Polymer Analysis – TEM, SEM, GPC
advertisement

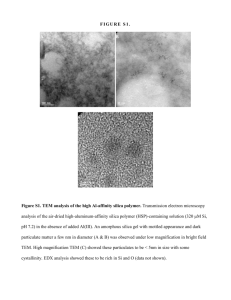
Polymer Analyses GPC, TEM, SEM Speaker : 王睿詡 Date : 2009/11/23 Outline • GPC (Gel Permeation Chromatography) • TEM (Transmission Electron Microscopy) • SEM (Scattering Electron Microscopy) GPC (Gel Permeation Chromatography, Size Exclusion Chromatography) A Kind of LC Mechanisms LC Separation Mechanisms Gel-Permeation Chromatography is a mechanical sorting of molecules based on the size of the molecules in solution. Small molecules are able to permeate more pores and are, therefore, retained longer than large molecules. Ref. : Rubinson and Rubinson, Contemporary Instrumental Analysis, Prentice Hall Publishing. Structural Picture Filter (ca 0.5 um) GPC Columns Pump Injector Loop To Waste Concentration Detector To Waste Waste Optional Detector #2 e.g Light Scattering Optional Detector #1 e.g. Viscosity Flow Voids: Uniform Diameter D helps minimize voids Pore: Size is given by the correlation length x x D = 1 - 50 mm Column of GPC Hydrodynamic radius (Stoke’s radius) K = cS /cM = (Ve - Vo)/Vi, since Vt = Vi + Vo + VG (Vi is the volume of solvent held in its pores) (Vg is the volume occupied by the solid matrix of the gel) (Vo is the free volume outside the gel particles.) K is distribution coefficient, we assume that VG ≈ 0 • • • • • Both are normally values between 0 and 1 Molecules that are too big to penetrate any of the pores elute in Vo and give K = 0 Molecules that are small enough to penetrate all of the pores elute in Vi + Vo and give K = 1 Between 0 and 1, larger molecules give smaller K values. If a molecule gives a K larger than 1, it is likely interacting with the gel beads themselves (adsorption). Retention Time vs. Molecular Weight Calibration Curve of GPC Common Detectors UV – one of most common Fluorescence – much greater sensitivity than UV Refractive Index – widely used general detector Electrochemical – based on amperometry, polarography, coulometry, or conductometry. High sensitivity, wide applicability range Mass Spectrometry – becoming increasingly used since interfacing problems figured out. Expensive. GPC Analysis Cheng-Jyun Huang and Feng-Chih Chang* Macromolecules 2008, 41, 7041-7052 GPC Analysis Chih-Feng Huanga, Hsin-Fang Leea, Shiao-Wei Kuoa, Hongyao Xua,b, Feng-Chih Changa,* Polymer 45 (2004) 2261–2269 GPC Analysis Chih-Feng Huang, Shiao-Wei Kuo, Hsin-Fang Lee, Feng-Chih Chang* Polymer 46 (2005) 1561–1565 TEM (Transmission Electron Microscopy) SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) Size !! 肉眼可見物體的範圍:~10-3m 光學顯微鏡(OM)可見的範 圍:~10-6m 掃描式電子顯微鏡(SEM)可 見的範圍: ~10-8 m (~10 nm) 穿透式電子顯微鏡(TEM)可 見的範圍: ~10-10 m (~0.1 nm) 光學顯微鏡 掃瞄式電鏡 穿透式電鏡 光源 可見光 電子槍 電子槍 透鏡 玻璃透鏡 電磁透鏡 電磁透鏡 放大倍率 1000~2000倍 10萬倍 100萬倍 解析度 0.2μm 1~10nm 0.1nm~ 真空環境 不需要 需要 需要 景深 0.1~5 μm 0.1mm 500 μm 影像色彩 真實色彩 黑白 黑白 成分分析 無 可 可 樣品 大 大 薄,小 金屬鍍膜 不需 需 不需 影像 表面或穿透影像 表面影像 穿透影像 TEM (Transmission Electron Microscopy) From 交通大學貴儀中心 TEM (Transmission Electron Microscopy) When E0-ΔE values become smaller, the Images become darker; When E0-ΔE values become bigger, the Images become lighter. http://www.jeol.com/tem/jem2100f.html Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) From 交通大學貴儀中心 Structural Image of SEM http://cem.ess.nthu.edu.tw/K12/Article.asp?ColId=7806A63102F19 Principle of Imaging 0~50 ev EDX(S) and WDX(S) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wavelength_dispersive_X-ray_spectroscopy Images are Different Between in TEM and SEM SEM Image OM Image TEM Image Material Science Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 688 Self-organization Morphology Solution state Bulk state N : polymerization index χ: Flory-Huggins interaction parameter ƒ A : volume fraction of block A in the block copolymer Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 688 TEM (Transmission Electron Microscopy) Ref : Wan-Chun Chen,† Shiao-Wei Kuo,*,‡ U-Ser Jeng,§ and Feng-Chih Chang*,† Macromolecules 2008, 41, 1401-1410 TEM (Transmission Electron Microscopy) Ref : Shiao-Wei Kuo a,*, Pao-Hsaing Tung b, Feng-Chih Chang b European Polymer Journal 45 (2009) TEM (Transmission Electron Microscopy) Ref : Chu-Hua Lu,† Chih-Feng Huang,† Shiao-Wei Kuo,‡ and Feng-Chih Chang*,† Macromolecules 2009, 42, 1067-1078 TEM (Transmission Electron Microscopy) Ref : Yuung-Ching Sheen a, Chu-Hua Lu a, Chih-Feng Huang a, Shiao-Wei Kuo b, Feng-Chih Chang a,* Polymer 49 (2008) 4017–4024 Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Y.-C. Yen et al. Polymer 49 (2008) 3625–3628 SHIH-CHI CHAN,1 SHIAO-WEI KUO,1 HWOSHUENN SHE,2 HO-MAY LIN,1 HSIN-FANG LEE,1 FENG-CHIH CHANG1 Journal of Polymer Science: Part A: Polymer Chemistry, Vol. 45, 125–135 (2007) Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Pao-Hsaing Tung, Shiao-Wei Kuo,*Shih-Chien Chan, Chih-Hao Hsu, Chih-Feng Wang, Feng-Chih Chang* Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2007, 208, 1823–1831 Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Chih-Feng Wang,1 Shih-Feng Chiou,2 Fu-Hsiang Ko,3 Cheng-Tung Chou,2 Han-Ching Lin,1 Chih-Feng Huang,1 Feng-Chih Chang*1; Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 333–337 Conclusion • Micro-Structural Analysis – TEM, SEM • Molecular Weight Determination - GPC Thank You for Your Attention