4. Notes-Reflection
advertisement

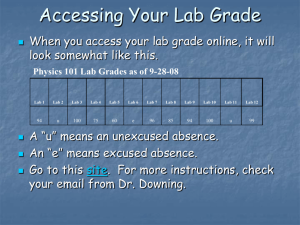
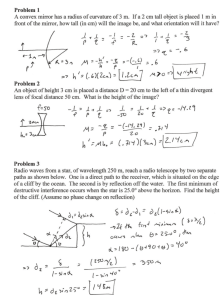
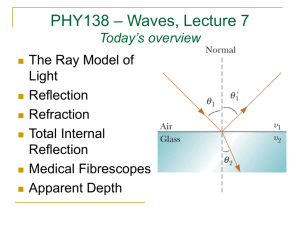
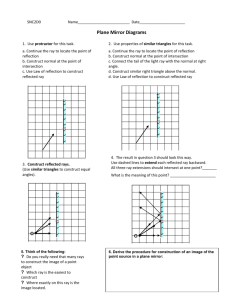
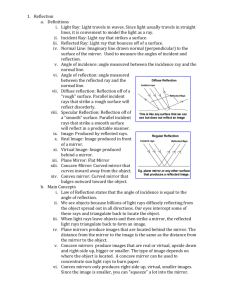
REFLECTION Plane (flat) mirrors LIGHT TRAVELS IN STRAIGHT LINES HOW LIGHT BEHAVES…. When light passes from one medium to another it may be reflected, refracted or both. Mirror: ALL the light reflects back Water: SOME of the light reflects back LAW OF REFLECTION Law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. θi° = θr° DEFINITIONS 1. Incidence Ray : The ray from the source. (it is the ray from the object to the mirror.) 2. Normal: It is an IMAGINARY line drawn perpendicular to the surface. (It bisects the mirror.) 3. Reflected Ray: The ray reflected from the mirror. REGULAR (SPECULAR) AND REFLECTION Regular or specular reflection Ex: Mirror DIFFUSE Diffuse reflection Ex: Piece of Paper REGULAR (SPECULAR) AND REFLECTION Regular or specular reflection. DIFFUSE Diffuse reflection. EXTEND YOUR THINKING Why is there a strong glare off the pavement after it rains? Why are glossy books sometimes hard to read? IMAGES • • • Image – where light rays converge Virtual image – rays do not pass through the image. Images that are formed in locations where light does not actually reach. Virtual images are upright. Real image – rays do pass through so the image can be projected on a screen. Real images are inverted. PLANE MIRROR AND IMAGE FORMATION https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ISbrAJHdvZU Images are formed because light travels in a straight line. Image is flipped or reversed RAYS OFF OF A POINT OBJECT. Your mind traces back the reflected light rays until they meet somewhere behind the mirror. RAYS OFF OF A POINT OBJECT. Distance mirror to image = distance mirror to object (di = do) RAYS OFF OF A POINT OBJECT. The image as seen by the eye is: Because light rays don’t actually meet in plane mirrors, all images produced are virtual IMAGE OF AN ACTUAL OBJECT. The image as seen by you is This picture shows that you actually need a mirror that is only half your length to be able to see your full image. PLANE MIRROR Where do you see your image in the mirror? http://www.physicsclassroom.com/mmedia/optics/ifpm .cfm IMAGES BETWEEN TWO MIRRORS The kaleidoscope lab show that the angle between the mirrors and the number of images are INVERSLY proportional. And the relationship is A=360º/N Here A is the angle between the mirrors and N is the # of faces.