Sensation and Perception Powerpoint
advertisement

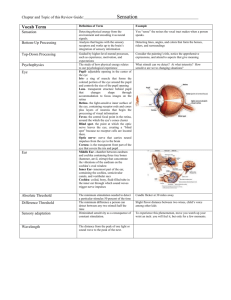
Sensation and Perception Sensation and Perception Sensation- How are sensory receptors and nervous system receive information (stimulus) from the environment Perception- The process of organizing and interpreting sensory information to recognize meaningful objects and events TYPES of PROCESSING Bottom Up Processing You notice something (your senses) and then you focus on it, access your memory that is related to it and fully process. Start by examining small details and putting them into a bigger picture Top Down Processing Opposite. See the total picture first, then your senses see the smaller details Signal Detection Theory How and when we detect the presence of a faint stimulus amid background stimulation (noise) Based on experience, fatigue level, expectations Subliminal Stimulation Selective attention Below your level of awareness Focus of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus, even when there are loud distractions all around Cocktail Party Effect The ability to listen to one person among many people talking Types of Thresholds Absolute Threshold The minimum amount of stimulation for an organism to detect stimuli 50% of the time Difference Threshold EX: When kids focusing on tv, they can’t always hear parents on the fist few attempts. However if the kids hear something that is more interesting than what they are viewing, they will “magically “ hear it, (like who wants Ice cream?) The minimum difference that a person can detect between2 stimulus required for detection 50% of the time EX: HD vs SD TV options Sensation Threshold- 2 stimulus must be different by a constant minimum percentage Sensory Adaptation You eat something hot or spicy, at first it is overwhelming but then it doesn’t feel as strong Weber’s law To perceive a difference between 2 stimuli they must differ by a constant percentage, not a constant amount Quarters shoes and envelopes example Vision WAVELENGTHS-One peak of one light wave to the next peak Hue- color- Short and long wavelengths change the hue (color) we see The rainbow displays the color hues in order from longest light waves to shortest waves. Roy.G.Biv All of the colorwaves together = white light (sunlight) Short wavelengths= high frequency, bluish colors, and high pitched sounds Long wavelengths= low frequency, reddish colors, and low pitched sounds Light wavelengths that are LONGER than visible light are infrared waves, microwaves, radio waves. We can’t see these. Intensity- correlates with the brightness of the colors we see The higher the wave the more intense (bright) the color is Saturation- by seeing differences in purity of light waves, we can see different shades of color. How deep the color looks. The Eye Vision- The Process STEP ONE: Gathering Light- Light reflects off of objects and is gathered by the eye. How we see color depends on light intensity (how much energy the light contains) and light wavelength (which affects the hue). STEP TWO: Within the Eye- Light enters through our cornea (our protective covering that helps focus light). Dialate- The pupil acts like a camera-is opened and closed by the muscles (iris). Opens to let light in and closes when less light is needed. Accommodation- The process of light entering through the pupil and being focused by the curved lens. Our eyes ability to focus, change size, and change depending on what we look at. Lens- changes shape to focus images onto the retina. It is a flipped image (your brain translates it correctly) Retina- Contains sensory receptors Optic Nerve- passes information from the eye to the brain STEP THREE: how light we sense is turned into the ability of our brain to perceive it Transduction- the transfer of one form of energy to another Light energy is transformed into electrical or neural energy that our brain interprets as light Light activates lights in retina. Cones- first layer of cells activated by and detect color, daylight, and well lit conditions. concentrated close to the retina. Rods- cells that are activated by and detect black, white, gray, twilight and low light. We have more Rods (120 million) than Cones (6-7million) and they are scattered. Blind spot- the area where we have no cones/rods Fovea- Center of the retina with the most cones. If enough Cones/Rods are activated-Bi-polar cells (which transmit messages to the ganglion cells) the next layer is activated (the ganglion cells). These cells send impulses to the LGN (lateral geniculate nucleus- a region in the thalamus). STEP FOUR: In the brain LGN sends to various lobes. The visual cortex of the brain receives these impulses. Transduction Order is Rods/Cones to Bipolar to Ganglion to Optic Nerve. Sends info to thalamus- area called lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN). Then sent to cerebral cortexes. Where the optic nerves cross is called the optic chiasm. Trichromatic Theory vs Opponent Processing Theory Trichromatic Theory: Opponent Processing Theory: Three types of cones: The sensory receptors come in pairs. Red Red/Green Blue Yellow/Blue Green Black/White These three types of cones can make millions of combinations of colors. If one color is stimulated, the other is inhibited. Does not explain afterimages or color blindness well. Vision Complications Myopia- Near sighted- nearby objects are seen more clearly than distant ones Hyperopia- faraway objects are seen more clearly than closer ones Hearing The height of the wave gives us the amplitude of the sound. The frequency of the wave gives us the pitch if the sound. Place Theory Different hairs vibrate in the cochlea when they hear different pitches. So some hairs vibrate when they hear high and other vibrate when they hear low pitches. The Ear Transduction in the ear Sound waves hit the eardrum then anvil then hammer then stirrup then oval window. Everything is just vibrating. Then the cochlea vibrates. The cochlea is lined with mucus called basilar membrane. In basilar membrane there are hair cells. When hair cells vibrate they turn vibrations into neural impulses which are called organ of Corti. Sent then to thalamus up auditory nerve. Deafness Conduction Deafness Something goes wrong with the sound and the vibration on the way to the cochlea. Nerve (sensorineural) Deafness The hair cells in the cochlea get damaged. Loud noises can cause this type of deafness. You can replace the bones or get NO WAY to replace the hairs. a hearing aid to help. Cochlea implant is possible. Optical Illusions Aoccdrnig to rscheearch at Cmabrigde Uinervtisy, it deosn't mttaer in waht oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoatnt tihng is taht the frist and lsat ltteer be at the rghit pclae. The rset can be a toatl mses and youcan sitll raed it wouthit a porbelm. Tihs is bcuseae the huamn mnid deos not raed ervey lteter by istlef, but the wrod as a wlohe. *This was not a real study and it is not always accurate!* Tricks Of The Brain Awareness Test https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ahg6qcgoa y4 Eye Hallucination videos https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tVgOLWVY ytM https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IWk5NkxQF8 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QTC0F3gJhQ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hrhGTR54 E5k https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=I8Bwzkz50 BI After Images http://izismile.com/2011/11/11/mind_blowing _afterimages_optical_illusions_3_pics_11_gifs2.html Brain Perception http://luxemodo.com/best-opticalillusions/ http://brainden.com/best-illusions.htm http://illusionoftheyear.com/cat/top10-finalists/2015/ Each year has different illusions http://channel.nationalgeographic.com /brain-games/videos/einstein-andmonroe/ Brain Games Television Show http://channel.nationalgeographic.com /brain-games/ http://www.dailymotion.com/video/xq 1rfl_national-geographic-test-yourbrain-episode-2-perception_shortfilms 45 minute show with many illusions Resources Mr. Duez- powerpoints and videos References This powerpoint presentation was adapted using information from the Barron’s AP Psychology 5th edition prep book. Sensation and Perception Crash Course Psychology Sensation and Perception Discovering Psychology Sensation and Perception Weseley, Allyson, Robert McEntarffer, and Robert McEntarffer. AP® Psychology. Hauppauge, N.Y.: Barron's Educational Series, 2014. Print. Fineburg, A., & Myers, D. (2010). Myers' Psychology for AP*: Teacher's edition (Teacher's ed.). New York: Worth /BFW.