High Reliability Organizations (HROs)
and High Performance
Karlene H. Roberts
Haas School of Business
University of California, Berkeley
karlene@haas.berkeley.edu
510.642.4700 (fax)
December 29, 2001 - As the sun rises on the deck of USS John C. Stennis (CVN 74), the ship is readied for flight operations. Stennis and her embarked Carrier Air
Wing Nine (CVW-9) are supporting Operation Enduring Freedom. U.S. Navy photo by Photographer's Mate 3rd Class Jayme Pastoric.
For internal use only / © Siemens AG 2010. All rights reserved.
Page 3
Siemens Leadership Excellence
The Arrow
General environmental
conditions
Government /
Regulators
Company
Management
Operational
Staff
Work
Actions
Incident
What is a High Reliability
Organization (HRO) ?
An organization
– Conducting relatively error free
operations
– Over a long period of time
– Making consistently good decisions
resulting in
– High quality and reliability operations
HRO and Fast Execution
It is our contention that
reliability enhancement is
fast execution
enhancement
What HRO theory does for you
Provides a common language
– Recognizes principles and practices shared by
high reliability firms
– Permits you to communicate lessons learned with
other High Reliability Organizations
– Enables executives to share HRO concepts with
managers and workers who will develop detailed
plans
– Changes attitudes about reporting important
information
– Establishes and supports a safety culture
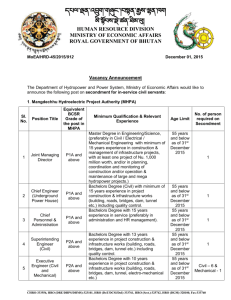
Naval Aviation Class A
Flight Mishap Rate
776 aircraft
destroyed in
1954
24 aircraft
destroyed in
FY03all in flight
mishaps
FY50-03
60
50
40
30
20
10
Angled Decks
Aviation Safety Center
Naval Aviation Maintenance Program
RAG (FRS) Concept Initiated
NATOPS Program
Squadron Safety Program
System Safety Aircraft Design
CRM
Aircrew reviews
ORM
Safety culture
96-2003
01
Fiscal Year
95
80
65
50
0
Nuclear Energy Institute Data
1985-2008
Rx Trips/
Scrams
Cost (¢/kwh)
Significant
Events/Unit
Capacity Factor
(% up)
An HRO must sustain a “mindful
infrastructure” which
1. Observes and tracks small failures and
anomalies
2. Resists oversimplification
3. Remains sensitive to operations
4. Maintains capabilities for resilience
5. Looks to expertise not rank to inform decisions
An HRO must sustain a “mindful
infrastructure” which
1. Observes and tracks small failures and
anomalies
2. Resists oversimplification
Principles of
anticipation
3. Remains sensitive to operations
4. Maintains capabilities for resilience
Principles of
containment
5. Looks to expertise not rank to inform decisions
1) Observe and track small failures and
anomalies
• Worry chronically about errors.
• Assume each day is a bad day.
• Difficult to do.
• “Collective bonds among suspicious
people.”
2) Resist oversimplification
• All organizations must ignore many
things.
• Doing so may force them to ignore key
sources of problems.
• Restrain temptations to simplify.
• Through checks and balances,
adversarial reviews, and multiple
perspectives.
3) Remain sensitive to operations
• Pay close attention to operations.
• Everyone values organizing to maintain
situational awareness.
• Use resources so people can see and
comprehend what is happening.
4) Maintain capabilities for resilience
• Anticipate trouble spots.
• Capability to improvise.
• Improve capacity to
– Do quick studies
– Develop swift trust
– Engage in just‐in‐time learning
5) Look to expertise not rank to inform
decisions
• Let decisions “migrate” to those with
expertise to make them.
• Avoid rigid hierarchies.
Businesses Targeting High Reliability
• Commercial Aviation (e.g. United Airlines)
• Commercial Banking (e.q. S.W.I.F.T.)
• Healthcare (e.g. Loma Linda Hospital, Totally Kids,
Kaiser Permanente, AHRQ hospital consortium)
• Nuclear Power (e.g. Diablo Canyon Power Plant,
INPO)
• Commercial Maritime
• Petroleum and chemical Industries (e.g. Chevron,
Shell, Gard Services)
Government Agencies Targeting High
Reliability
• US Naval Carrier Aviation
• US Navy Submarine Service (e.g., Admiral Rickover)
• US Department of Energy Laboratories
• Community Emergency Services (U.S. Forest
Service, Orange County California Fire Authority, San
Bernardino County and City Fire)
• Manned Space Flight (Columbia Accident
Investigation Board)
• Deep Underground Science and Engineering
Laboratory - DUSEL (under design)
Non-HROs
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Focus on success
Underdeveloped cognitive infrastructure
Focus on efficiency
Inefficient learning (episodic)
Lack of diversity (focused conformity)
Information & communications filtering
Reject or excuse early warning signs of
quality degradation
Source: Weick and Sutcliffe
Characteristics of a Non-HRO
•
•
•
•
•
Attend meetings and solve nothing
Catch airplanes and miss ‘connections’
Conduct briefings and persuade no one
Evaluate proposals and miss the winners
Meet deadlines for projects on which the
plugs have been (or should be) pulled
• Organizations in which people shuffle
papers and lose a few
Source: Weick and Sutcliffe
Is your organization an HRO?
Is your organization an HRO?
• How do you get there?
• How do you stay there?
HRO is not a one time change like adopting
a currency or language, it is a way of
conducting business and a continual effort.
HRO – High Reliability
Organizations
Statoil Experience
Siemens 20 May 2010
Why the HRO initiative ?
• Statfjord field –
Statfjord B ,A and C
Statoil’s experience
• The HRO journey startet with
inviting the PSA and OLF together
with Statoil Managers
• HRO Workshop at University of
California, Berkeley
The Norwegian Oil Industry Association
Statoil’s HRO experience
• What happened when back
in business and introducing
HRO?
− Great enthusiasm in
the group
− Realized that the
process needed
maturation and time
− Not the great buy-in,
but not rejection either!
Gjøa Development - topside facility on the move
Statoil
What we do – and how we do it
•A values based performance culture
•Firm commitment to health, safety and environment (HSE)
•Stringent ethical requirements and a code of conduct which promotes
personal integrity
Is Statoil a high or low reliability organization?
HRO’s
Crisis Management Preparedness
Elementary versus advanced Denial
HRO – High Reliability Organizations
• Leadership training
• Good structures
• Value based organisation
• Emergency preparedness
LRO’s
• Consensus culture
LRO- Low Reliability Organizations
Number of Denials
• Focus on success
• Expertise focus
Culture/HRO step-change
• Cultural / HRO step-change is not
triggered by magic bullet or directive
Rather
• Culture / HRO is changed by series
of small steps taken by the leading
members of the organization at all
levels
• Leadership is standing up and
leading the way
• Changing the way business is
conducted requires people at all
levels to lead by personal example
Recommendations
• Start at the Top Management
• Use time to implement
• Training, training, training and
discussions
• External inspiration
• Establish network / forum meetings
“Troll A Platform shaft
Thank you
HRO – Statoil Experience
Ståle Tungesvik
Senior Vice President, Reserve and Business Development
Exploration and Production Norway
sttu@statoil.com
www.statoil.com
An HRO must sustain a “mindful
infrastructure” which
1. Observes and tracks small failures and
anomalies
2. Resists oversimplification
3. Remains sensitive to operations
4. Maintains capabilities for resilience
5. Looks to expertise not rank to inform decisions
Exercise on 5 HRO leadership
principles