of the results. Practice Activity: Sample Three Design a statistical experiment to study a problem and communicate the outcomes. No longer will teachers be able to “check off” CSOs as being “covered” in one class period. Where do we begin? Deconstructing the Standards is… …a systematic process to identify embedded learning targets in standards and objectives so that nothing essential is missed during instruction. Learning Targets What students should know, understand and be able to do to master the standards/objectives We Need Clear Targets to. . . Correctly identify what students know and don’t know Select appropriate assessments Plan effective instruction Keep track of student learning target by target or standard by standard Have students self-assess or set goals likely to help them learn more Types of Learning Targets Knowledge knowing and understanding facts and concepts learned outright or via reference Reasoning mental processes we want students to engage in USING knowledge to solve problems Performance Skills process is most important Products using knowledge, reasoning, and skills to create a product Product Objective Product Performance Skill Reasoning Knowledge Performance Skill Objective Performance Skill Reasoning Knowledge Reasoning Objective Reasoning Knowledge Knowledge Objective Knowledge Examples: Knowledge Targets Identify sight words Identify similes and metaphors Know defining characteristics of various literary genres Count and group concrete manipulatives by ones, tens, and hundreds to 1,000 Examples: Reasoning Targets Make a prediction based on evidence Distinguish between fact and opinion Evaluate information from a variety of resources Classify and compare triangles by sides and angles Examples: Performance/Skill Targets Read aloud with fluency and expression Use self-correction strategies Use inductive reasoning to find and justify the laws of exponents with numeric bases Model, identify and describe square, prime and composite numbers Examples: Product Targets Produce a grammatically correct sentence Develop a proper paragraph form in a written composition Compose a written composition using the five-step writing process Create a design with more than one line of symmetry Deconstruction Steps Choose a standard/objective for which the embedded learning might not be consistently identified. Identify its ultimate type: knowledge, reasoning, performance skill, or product. Ask four questions: What knowledge do students need ? What reasoning proficiencies (if any) do students need? What performance skills (if any) do students need? What products (if any) do students need to practice? Step One Standard/Objective: Step Two Type: Knowledge Reasoning Performance Skill Product Learning Targets What are the knowledge, reasoning, skill or product targets underpinning this objective? Step Three Knowledge Targets What must students know to master this standard? Reasoning Targets Performance Skill Targets How are students using knowledge to solve a problem, make a decision, form a plan, etc.? What must students be able to do ? How are they using knowledge and reasoning to perform a task? Product Targets What are students asked to produce or create? Activity: Learning Target Verb Sort Categorize verbs under correct learning target headings: • • • • Knowledge Reasoning Performance Skill Product Knowledge Reasoning Performance Product Explain Predict Observe Design Understand Infer Perform Produce Describe Classify Do Make Identify Compare Conduct Write Define Summarize Speak Draw Recall Analyze Operate Represent Recognize Evaluate Investigate Display Select Generalize Collect Model Tips for Deconstructing the CSOs Analyze the wording of the standard/objective to determine key concepts and key skills • • • Read through indicators Circle verbs to identify key skills Underline nouns and noun phrases to identify key concepts Example M.O. 3.1.14: Create grade-appropriate real-world problems involving any of the four operations using multiple strategies, explain the reasoning used, and justify the procedures selected when presenting solutions. How Many Types of Learning Targets? EXAMPLE 1: 8th Grade Reading/L.A., RLA.O.8.1.5 Use pre-reading and comprehension strategies (e.g. generating questions and previewing, activating and evaluating prior knowledge and scanning or skimming texts) to critically analyze and evaluate the comparison of literary and informational texts for • • • Making judgments Hypothesizing Making complex or abstract summaries How Many Types of Learning Targets? EXAMPLE 2: Grade 3 Mathematics, M.O.3.5.1 Collect and organize grade-appropriate real-world data from observation, surveys, and experiments, and identify and construct appropriate ways to display data. Activity Let’s deconstruct one together! Standard/Objective: RLA.O.4.1.9 Determine the author's purpose in literary and informational text and use supporting material to justify the author’s intent to persuade, entertain, inform and determine a specific viewpoint. Type: Knowledge Reasoning Performance Skill Product Learning Targets What are the knowledge, reasoning, skill or product targets underpinning this objective? Knowledge Targets Reasoning Targets Performance Skill Targets What must students know? How are students using knowledge to solve a problem, make a decision, etc.? What must students be able to do? How are they using knowledge and reasoning to perform a task? Product Targets What are students asked to produce or create? Standard/Objective: RLA.O.4.1.9 Determine the author's purpose in literary and informational text and use supporting material to justify the author’s intent to persuade, entertain, inform and determine a specific viewpoint. Type: Knowledge Reasoning X Performance Skill Product Learning Targets What are the knowledge, reasoning, skill or product targets underpinning this objective? Knowledge Target Reasoning Targets Performance Skill Targets Identify main idea Identify supporting details. Understand the meaning of persuade, entertain, & inform. Identify the 2 types of writing (informational & narrative) Understand why authors write. Understand the concept of compare/contrast. Understand summarization techniques. Compare and contrast two types of reading genres Draw a conclusion about author’s purpose by identifying words in text to justify the intent. Draw a conclusion about author’s pt. of view based on key words in text. Use supporting materials to justify the author’s purpose. Product Targets Your Turn to Deconstruct Divide into teams. 2. Choose one standard/objective that everyone in the group will tackle. 3. Each group deconstructs the chosen standard/objective. 4. Groups compare learning targets and come to consensus. 1. Choose a CSO to Practice Deconstructing Estimate, measure, compare, order and draw lengths of real objects in parts of an inch up to 1/8 of an inch and millimeters. (M.O.5.4.1) write to persuade using order of importance, classifying differences and similarities, classifying advantages and disadvantages. (RLA.O.4.2.6) use examples, and details in practical texts to make inferences and logical predictions about outcomes of procedures in such texts. (RLA.O.7.1.10) QUESTIONS?????