Chapter 4
advertisement

TMAT 103
Chapter 4
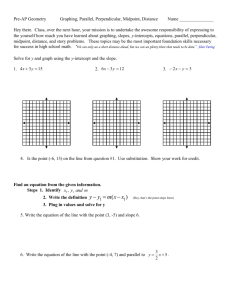
Equations and Their Graphs
TMAT 103
§4.1
Functions
§4.1 – Functions
• Relations
– Set of ordered pairs (x, y)
– Independent variable
•x
• Domain
– Dependent variable
•y
• Range
§4.1 – Functions
• Ex: Find the domain and range of the
relation y + x = 2
• Ex: Find the domain and range of the
relation y x 3
§4.1 – Functions
• Function
– Relation where no 2 ordered pairs have the
same first element
• Ex:
– Is {(1, 2), (5, 11), (4, 2), (1, 7)} a function?
• Ex:
– Is {(1, 1), (5, 11), (4, 1), (-21, 7)} a function?
§4.1 – Functions
• Ex: Is y + x = 2 a function?
• Ex: Is x = y2 a function?
§4.1 – Functions
• Functional notation
– Isolate y and replace it with f(x)
Equation
Function Notation
y=3+x
f(x) = 3 + x
y – x2 = 0
f(x) = x2
y = x3 + x – 7
f(x) = x3 + x – 7
§4.1 – Functions
• Using function notation
• Ex: Given f(x) = x2 – 3, find:
f(7)
f(–2)
f(z)
f(a + b)
§4.1 – Functions
• Ex: Given f(t) = 5 – 2t + t2 and g(t) = t2 – 4t + 4 find:
f(4)
g(0)
f(t) + g(t)
TMAT 103
§4.2
Graphing Equations
§4.2 – Graphing Equations
• Cartesian Coordinate System
– Descartes
– Rectangular coordinate system
•
•
•
•
x – axis
y – axis
origin
quadrants
§4.2 – Graphing Equations
Cartesian Coordinate System
§4.2 Graphing Equations
• Plot each of the following points on the
Cartesian coordinate system:
A(3,1) B(2, –3) C(–4,–2) D(–3, 0) E(–6, 2) F(0, 2)
§4.2 Graphing Equations
• Examples:
– Graph y = –3x – 2
– Graph y = x2 + 3
– Graph y = –3x2 – x + 2
§4.2 Graphing Equations
• Solving equations by graphing
– Ex: Given the graph of y = x3 + 4x2 – x – 4
below, solve the equation y = x3 + 4x2 – x – 4
when:
y=0
y=3
y=6
§4.2 Graphing Equations
• Ex: Solve the equation y = 2x2 – 5x – 3
graphically for y = 1, –2, and –10
TMAT 103
§4.3
The Straight Line
§4.3 – The Straight Line
• Slope of a line
– If P1(x1, y1) and P2(x2, y2) represent any two
points on a straight line, then the slope m of the
line is:
y2 y1
m
x2 x1
§4.3 The Straight Line
• Examples:
– Find the slope of the line passing through (1, 7)
and (4, –3)
– Find the slope of the line passing through (1, 5),
and (3, 2)
§4.3 The Straight Line
•
Properties of the slope of a line
1. If a line has positive slope, then the line
slopes upward from left to right (rises)
2. If the line has negative slope, then the line
slopes downward from left to right (falls)
3. If the line has zero slope, then the line is
horizontal (flat)
4. If the line is vertical, then the line has no
slope since x1 = x2 in all cases
§4.3 The Straight Line
•
Examples
–
–
–
–
Graph the line with slope 3 that passes
through (1, 4)
Graph the line with slope –2 that passes
through (0, 7)
Graph the line with slope 0 that passes
through (–1, 2)
Graph the line with no slope that passes
through (3, 5)
§4.3 The Straight Line
•
Point slope form of a straight line
–
If m is the slope and (x1, y1) is any point on a
non-vertical line, its equation is:
y – y1 = m(x – x1)
§4.3 The Straight Line
• Examples:
– Find the equation of the line with slope –2 and
which passes through (4, –1)
– Find the equation of the line passing through
(10, 3), and (3, 0)
§4.3 The Straight Line
•
Slope-intercept form of a straight line
–
If m is the slope and (0, b) is the y-intercept
of a non-vertical line, its equation is:
y = mx + b
§4.3 The Straight Line
• Examples:
– Find the equation of the line with slope –2 and
which passes through (0, –1)
– Find the equation of the line with slope 5 and
y-intercept 16
§4.3 The Straight Line
•
Equation of a horizontal line
–
If a horizontal line passes through the point
(a, b), its equation is:
y=b
§4.3 The Straight Line
•
Equation of a vertical line
–
If a vertical line passes through the point
(a, b), its equation is:
x=a
§4.3 The Straight Line
• Examples:
– Find the equation of the line parallel to and 7
units below the x-axis
– Graph the line x = 4
TMAT 103
§4.4
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
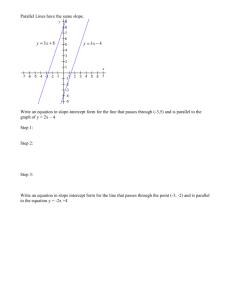
§4.4 – Parallel and Perpendicular
Lines
•
Parallel Lines
–
Two lines are parallel if either of the
following conditions holds:
1. They are both parallel to the x-axis
2. They both have the same slope
§4.4 – Parallel and Perpendicular
Lines
Parallel Lines
§4.4 – Parallel and Perpendicular
Lines
• Examples:
– Determine if l1 and l2 are parallel:
• l1: y = 3x – 15
• l2: y = 3x + 7
– Determine if l3 and l4 are parallel:
• l3: y = –2x – 15
• l4: 2y – 4x = 7
§4.4 – Parallel and Perpendicular
Lines
•
Perpendicular Lines
–
Two lines are perpendicular if either of the
following conditions holds:
1. One line is vertical with equation x = a, and the
other line is horizontal with equation y = b
2. Neither is vertical and the slope of one line is the
negative reciprocal of the other.
§4.4 – Parallel and Perpendicular
Lines
Perpendicular Lines
§4.4 – Parallel and Perpendicular
Lines
• Examples:
– Determine if l1 and l2 are perpendicular:
• l1: y = 2x – 15
• l2: y = –½x + 7
– Determine if l3 and l4 are perpendicular :
• l3: y = –3x – 15
• l4: 9y – 3x = 7
TMAT 103
§4.5
The Distance and Midpoint Formulas
§4.5 The Distance and Midpoint
Formulas
The Distance Formula
§4.5 The Distance and Midpoint
Formulas
•
Distance Formula
–
The distance between two points P(x1, y1) and
Q(x2, y2) is given by the formula
§4.5 The Distance and Midpoint
Formulas
• Examples:
– Find the distance between the points (1, 2) and
(7, 14)
– Find the distance between the points (–3, 2) and
(4, –7)
§4.5 The Distance and Midpoint
Formulas
The Midpoint Formula
§4.5 The Distance and Midpoint
Formulas
•
Midpoint Formula
–
The coordinates of the point Q(xm, ym) which
is midway between the two points P(x1, y1)
and R(x2, y2) are given by:
x1 x2
xm
2
y1 y2
ym
2
§4.5 The Distance and Midpoint
Formulas
• Examples:
– Find the midpoint of the points (1, 2) and
(7, 14)
– Find the midpoint of the points (–3, 2) and
(4, –7)